Extracellular vesicles of bone marrow stromal cells rescue chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis, enhance their migration and induce gene expression modifications
- PMID: 28596280
- PMCID: PMC5685228
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2016.163337
Extracellular vesicles of bone marrow stromal cells rescue chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis, enhance their migration and induce gene expression modifications
Abstract
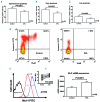
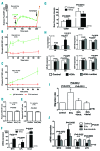
Interactions between chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B cells and the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment play a major function in the physiopathology of CLL. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), which are composed of exosomes and microparticles, play an important role in cell communication. However, little is known about their role in CLL / microenvironment interactions. In the present study, EVs purified by ultracentrifugation from BM mesenchymal stromal cell (BM-MSC) cultures were added to CLL B cells. After their integration into CLL B cells, we observed a decrease of leukemic cell spontaneous apoptosis and an increase in their chemoresistance to several drugs, including fludarabine, ibrutinib, idelalisib and venetoclax after 24 hours. Spontaneous (P=0.0078) and stromal cell-derived factor 1α -induced migration capacities of CLL B cells were also enhanced (P=0.0020). A microarray study highlighted 805 differentially expressed genes between leukemic cells cultured with or without EVs. Of these, genes involved in the B-cell receptor pathway such as CCL3/4, EGR1/2/3, and MYC were increased. Interestingly, this signature presents important overlaps with other microenvironment stimuli such as B-cell receptor stimulation, CLL/nurse-like cells co-culture or those provided by a lymph node microenvironment. Finally, we showed that EVs from MSCs of leukemic patients also rescue leukemic cells from spontaneous or drug-induced apoptosis. However, they induce a higher migration and also a stronger gene modification compared to EVs of healthy MSCs. In conclusion, we show that EVs play a crucial role in CLL B cells/BM microenvironment communication.
Copyright© 2017 Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) tumor B cells and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs): implications for neoplastic cell survival.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8;6(39):42130-49. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6239. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26517523 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic lymphocytic leukemic B cells but not normal B cells are rescued from apoptosis by contact with normal bone marrow stromal cells.Blood. 1998 Apr 1;91(7):2387-96. Blood. 1998. PMID: 9516138
-
Regulation of Mcl-1 expression in context to bone marrow stromal microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Neoplasia. 2014 Dec;16(12):1036-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.10.002. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25499217 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between bone marrow stromal microenvironment and B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: any role for Notch, Wnt and Hh signaling pathways?Cell Signal. 2012 Jul;24(7):1433-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22446006 Review.
-
Survival and Immunosuppression Induced by Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(1):24-33. doi: 10.2174/1566524017666170220095838. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28231754 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived vesicular cargo on B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia progression.Blood Adv. 2023 Apr 11;7(7):1190-1203. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007528. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 36044386 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) in Cell Stress Response and Resistance to Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 24;11(2):136. doi: 10.3390/cancers11020136. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30682793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles from type-2 macrophages increase the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells ex vivo.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Aug;31(8):1164-1176. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00802-7. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38918490 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemogenesis occurs in a microenvironment enriched by extracellular microvesicles/exosomes: recent discoveries and questions to be answered.Leukemia. 2024 Apr;38(4):692-698. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02188-9. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Leukemia. 2024. PMID: 38388648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cells and extracellular vesicles: biological regulators of physiology and disease.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):C155-C166. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00017.2019. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30917031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ten Hacken E, Burger JA. Microenvironment dependency in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: The basis for new targeted therapies. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;144(3):338–348. - PubMed
-
- Lagneaux L, Delforge A, Bron D, De Bruyn C, Stryckmans P. Chronic lymphocytic leukemic B cells but not normal B cells are rescued from apoptosis by contact with normal bone marrow stromal cells. Blood. 1998;91(7):2387–2396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

