The effect of manganese exposure in Atp13a2-deficient mice
- PMID: 28595912
- PMCID: PMC10178982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2017.06.005
The effect of manganese exposure in Atp13a2-deficient mice
Abstract
Loss of function mutations in the P5-ATPase ATP13A2 are associated with Kufor-Rakeb Syndrome and Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis. While the function of ATP13A2 is unclear, in vitro studies suggest it is a lysosomal protein that interacts with the metals manganese (Mn) and zinc and the presynaptic protein alpha-synuclein. Loss of ATP13A2 function in mice causes sensorimotor deficits, enhanced autofluorescent storage material, and accumulation of alpha-synuclein. The present study sought to determine the effect of Mn administration on these same outcomes in ATP13A2-deficient mice. Wildtype and ATP13A2-deficient mice received saline or Mn at 5-9 or 12-19 months for 45days. Sensorimotor function was assessed starting at day 30. Autofluorescence was quantified in multiple brain regions and alpha-synuclein protein levels were determined in the ventral midbrain. Brain Mn, iron, zinc, and copper concentrations were measured in 5-9 month old mice. The results show Mn enhanced sensorimotor function, increased autofluorescence in the substantia nigra, and increased insoluble alpha-synuclein in the ventral midbrain in older ATP13A2-deficient mice. In addition, the Mn regimen used increased Mn concentration in the brain and levels were higher in Mn-treated mutants than controls. These results indicate loss of ATP13A2 function leads to increased sensitivity to Mn in vivo.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Lipofuscin; Manganese; Mice; Parkinson’s disease; Sensorimotor function.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
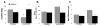
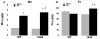
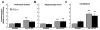




References
-
- Behrens MI, Brüggemann N, Chana P, Venegas P, Kägi M, Parrao T, Orellana P, Garrido C, Rojas CV, Hauke J, Hahnen E, González R, Seleme N, Fernández V, Schmidt A, Binkofski F, Kömpf D, Kubisch C, Hagenah J, Klein C, Ramirez A. Clinical spectrum of Kufor-Rakeb syndrome in the Chilean kindred with ATP13A2 mutations. Mov Disord. 2010;25(12):1929–1937. - PubMed
-
- Bonilla E. Chronic manganese intake induces changes in the motor activity of rats. Exp Neurol. 1984;84(3):696–700. - PubMed
-
- Brüggemann N, Hagenah J, Reetz K, Schmidt A, Kasten M, Buchmann I, Eckerle S, Bähre M, Münchau A, Djarmati A, van der Vegt J, Siebner H, Binkofski F, Ramirez A, Behrens MI, Klein C. Recessively inherited parkinsonism: effect of ATP13A2 mutations on the clinical and neuroimaging phenotype. Arch Neurol. 2010;67(11):1357–1363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

