Regulating STING in health and disease
- PMID: 28596706
- PMCID: PMC5463399
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-017-0159-2
Regulating STING in health and disease
Abstract
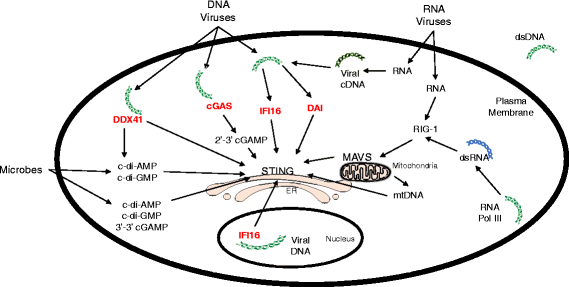
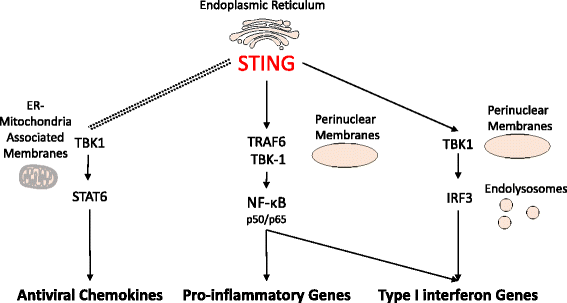
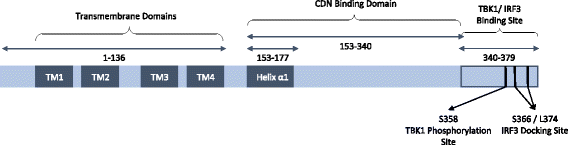
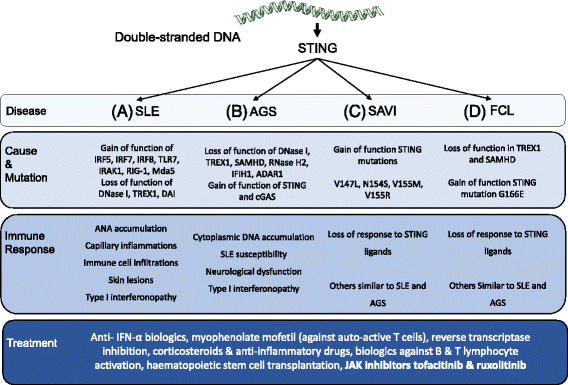
The presence of cytosolic double-stranded DNA molecules can trigger multiple innate immune signalling pathways which converge on the activation of an ER-resident innate immune adaptor named "STimulator of INterferon Genes (STING)". STING has been found to mediate type I interferon response downstream of cyclic dinucleotides and a number of DNA and RNA inducing signalling pathway. In addition to its physiological function, a rapidly increasing body of literature highlights the role for STING in human disease where variants of the STING proteins, as well as dysregulated STING signalling, have been implicated in a number of inflammatory diseases. This review will summarise the recent structural and functional findings of STING, and discuss how STING research has promoted the development of novel therapeutic approaches and experimental tools to improve treatment of tumour and autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: Cyclic dinucleotide; Double-stranded DNA sensor; Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING); cGAS.
Figures

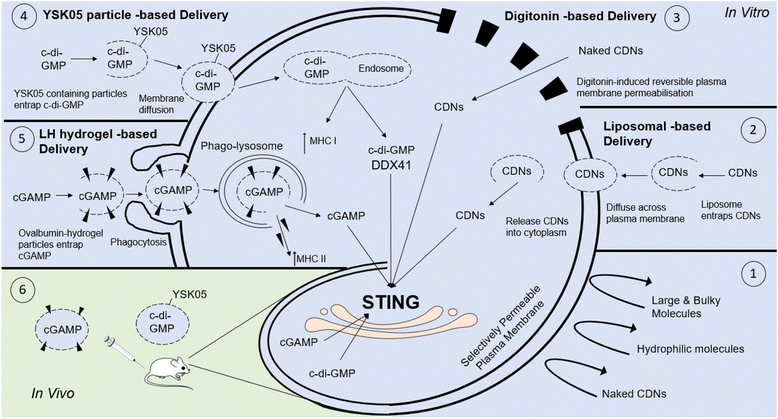
Similar articles
-
The role of cGAS-STING signalling in liver diseases.JHEP Rep. 2021 Jun 24;3(5):100324. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100324. eCollection 2021 Oct. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 34381984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA sensing in cancer: Pro-tumour and anti-tumour functions of cGAS-STING signalling.Essays Biochem. 2023 Sep 28;67(6):905-918. doi: 10.1042/EBC20220241. Essays Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37534795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic di-GMP.Nature. 2011 Sep 25;478(7370):515-8. doi: 10.1038/nature10429. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21947006 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering and Delivery of cGAS-STING Immunomodulators for the Immunotherapy of Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases.Acc Chem Res. 2023 Nov 7;56(21):2933-2943. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00394. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 37802125 Free PMC article.
-
cGAS/STING: novel perspectives of the classic pathway.Mol Biomed. 2020 Sep 20;1(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s43556-020-00006-z. Mol Biomed. 2020. PMID: 35006429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of gingival epithelial cytokine response by bacterial cyclic dinucleotides.J Oral Microbiol. 2018 Nov 27;11(1):1538927. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2018.1538927. eCollection 2019. J Oral Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30598733 Free PMC article.
-
The Ca2+ sensor STIM1 regulates the type I interferon response by retaining the signaling adaptor STING at the endoplasmic reticulum.Nat Immunol. 2019 Feb;20(2):152-162. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0287-8. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Nat Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30643259 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Mild Cases of COVID-19 Are Dedicated to Proliferation; In Severe Cases, They Control Inflammation, Make Cell Dispersion, and Tissue Regeneration.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:780900. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.780900. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095855 Free PMC article.
-
cGAMP/Saponin Adjuvant Combination Improves Protective Response to Influenza Vaccination by Microneedle Patch in an Aged Mouse Model.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 2;11:583251. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.583251. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33603732 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advancements in cGAS-STING activation, tumor immune evasion, and therapeutic implications.Med Oncol. 2024 Oct 18;41(11):291. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02539-7. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39419913 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

