Video Game Rehabilitation for Outpatient Stroke (VIGoROUS): protocol for a multi-center comparative effectiveness trial of in-home gamified constraint-induced movement therapy for rehabilitation of chronic upper extremity hemiparesis
- PMID: 28595611
- PMCID: PMC5465449
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-017-0888-0
Video Game Rehabilitation for Outpatient Stroke (VIGoROUS): protocol for a multi-center comparative effectiveness trial of in-home gamified constraint-induced movement therapy for rehabilitation of chronic upper extremity hemiparesis
Abstract
Background: Constraint-Induced Movement therapy (CI therapy) is shown to reduce disability, increase use of the more affected arm/hand, and promote brain plasticity for individuals with upper extremity hemiparesis post-stroke. Randomized controlled trials consistently demonstrate that CI therapy is superior to other rehabilitation paradigms, yet it is available to only a small minority of the estimated 1.2 million chronic stroke survivors with upper extremity disability. The current study aims to establish the comparative effectiveness of a novel, patient-centered approach to rehabilitation utilizing newly developed, inexpensive, and commercially available gaming technology to disseminate CI therapy to underserved individuals. Video game delivery of CI therapy will be compared against traditional clinic-based CI therapy and standard upper extremity rehabilitation. Additionally, individual factors that differentially influence response to one treatment versus another will be examined.
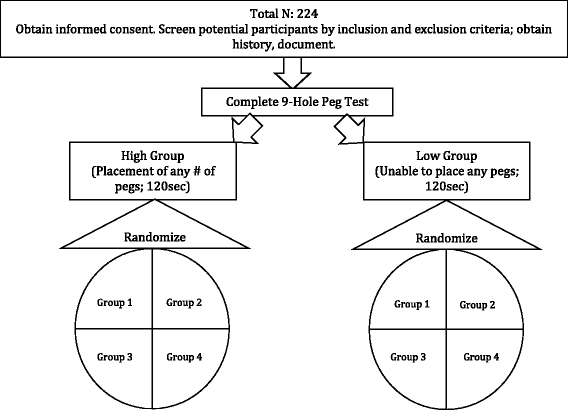
Methods: This protocol outlines a multi-site, randomized controlled trial with parallel group design. Two hundred twenty four adults with chronic hemiparesis post-stroke will be recruited at four sites. Participants are randomized to one of four study groups: (1) traditional clinic-based CI therapy, (2) therapist-as-consultant video game CI therapy, (3) therapist-as-consultant video game CI therapy with additional therapist contact via telerehabilitation/video consultation, and (4) standard upper extremity rehabilitation. After 6-month follow-up, individuals assigned to the standard upper extremity rehabilitation condition crossover to stand-alone video game CI therapy preceded by a therapist consultation. All interventions are delivered over a period of three weeks. Primary outcome measures include motor improvement as measured by the Wolf Motor Function Test (WMFT), quality of arm use for daily activities as measured by Motor Activity Log (MAL), and quality of life as measured by the Quality of Life in Neurological Disorders (NeuroQOL).
Discussion: This multi-site RCT is designed to determine comparative effectiveness of in-home technology-based delivery of CI therapy versus standard upper extremity rehabilitation and in-clinic CI therapy. The study design also enables evaluation of the effect of therapist contact time on treatment outcomes within a therapist-as-consultant model of gaming and technology-based rehabilitation.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov, NCT02631850 .
Keywords: CI therapy; Constraint-induced movement therapy; Hemiparesis; Motor; Protocol; Randomized controlled trial; Rehabilitation; Research design; Stroke; Video game; Virtual reality.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparing Ways to Treat Arm Weakness Due to Stroke [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 May. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 May. PMID: 38556969 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Video game rehabilitation for outpatient stroke (VIGoROUS): A multi-site randomized controlled trial of in-home, self-managed, upper-extremity therapy.EClinicalMedicine. 2021 Dec 17;43:101239. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101239. eCollection 2022 Jan. EClinicalMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34977516 Free PMC article.
-
Home-based constraint-induced movement therapy for patients with upper limb dysfunction after stroke (HOMECIMT): a cluster-randomised, controlled trial.Lancet Neurol. 2015 Sep;14(9):893-902. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00147-7. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Lancet Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26231624 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of aerobic exercise prior to modified constraint-induced movement therapy outcomes in individuals with chronic hemiparesis: a study protocol for a randomized clinical trial.BMC Neurol. 2019 Aug 15;19(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12883-019-1421-4. BMC Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31416436 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of Virtual Reality- and Gaming-Based Interventions for Upper Extremity Rehabilitation Poststroke: A Meta-analysis.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020 May;101(5):885-896. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2019.10.195. Epub 2019 Dec 7. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 31821799
Cited by
-
Converging Evidence Supporting the Cognitive Link between Exercise and Esport Performance: A Dual Systematic Review.Brain Sci. 2020 Nov 15;10(11):859. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10110859. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33203067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Sensory Impairments on Recovery and Rehabilitation After Stroke.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025 Mar 6;25(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s11910-025-01407-9. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40047982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of physical rehabilitation movements through dimensionality reduction and statistical modeling.Med Eng Phys. 2019 Dec;74:13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2019.10.003. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Med Eng Phys. 2019. PMID: 31668858 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing the delivery of telerehabilitation for stroke: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2022 May 11;17(5):e0265828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265828. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35544471 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation of Upper Extremity by Telerehabilitation Combined With Exergames in Survivors of Chronic Stroke: Preliminary Findings From a Feasibility Clinical Trial.JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2022 Jun 22;9(2):e33745. doi: 10.2196/33745. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2022. PMID: 35731560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gladstone DJ, Black SE, Hakim AM. Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario Centre of Excellence in stroke recovery. Toward wisdom from failure: lessons from neuroprotective stroke trials and new therapeutic directions. Stroke. 2002;33(8):2123–2136. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000025518.34157.51. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials