Phenol-Soluble Modulin Toxins of Staphylococcus haemolyticus
- PMID: 28596942
- PMCID: PMC5442197
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00206
Phenol-Soluble Modulin Toxins of Staphylococcus haemolyticus
Abstract
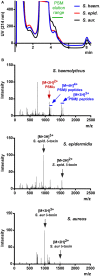
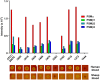
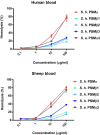
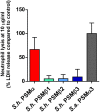
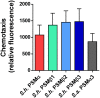
Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) are important nosocomial pathogens and the leading cause of sepsis. The second most frequently implicated species, after Staphylococcus epidermidis, is Staphylococcus haemolyticus. However, we have a significant lack of knowledge about what causes virulence of S. haemolyticus, as virulence factors of this pathogen have remained virtually unexplored. In contrast to the aggressive pathogen Staphylococcus aureus, toxin production has traditionally not been associated with CoNS. Recent findings have suggested that phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs), amphipathic peptide toxins with broad cytolytic activity, are widespread in staphylococci, but there has been no systematic assessment of PSM production in CoNS other than S. epidermidis. Here, we identified, purified, and characterized PSMs of S. haemolyticus. We found three PSMs of the β-type, which correspond to peptides that before were described to have anti-gonococcal activity. We also detected an α-type PSM that has not previously been described. Furthermore, we confirmed that S. haemolyticus does not produce a δ-toxin, as results from genome sequencing had indicated. All four S. haemolyticus PSMs had strong pro-inflammatory activity, promoting neutrophil chemotaxis. Notably, we identified in particular the novel α-type PSM, S. haemolyticus PSMα, as a potent hemolysin and leukocidin. For the first time, our study describes toxins of this important staphylococcal pathogen with the potential to have a significant impact on virulence during blood infection and sepsis.
Keywords: Staphylococcus haemolyticus; coagulase-negative staphylococci; hemolysin; leukocidin; phenol-soluble modulin; toxin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct and synergistic hemolysis caused by Staphylococcus phenol-soluble modulins: implications for diagnosis and pathogenesis.Microbes Infect. 2012 Apr;14(4):380-6. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.11.013. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Microbes Infect. 2012. PMID: 22178792 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus epidermidis strategies to avoid killing by human neutrophils.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Oct 7;6(10):e1001133. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001133. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20949069 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of exotoxin production by mobile genetic element SCCmec-encoded psm-mec RNA is conserved in staphylococcal species.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 13;9(6):e100260. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100260. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24926994 Free PMC article.
-
Phenol-soluble modulins--critical determinants of staphylococcal virulence.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2014 Jul;38(4):698-719. doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12057. Epub 2014 Jan 16. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24372362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenol-soluble modulins: novel virulence-associated peptides of staphylococci.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(2):203-16. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.153. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24295365 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Functions in Gram-Positive Bacteria.Infect Immun. 2020 Nov 16;88(12):e00433-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00433-20. Print 2020 Nov 16. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32989035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of the pathogenic potential of phenol-soluble modulin toxins in the mouse commensal Staphylococcus xylosus.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 15;13:999201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.999201. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36189200 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Contained in Gut Microbiota as a Primary Source of Sepsis in Low- and Very Low Birth Weight Neonates.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 4;9(8):2517. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082517. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32759861 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of Staphylococcus haemolyticus nosocomial bacteraemia in neonatal intensive care units, France, 2019 to 2023: predominance of the ST29 (CC3) multidrug-resistant lineage.Euro Surveill. 2025 Mar;30(11):2400309. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.11.2400309. Euro Surveill. 2025. PMID: 40116031 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Occurrence and Phenotypic Resistance of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CoNS) Found in Human Blood in the Northern Netherlands between 2013 and 2019.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 7;10(9):1801. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091801. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36144403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheung G. Y., Kretschmer D., Queck S. Y., Joo H. S., Wang R., Duong A. C., et al. . (2014b). Insight into structure-function relationship in phenol-soluble modulins using an alanine screen of the phenol-soluble modulin (PSM) α3 peptide. FASEB J. 28, 153–161. 10.1096/fj.13-232041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

