PCGF3/5-PRC1 initiates Polycomb recruitment in X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 28596365
- PMCID: PMC6522364
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aal2512
PCGF3/5-PRC1 initiates Polycomb recruitment in X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
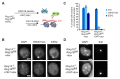
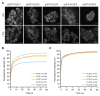
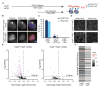
Recruitment of the Polycomb repressive complexes PRC1 and PRC2 by Xist RNA is an important paradigm for chromatin regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Here, we show that the noncanonical Polycomb group RING finger 3/5 (PCGF3/5)-PRC1 complex initiates recruitment of both PRC1 and PRC2 in response to Xist RNA expression. PCGF3/5-PRC1-mediated ubiquitylation of histone H2A signals recruitment of other noncanonical PRC1 complexes and of PRC2, the latter leading to deposition of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation chromosome-wide. Pcgf3/5 gene knockout results in female-specific embryo lethality and abrogates Xist-mediated gene repression, highlighting a key role for Polycomb in Xist-dependent chromosome silencing. Our findings overturn existing models for Polycomb recruitment by Xist RNA and establish precedence for H2AK119u1 in initiating Polycomb domain formation in a physiological context.
Copyright © 2017, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

References
-
- de Napoles M, Mermoud JE, Wakao R, Tang YA, Endoh M, Appanah R, Nesterova TB, Silva J, Otte AP, Vidal M, Koseki H, et al. Polycomb group proteins Ring1A/B link ubiquitylation of histone H2A to heritable gene silencing and X inactivation. Developmental cell. 2004;7:663–676. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.10.005. published online EpubNov. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Silva J, Mak W, Zvetkova I, Appanah R, Nesterova TB, Webster Z, Peters AH, Jenuwein T, Otte AP, Brockdorff N. Establishment of histone h3 methylation on the inactive X chromosome requires transient recruitment of Eed-Enx1 polycomb group complexes. Developmental cell. 2003;4:481–495. published online EpubApr. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

