Human Blood Monocyte Subsets: A New Gating Strategy Defined Using Cell Surface Markers Identified by Mass Cytometry
- PMID: 28596372
- PMCID: PMC5828170
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309145
Human Blood Monocyte Subsets: A New Gating Strategy Defined Using Cell Surface Markers Identified by Mass Cytometry
Abstract
Objective: Human monocyte subsets are defined as classical (CD14++CD16-), intermediate (CD14++CD16+), and nonclassical (CD14+CD16+). Alterations in monocyte subset frequencies are associated with clinical outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, in which circulating intermediate monocytes independently predict cardiovascular events. However, delineating mechanisms of monocyte function is hampered by inconsistent results among studies.
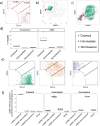
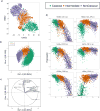
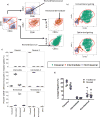
Approach and results: We use cytometry by time-of-flight mass cytometry to profile human monocytes using a panel of 36 cell surface markers. Using the dimensionality reduction approach visual interactive stochastic neighbor embedding (viSNE), we define monocytes by incorporating all cell surface markers simultaneously. Using viSNE, we find that although classical monocytes are defined with high purity using CD14 and CD16, intermediate and nonclassical monocytes defined using CD14 and CD16 alone are frequently contaminated, with average intermediate and nonclassical monocyte purity of ≈86.0% and 87.2%, respectively. To improve the monocyte purity, we devised a new gating scheme that takes advantage of the shared coexpression of cell surface markers on each subset. In addition to CD14 and CD16, CCR2, CD36, HLA-DR, and CD11c are the most informative markers that discriminate among the 3 monocyte populations. Using these additional markers as filters, our revised gating scheme increases the purity of both intermediate and nonclassical monocyte subsets to 98.8% and 99.1%, respectively. We demonstrate the use of this new gating scheme using conventional flow cytometry of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from subjects with cardiovascular disease.
Conclusions: Using cytometry by time-of-flight mass cytometry, we have identified a small panel of surface markers that can significantly improve monocyte subset identification and purity in flow cytometry. Such a revised gating scheme will be useful for clinical studies of monocyte function in human cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; flow cytometry; inflammation; monocytes.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
By CyTOF: Heterogeneity of Human Monocytes.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Aug;37(8):1423-1424. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309645. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28747454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ziegler-Heitbrock L, Ancuta P, Crowe S, Dalod M, Grau V, Hart DN, Leenen PJM, Liu Y-J, MacPherson G, Randolph GJ, Scherberich J, Schmitz J, Shortman K, Sozzani S, Strobl H, Zembala M, Austyn JM, Lutz MB. Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood. Blood. 2010;116:e74–e80. - PubMed
-
- Wong KL, Yeap WH, Tai JJY, Ong SM, Dang TM, Wong SC. The three human monocyte subsets: implications for health and disease. Immunol Res. 2012;53:41–57. - PubMed
-
- Azeredo EL, Neves-Souza PC, Alvarenga AR, Reis SRNI, Torrentes-Carvalho A, Zagne S-MO, Nogueira RMR, Oliveira-Pinto LM, Kubelka CF. Differential regulation of toll-like receptor-2, toll-like receptor-4, CD16 and human leucocyte antigen-DR on peripheral blood monocytes during mild and severe dengue fever. Immunology. 2010;130:202–216. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grip O, Bredberg A, Lindgren S, Henriksson G. Increased subpopulations of CD16(+) and CD56(+) blood monocytes in patients with active Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007;13:566–572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

