Characterization of PKACα enzyme kinetics and inhibition in an HPLC assay with a chromophoric substrate
- PMID: 28595966
- PMCID: PMC5889107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2017.06.001
Characterization of PKACα enzyme kinetics and inhibition in an HPLC assay with a chromophoric substrate
Abstract
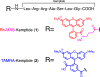
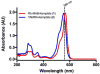
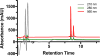
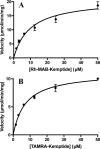
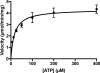
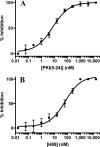
Here we describe a convenient, inexpensive, and non-hazardous method for the measurement of the kinase activity of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKACα). The assay is based on the separation of a substrate peptide labeled with a strong chromophore from the phosphorylated product peptide by high-performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC) and quantification of the product ratiometrically at a wavelength in the visual spectrum (Vis). The utility and reliability of the HPLC-Vis assay were demonstrated by characterizing the kinetic parameters (KM, Vmax) of the new Rh-MAB-Kemptide substrate, a commercially prepared TAMRA-Kemptide substrate, and ATP as well as the potency (IC50, Ki) of the known PKACα inhibitors H89 and PKI(5-24). The advantages of this assay are that it is convenient and inexpensive, uses readily synthesized or commercially available substrates that are shelf-stable, uses a common piece of laboratory equipment, and does not require any hazardous materials such as radioactive γ-32P-ATP. The assay format is also highly flexible and could be adapted for the testing of many different kinases by changing the peptide substrate sequence.
Keywords: Chromophore; HPLC; Inhibition assay; Kinase assay; Kinetics assay; cAMP-dependent protein kinase.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang J, Yang PL, Gray NS. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:28–39. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, Boehm J, Lee JC. p38 MAP kinases: key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2003;2:717–726. - PubMed
-
- Whang JA, Chang BY. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Discovery Today. 2014;19:1200–1204. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki K, Churchill E, Mochly-Rosen D. Epsilon protein kinase C as a potential therapeutic target for the ischemic heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;70:222–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

