Analysis of EF-Hand Proteins in Soybean Genome Suggests Their Potential Roles in Environmental and Nutritional Stress Signaling
- PMID: 28596783
- PMCID: PMC5443154
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00877
Analysis of EF-Hand Proteins in Soybean Genome Suggests Their Potential Roles in Environmental and Nutritional Stress Signaling
Abstract
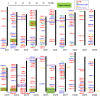
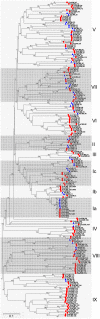
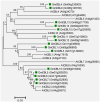
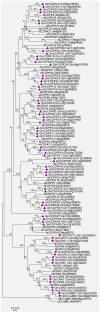
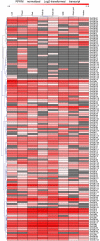
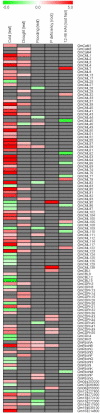
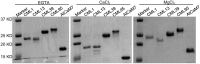
Calcium ion (Ca2+) is a universal second messenger that plays a critical role in plant responses to diverse physiological and environmental stimuli. The stimulus-specific signals are perceived and decoded by a series of Ca2+ binding proteins serving as Ca2+ sensors. The majority of Ca2+ sensors possess the EF-hand motif, a helix-loop-helix structure which forms a turn-loop structure. Although EF-hand proteins in model plant such as Arabidopsis have been well described, the identification, classification, and the physiological functions of EF-hand-containing proteins from soybean are not systemically reported. In this study, a total of at least 262 genes possibly encoding proteins containing one to six EF-hand motifs were identified in soybean genome. These genes include 6 calmodulins (CaMs), 144 calmodulin-like proteins (CMLs), 15 calcineurin B-like proteins, 50 calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs), 13 CDPK-related protein kinases, 2 Ca2+- and CaM-dependent protein kinases, 17 respiratory burst oxidase homologs, and 15 unclassified EF-hand proteins. Most of these genes (87.8%) contain at least one kind of hormonal signaling- and/or stress response-related cis-elements in their -1500 bp promoter regions. Expression analyses by exploring the published microarray and Illumina transcriptome sequencing data revealed that the expression of these EF-hand genes were widely detected in different organs of soybean, and nearly half of the total EF-hand genes were responsive to various environmental or nutritional stresses. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to confirm their responsiveness to several stress treatments. To confirm the Ca2+-binding ability of these EF-hand proteins, four CMLs (CML1, CML13, CML39, and CML95) were randomly selected for SDS-PAGE mobility-shift assay in the presence and absence of Ca2+. Results showed that all of them have the ability to bind Ca2+. This study provided the first comprehensive analyses of genes encoding for EF-hand proteins in soybean. Information on the classification, phylogenetic relationships and expression profiles of soybean EF-hand genes in different tissues and under various environmental and nutritional stresses will be helpful for identifying candidates with potential roles in Ca2+ signal-mediated physiological processes including growth and development, plant-microbe interactions and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses.
Keywords: EF-hand motif; Rboh (respiratory burst oxidase homolog); calcineurin B-like protein (CBL); calcium signal; calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK); calmodulin; calmodulin-like protein (CML); soybean (Glycine max).
Figures






Similar articles
-
Molecular Players of EF-hand Containing Calcium Signaling Event in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 23;20(6):1476. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061476. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30909616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomics and evolutionary aspect of calcium signaling event in calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plants.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Feb 3;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-0989-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28158973 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, characterization, and expression analysis of calmodulin and calmodulin-like genes in grapevine (Vitis vinifera) reveal likely roles in stress responses.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018 Aug;129:221-237. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.06.003. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29908490
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of calmodulin and calmodulin-like genes in apple (Malus × domestica).Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019 Jun;139:600-612. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.04.014. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31030028
-
Calmodulin and calmodulin-like protein-mediated plant responses to biotic stresses.Plant Cell Environ. 2023 Dec;46(12):3680-3703. doi: 10.1111/pce.14686. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Plant Cell Environ. 2023. PMID: 37575022 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Association Analysis for Resistance to Coniothyrium glycines Causing Red Leaf Blotch Disease in Soybean.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 15;14(6):1271. doi: 10.3390/genes14061271. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372451 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Calmodulin and Calmodulin-like Genes, Revealing CaM3 and CML13 Participating in Drought Stress in Phoebe bournei.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 30;25(1):545. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010545. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203715 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating Calcium Signaling Machinery in Plants: Tapping the Potential through Functional Genomics.Curr Genomics. 2021 Dec 30;22(6):404-439. doi: 10.2174/1389202922666211130143328. Curr Genomics. 2021. PMID: 35340362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative time-course transcriptome analysis of two contrasting alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) genotypes reveals tolerance mechanisms to salt stress.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 8;13:1070846. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1070846. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36570949 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Calmodulin-Like Gene Family in Paspalums vaginatium Revealed Their Role in Response to Salt and Cold Stress.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Feb 16;45(2):1693-1711. doi: 10.3390/cimb45020109. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36826054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asano T., Tanaka N., Yang G., Hayashi N., Komatsu S. (2005). Genome-wide identification of the rice calcium-dependent protein kinase and its closely related kinase gene families: comprehensive analysis of the CDPKs gene family in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 46 356–366. 10.1093/pcp/pci035 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

