A new long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is induced in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and down-regulates several anticancer and cell differentiation genes in mouse
- PMID: 28596382
- PMCID: PMC5535023
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.776260
A new long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is induced in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and down-regulates several anticancer and cell differentiation genes in mouse
Abstract
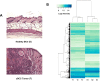
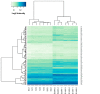
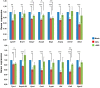
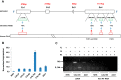
Keratinocyte-derived cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is the most common metastatic skin cancer. Although some of the early events involved in this pathology have been identified, the subsequent steps leading to tumor development are poorly defined. We demonstrate here that the development of mouse tumors induced by the concomitant application of a carcinogen and a tumor promoter (7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), respectively) is associated with the up-regulation of a previously uncharacterized long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), termed AK144841. We found that AK144841 expression was absent from normal skin and was specifically stimulated in tumors and highly tumorigenic cells. We also found that AK144841 exists in two variants, one consisting of a large 2-kb transcript composed of four exons and one consisting of a 1.8-kb transcript lacking the second exon. Gain- and loss-of-function studies indicated that AK144841 mainly inhibited gene expression, specifically down-regulating the expression of genes of the late cornified envelope-1 (Lce1) family involved in epidermal terminal differentiation and of anticancer genes such as Cgref1, Brsk1, Basp1, Dusp5, Btg2, Anpep, Dhrs9, Stfa2, Tpm1, SerpinB2, Cpa4, Crct1, Cryab, Il24, Csf2, and Rgs16 Interestingly, the lack of the second exon significantly decreased AK144841's inhibitory effect on gene expression. We also noted that high AK144841 expression correlated with a low expression of the aforementioned genes and with the tumorigenic potential of cell lines. These findings suggest that AK144841 could contribute to the dedifferentiation program of tumor-forming keratinocytes and to molecular cascades leading to tumor development.
Keywords: RNA; cancer biology; long noncoding RNA (long ncRNA, lncRNA); microarray; skin.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



References
-
- Madan V., Lear J. T., and Szeimies R. (2010) Non-melanoma skin cancer. Lancet 375, 673–685 - PubMed
-
- Emmert S., Schön M. P., and Haenssle H. A. (2014) Molecular biology of basal and squamous cell carcinomas. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 810, 234–252 - PubMed
-
- Rentoft M., Fahlén J., Coates P. J., Laurell G., Sjöström B., Rydén P., and Nylander K. (2011) miRNA analysis of formalin-fixed squamous cell carcinomas of the tongue is affected by age of the samples. Int. J. Oncol. 38, 61–69 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

