Multifunctional nanodiamonds in regenerative medicine: Recent advances and future directions
- PMID: 28596105
- PMCID: PMC5560434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.05.033
Multifunctional nanodiamonds in regenerative medicine: Recent advances and future directions
Abstract
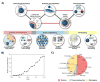
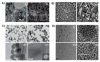
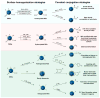
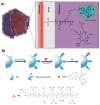
With recent advances in the field of nanomedicine, many new strategies have emerged for diagnosing and treating diseases. At the forefront of this multidisciplinary research, carbon nanomaterials have demonstrated unprecedented potential for a variety of regenerative medicine applications including novel drug delivery platforms that facilitate the localized and sustained release of therapeutics. Nanodiamonds (NDs) are a unique class of carbon nanoparticles that are gaining increasing attention for their biocompatibility, highly functional surfaces, optical properties, and robust physical properties. Their remarkable features have established NDs as an invaluable regenerative medicine platform, with a broad range of clinically relevant applications ranging from targeted delivery systems for insoluble drugs, bioactive substrates for stem cells, and fluorescent probes for long-term tracking of cells and biomolecules in vitro and in vivo. This review introduces the synthesis techniques and the various routes of surface functionalization that allow for precise control over the properties of NDs. It also provides an in-depth overview of the current progress made toward the use of NDs in the fields of drug delivery, tissue engineering, and bioimaging. Their future outlook in regenerative medicine including the current clinical significance of NDs, as well as the challenges that must be overcome to successfully translate the reviewed technologies from research platforms to clinical therapies will also be discussed.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Vul AY, et al. Nanodiamond. The Royal Society of Chemistry; 2014. CHAPTER 2 Detonation Nanodiamonds: Synthesis, Properties and Applications; pp. 27–48.
-
- Chow EK, et al. Nanodiamond therapeutic delivery agents mediate enhanced chemoresistant tumor treatment. Science translational medicine. 2011;3(73):73ra21–73ra21. - PubMed
-
- Zhang XQ, et al. Polymer-functionalized nanodiamond platforms as vehicles for gene delivery. ACS nano. 2009;3(9):2609–2616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

