Characterization and Expression of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptors in Human and Rat Heart
- PMID: 28596734
- PMCID: PMC5442178
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00312
Characterization and Expression of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptors in Human and Rat Heart
Abstract
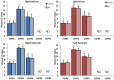
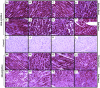
Aim: Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), sphingolipid derivatives are known anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and anti-oxidant agent. S1P have been demonstrated to have a role in the cardiovascular system. The purpose of this study was to understand the precise expression and distribution of S1P receptors (S1PRs) in human and rat cardiovascular tissues to know the significance and possible implementation of our experimental studies in rat models. Methods and Results: In this study, we investigated the localization of S1PRs in human heart samples from cardiac surgery department, University of Verona Hospital and rat samples. Immunohistochemical investigation of paraffin-embedded sections illustrated diffused staining of the myocardial samples from human and rat. The signals of the human heart were similar to those of the rat heart in all chambers of the heart. The immunohistochemical expression levels correlated well with the results of RT-PCR-based analysis and western blotting. We confirmed by all techniques that S1PR1 expressed strongly as compared to S1PR3, and are uniformly distributed in all chambers of the heart with no significant difference in human and rat myocardial tissue. S1PR2 expression was significantly weak while S1PR4 and S1PR5 were not detectable in RT-PCR results in both human and rat heart. Conclusion: These results indicate that experimental studies using S1PR agonists on rat models are more likely to have a potential for translation into clinical studies, and second important information revealed by this study is, S1P receptor agonist can be used for cardioprotection in global ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Keywords: cardioprotection; heart; human; ischemia-reperfusion injury; rat; sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

