Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus enters CHSE-214 cells via macropinocytosis
- PMID: 28596575
- PMCID: PMC5465193
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03036-w
Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus enters CHSE-214 cells via macropinocytosis
Abstract
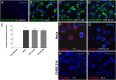
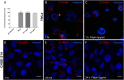
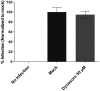
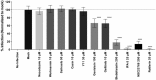
Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) is a non-enveloped virus belonging to the Birnaviridae family. IPNV produces an acute disease in salmon fingerlings, with high mortality rates and persistent infection in survivors. Although there are reports of IPNV binding to various cells, the viral receptor and entry pathways remain unknown. The aim of this study was to determine the endocytic pathway that allows for IPNV entry. We observed that IPNV stimulated fluid uptake and virus particles co-localysed with the uptake marker dextran in intracellular compartments, suggesting a role for macropinocytosis in viral entry. Consistent with this idea, viral infection was significantly reduced when the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 was inhibited with 5-(N-Ethyl-N-isopropyl) amiloride (EIPA). Neither chlorpromazine nor filipin complex I affected IPNV infection. To examine the role of macropinocytosis regulators, additional inhibitors were tested. Inhibitors of the EGFR pathway and the effectors Pak1, Rac1 and PKC reduced viral infection. Together, our results indicate that IPNV is mainly internalized into CHSE-214 cells by macropinocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Smail DA, et al. Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., post-smolts in the Shetland Isles, Scotland: virus identification, histopathology, immunohistochemistry and genetic comparison with Scottish mainland isolates. J Fish Dis. 2006;29:31–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2005.00678.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

