The use of bioactive peptides to modify materials for bone tissue repair
- PMID: 28596916
- PMCID: PMC5458541
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbx011
The use of bioactive peptides to modify materials for bone tissue repair
Abstract
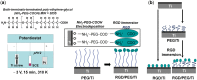
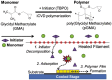
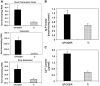
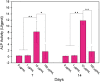
It has been well recognized that the modification of biomaterials with appropriate bioactive peptides could further enhance their functions. Especially, it has been shown that peptide-modified bone repair materials could promote new bone formation more efficiently compared with conventional ones. The purpose of this article is to give a general review of recent studies on bioactive peptide-modified materials for bone tissue repair. Firstly, the main peptides for inducing bone regeneration and commonly used methods to prepare peptide-modified bone repair materials are introduced. Then, current in vitro and in vivo research progress of peptide-modified composites used as potential bone repair materials are reviewed and discussed. Generally speaking, the recent related studies have fully suggested that the modification of bone repair materials with osteogenic-related peptides provide promising strategies for the development of bioactive materials and substrates for enhanced bone regeneration and the therapy of bone tissue diseases. Furthermore, we have proposed some research trends in the conclusion and perspectives part.
Keywords: bone repair material; osteogenic activity; peptide.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioactive peptide-modified biomaterials for bone regeneration.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(25):2663-76. doi: 10.2174/138161211797416011. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21728982 Review.
-
Bioactive Materials for Bone Regeneration: Biomolecules and Delivery Systems.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023 Sep 11;9(9):5222-5254. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c00609. Epub 2023 Aug 16. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023. PMID: 37585562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication and Application of Novel Porous Scaffold in Situ-Loaded Graphene Oxide and Osteogenic Peptide by Cryogenic 3D Printing for Repairing Critical-Sized Bone Defect.Molecules. 2019 Apr 28;24(9):1669. doi: 10.3390/molecules24091669. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31035401 Free PMC article.
-
GelMA-based bioactive hydrogel scaffolds with multiple bone defect repair functions: therapeutic strategies and recent advances.Biomater Res. 2023 Sep 15;27(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s40824-023-00422-6. Biomater Res. 2023. PMID: 37715230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graphene and its nanostructure derivatives for use in bone tissue engineering: Recent advances.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016 May;104(5):1250-75. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35645. Epub 2016 Jan 29. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016. PMID: 26748447 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-site enhancement of osteogenesis: peptide-functionalized GelMA hydrogels with three-dimensional cultures of human dental pulp stem cells.Regen Biomater. 2024 Aug 10;11:rbae090. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae090. eCollection 2024. Regen Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39193556 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterials research of China from 2013 to 2017 based on bibliometrics and visualization analysis.PeerJ. 2019 May 6;7:e6859. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6859. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31119079 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan Covalently Functionalized with Peptides Mapped on Vitronectin and BMP-2 for Bone Tissue Engineering.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Oct 21;11(11):2784. doi: 10.3390/nano11112784. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835549 Free PMC article.
-
Proteins and Peptides as Important Modifiers of the Polymer Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications-A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Apr 6;12(4):844. doi: 10.3390/polym12040844. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32268607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered biomaterials in stem cell-based regenerative medicine.Life Med. 2023 Jul 20;2(4):lnad027. doi: 10.1093/lifemedi/lnad027. eCollection 2023 Aug. Life Med. 2023. PMID: 39872549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li XM, Yang Y, Fan YB. et al. Biocomposites reinforced by fibers or tubes, as scaffolds for tissue engineering or regenerative medicine. J Biomed MaterResPart A 2014;102A:1580–94. - PubMed
-
- Shi S, Jiang WB, Aifantis KE. et al. The application of nanomaterials in controlled drug delivery for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mat Res Part A 2015;103:3978–92. - PubMed
-
- Bilem I, Chevallier P, Plawinski L. et al. RGD and BMP-2 mimetic peptide crosstalk enhances osteogenic commitment of human bone marrow stem cells. Acta Biomater 2016; 36:132–42. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

