The effects of different frequency treadmill exercise on lipoxin A4 and articular cartilage degeneration in an experimental model of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats
- PMID: 28594958
- PMCID: PMC5464632
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179162
The effects of different frequency treadmill exercise on lipoxin A4 and articular cartilage degeneration in an experimental model of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats
Abstract
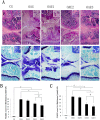
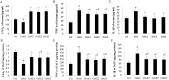
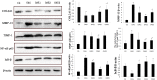
The aim was to investigate the effects of different frequencies treadmill exercise with total exercise time being constancy on articular cartilage, lipoxin A4 (LXA4) and the NF-κB pathway in rat model of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis (OA). Fifty male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into five groups (n = 10): controls (CG), knee OA model (OAG), OA + treadmill exercise once daily (OAE1), OA + treadmill exercise twice daily, rest interval between exercise>4h (OAE2) and OA + treadmill exercise three times daily, rest interval between exercise>4h (OAE3). Rats were evaluated after completing the treadmill exercise program (speed, 18 m/min; total exercise time 60 min/day; 5 days/week for 8 weeks). Interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and LXA4 in serum and intra-articular lavage fluid were measured by ELISA. Changes in articular cartilage were evaluated by histology, immunohistochemistry, western blotting and quantitative real-time-PCR. LXA4 in the serum and intra-articular lavage fluid increased in all OAE groups, and histological evaluation indicated that the OAE3 group had the best treatment response. The expression of COL2A1 and IκB-β in articular cartilage increased in all OAE groups vs the OAG group, whereas expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13, and NF-κB p65 was reduced in all OAE groups compared with the OAG. Under the condition of 60 min treadmill exercise with moderate-intensity, to fulfill in three times would have better chondroprotective effects than to fulfill in two or one time on monosodium iodoacetate-induced OA in rats. And it may be worked through the anti-inflammatory activity of LXA4 and the NF-κB pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
The therapeutic effects of lipoxin A4 during treadmill exercise on monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats.Mol Immunol. 2018 Nov;103:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.08.027. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30196232
-
Alterations of autophagy in knee cartilage by treatment with treadmill exercise in a rat osteoarthritis model.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Jan;43(1):336-344. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3948. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30365059 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking of the P2X7 receptor inhibits the activation of the MMP-13 and NF-κB pathways in the cartilage tissue of rats with osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Dec;38(6):1922-1932. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2770. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27748894
-
Skeletal Muscle Wasting and Its Relationship With Osteoarthritis: a Mini-Review of Mechanisms and Current Interventions.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019 Jun 15;21(8):40. doi: 10.1007/s11926-019-0839-4. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31203463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise and osteoarthritis.J Anat. 2009 Feb;214(2):197-207. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.01013.x. J Anat. 2009. PMID: 19207981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Moderate Mechanical Stimulation Protects Rats against Osteoarthritis through the Regulation of TRAIL via the NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 May 23;2020:6196398. doi: 10.1155/2020/6196398. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32566090 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effects of exercise with chondroitin sulfate on knee osteoarthritis in rabbits.J Orthop Surg Res. 2018 Jan 22;13(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0722-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018. PMID: 29357891 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical stress protects against osteoarthritis via regulation of the AMPK/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9156-9167. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27592. Epub 2018 Oct 12. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30311192 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of treadmill running on distal femoral cartilage thickness: a cross-sectional study of professional athletes and healthy controls.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024 May 6;16(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-00896-4. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38711058 Free PMC article.
-
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Conversion to Lipid Mediators, Roles in Inflammatory Diseases and Dietary Sources.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 16;24(10):8838. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108838. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Udo M, Muneta T, Tsuji K, Ozeki N, Nakagawa Y, Ohara T, et al. Monoiodoacetic acid induces arthritis and synovitis in rats in a dose and time-dependent manner: proposed model-specific scoring systems. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2016;23:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Cifuentes DJ, Rocha LG, Silva LA, Brito AC, Rueff-Barroso CR, Porto LC, et al. Decrease in oxidative stress and histological changes induced by physical exercise calibrated in rats with osteoarthritis induced by monosodium iodoacetate. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2010;18:1088–1095. 10.1016/j.joca.2010.04.004 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

