A Critical Role of Zinc Importer AdcABC in Group A Streptococcus-Host Interactions During Infection and Its Implications for Vaccine Development
- PMID: 28596134
- PMCID: PMC5514391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.05.030
A Critical Role of Zinc Importer AdcABC in Group A Streptococcus-Host Interactions During Infection and Its Implications for Vaccine Development
Abstract
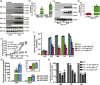
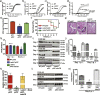
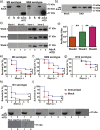
Bacterial pathogens must overcome host immune mechanisms to acquire micronutrients for successful replication and infection. Streptococcus pyogenes, also known as group A streptococcus (GAS), is a human pathogen that causes a variety of clinical manifestations, and disease prevention is hampered by lack of a human GAS vaccine. Herein, we report that the mammalian host recruits calprotectin (CP) to GAS infection sites and retards bacterial growth by zinc limitation. However, a GAS-encoded zinc importer and a nuanced zinc sensor aid bacterial defense against CP-mediated growth inhibition and contribute to GAS virulence. Immunization of mice with the extracellular component of the zinc importer confers protection against systemic GAS challenge. Together, we identified a key early stage host-GAS interaction and translated that knowledge into a novel vaccine strategy against GAS infection. Furthermore, we provided evidence that a similar struggle for zinc may occur during other streptococcal infections, which raises the possibility of a broad-spectrum prophylactic strategy against multiple streptococcal pathogens.
Keywords: GAS vaccine; Gene regulation; Group A streptococcus; Host-pathogen interactions; Nutritional immunity.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Achouiti A., Vogl T., Endeman H., Mortensen B.L., Laterre P.-F., Wittebole X., van Zoelen M.A.D., Zhang Y., Hoogerwerf J.J., Florquin S. Myeloid-related protein-8/14 facilitates bacterial growth during pneumococcal pneumonia. Thorax. 2014;69:1034–1042. - PubMed
-
- Ammendola S., Pasquali P., Pistoia C., Petrucci P., Petrarca P., Rotilio G., Battistoni A. High-affinity Zn2 + uptake system ZnuABC is required for bacterial zinc homeostasis in intracellular environments and contributes to the virulence of Salmonella enterica. Infect. Immun. 2007;75:5867–5876. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayle L., Chimalapati S., Schoehn G., Brown J., Vernet T. Low, and Durmort, C. Zinc uptake by Streptococcus pneumoniae depends on both AdcA and AdcAII and is essential for normal bacterial morphology and virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2011;82:904–916. - PubMed
-
- Blencowe D.K., Morby A.P. Zn(II) metabolism in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003;27:291–311. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

