Plant pectin acetylesterase structure and function: new insights from bioinformatic analysis
- PMID: 28595570
- PMCID: PMC5465549
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-3833-0
Plant pectin acetylesterase structure and function: new insights from bioinformatic analysis
Abstract
Background: Pectins are plant cell wall polysaccharides that can be acetylated on C2 and/or C3 of galacturonic acid residues. The degree of acetylation of pectin can be modulated by pectin acetylesterase (EC 3.1.1.6, PAE). The function and structure of plant PAEs remain poorly understood and the role of the fine-tuning of pectin acetylation on cell wall properties has not yet been elucidated.
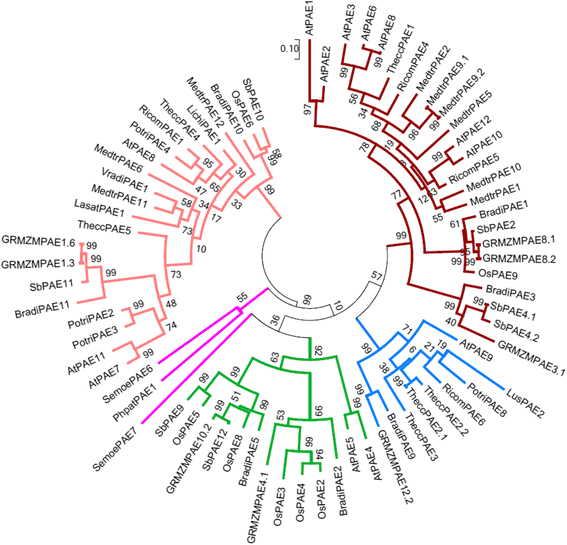
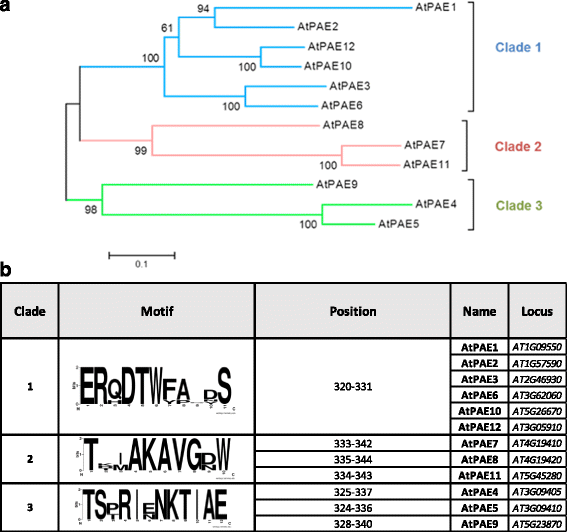
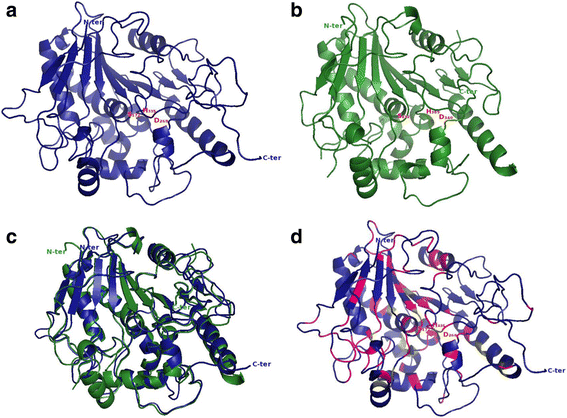
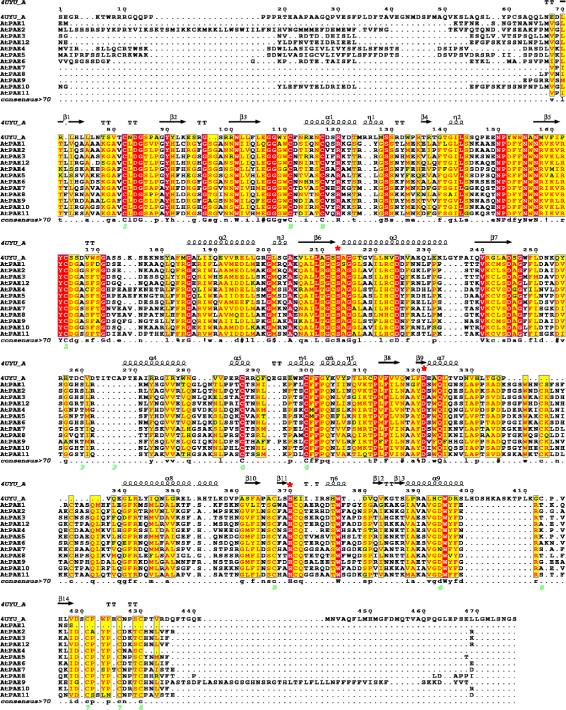
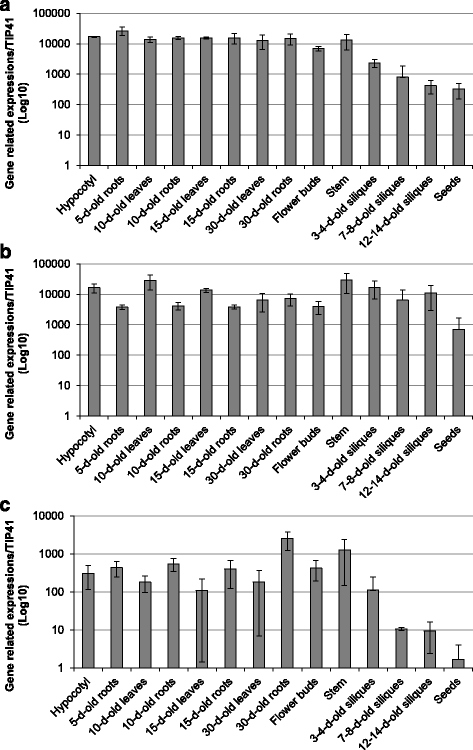
Results: In the present study, a bioinformatic approach was used on 72 plant PAEs from 16 species among 611 plant PAEs available in plant genomic databases. An overview of plant PAE proteins, particularly Arabidopsis thaliana PAEs, based on phylogeny analysis, protein motif identification and modeled 3D structure is presented. A phylogenetic tree analysis using protein sequences clustered the plant PAEs into five clades. AtPAEs clustered in four clades in the plant kingdom PAE tree while they formed three clades when a phylogenetic tree was performed only on Arabidopsis proteins, due to isoform AtPAE9. Primitive plants that display a smaller number of PAEs clustered into two clades, while in higher plants, the presence of multiple members of PAE genes indicated a diversification of AtPAEs. 3D homology modeling of AtPAE8 from clade 2 with a human Notum protein showed an α/β hydrolase structure with the hallmark Ser-His-Asp of the active site. A 3D model of AtPAE4 from clade 1 and AtPAE10 from clade 3 showed a similar shape suggesting that the diversification of AtPAEs is unlikely to arise from the shape of the protein. Primary structure prediction analysis of AtPAEs showed a specific motif characteristic of each clade and identified one major group of AtPAEs with a signal peptide and one group without a signal peptide. A multiple sequence alignment of the putative plant PAEs revealed consensus sequences with important putative catalytic residues: Ser, Asp, His and a pectin binding site. Data mining of gene expression profiles of AtPAE revealed that genes from clade 2 including AtPAE7, AtPAE8 and AtPAE11, which are duplicated genes, are highly expressed during plant growth and development while AtPAEs without a signal peptide, including AtPAE2 and AtPAE4, are more regulated in response to plant environmental conditions.
Conclusion: Bioinformatic analysis of plant, and particularly Arabidopsis, AtPAEs provides novel insights, including new motifs that could play a role in pectin binding and catalytic sites. The diversification of AtPAEs is likely to be related to neofunctionalization of some AtPAE genes.
Keywords: 3D homology; Arabidopsis thaliana; Conserved motifs; Pectin acetylesterase; Phylogenetic tree.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

