A Kidney Graft Survival Calculator that Accounts for Mismatches in Age, Sex, HLA, and Body Size
- PMID: 28596416
- PMCID: PMC5498352
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09330916
A Kidney Graft Survival Calculator that Accounts for Mismatches in Age, Sex, HLA, and Body Size
Abstract
Background and objectives: Outcomes for transplants from living unrelated donors are of particular interest in kidney paired donation (KPD) programs where exchanges can be arranged between incompatible donor-recipient pairs or chains created from nondirected/altruistic donors.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Using Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients data, we analyzed 232,705 recipients of kidney-alone transplants from 1998 to 2012. Graft failure rates were estimated using Cox models for recipients of kidney transplants from living unrelated, living related, and deceased donors. Models were adjusted for year of transplant and donor and recipient characteristics, with particular attention to mismatches in age, sex, human leukocyte antigens (HLA), body size, and weight.
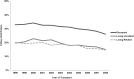
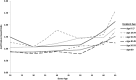
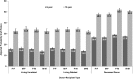
Results: The dependence of graft failure on increasing donor age was less pronounced for living-donor than for deceased-donor transplants. Male donor-to-male recipient transplants had lower graft failure, particularly better than female to male (5%-13% lower risk). HLA mismatch was important in all donor types. Obesity of both the recipient (8%-18% higher risk) and donor (5%-11% higher risk) was associated with higher graft loss, as were donor-recipient weight ratios of <75%, compared with transplants where both parties were of similar weight (9%-12% higher risk). These models are used to create a calculator of estimated graft survival for living donors.
Conclusions: This calculator provides useful information to donors, candidates, and physicians of estimated outcomes and potentially in allowing candidates to choose among several living donors. It may also help inform candidates with compatible donors on the advisability of joining a KPD program.
Keywords: Attention; Female; HLA Antigens; Living Donors; Organ Procurement; Proportional Hazards Models; Registries; Survival Rate; Transplant Recipients; Unrelated Donors; age; body size; donor exchange; end-stage renal disease; gender; graft survival; kidney donation; kidney transplantation; obesity; renal failure; risk factors; transplant outcomes; transplantation.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Matas AJ, Smith JM, Skeans MA, Thompson B, Gustafson SK, Stewart DE, Cherikh WS, Wainright JL, Boyle G, Snyder JJ, Israni AK, Kasiske BL: OPTN/SRTR 2013 annual data report: Kidney. Am J Transplant 15[Suppl 2]: 1–34, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Tullius SG, Tran H, Guleria I, Malek SK, Tilney NL, Milford E: The combination of donor and recipient age is critical in determining host immunoresponsiveness and renal transplant outcome. Ann Surg 252: 662–674, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Meier-Kriesche HU, Cibrik DM, Ojo AO, Hanson JA, Magee JC, Rudich SM, Leichtman AB, Kaplan B: Interaction between donor and recipient age in determining the risk of chronic renal allograft failure. J Am Geriatr Soc 50: 14–17, 2002 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

