Standardization of 123I- meta-iodobenzylguanidine myocardial sympathetic activity imaging: phantom calibration and clinical applications
- PMID: 28596948
- PMCID: PMC5437131
- DOI: 10.1007/s40336-017-0230-2
Standardization of 123I- meta-iodobenzylguanidine myocardial sympathetic activity imaging: phantom calibration and clinical applications
Abstract
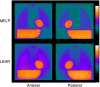
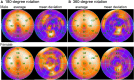
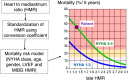
Purpose: Myocardial sympathetic imaging with 123I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine (123I-mIBG) has gained clinical momentum. Although the need for standardization of 123I-mIBG myocardial uptake has been recognized, the availability of practical clinical standardization approaches is limited. The need for standardization includes the heart-to-mediastinum ratio (HMR) and washout rate with planar imaging, and myocardial defect scoring with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
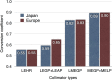
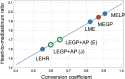
Methods: The planar HMR shows considerable variation due to differences in collimator design. These camera-collimator differences can be overcome by cross-calibration phantom experiments. The principles of these cross-calibration phantom experiments are summarized in this article. 123I-mIBG SPECT databases were compiled by Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine working group. Literature was searched based on the words "123I-mIBG quantification method", "standardization", "heart-to-mediastinum ratio", and its application to "risk model".
Results: Calibration phantom experiments have been successfully performed in Japan and Europe. The benefit of these cross-calibration phantom experiments is that variation in the HMR between institutions is minimized including low-energy, low-medium-energy and medium-energy collimators. The use of myocardial 123I-mIBG SPECT can be standardized using 123I-mIBG normal databases as a basis for quantitative evaluation. This standardization method can be applied in cardiac event prediction models.
Conclusion: Standardization of myocardial 123I-mIBG outcome parameters may facilitate a universal implementation of myocardial 123I-mIBG scintigraphy.
Keywords: Calibration phantom; Collimator; Conversion coefficient; Heart-to-mediastinum ratio; Quantification.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
K. Nakajima and K. Okuda have collaborative works to develop software with FUJIFILM RI Pharma, Co. Ltd, Tokyo, Japan.
Ethical approval and informed consent
Ethical approval and informed consent statements were shown in individual studies in references.
Figures

References
-
- Agostini D, Verberne HJ, Burchert W, Knuuti J, Povinec P, Sambuceti G, et al. I-123-mIBG myocardial imaging for assessment of risk for a major cardiac event in heart failure patients: insights from a retrospective European multicenter study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:535–546. doi: 10.1007/s00259-007-0639-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jacobson AF, Senior R, Cerqueira MD, Wong ND, Thomas GS, Lopez VA, et al. Myocardial iodine-123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine imaging and cardiac events in heart failure. Results of the prospective ADMIRE-HF (AdreView Myocardial Imaging for Risk Evaluation in Heart Failure) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:2212–2221. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.01.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nakata T, Nakajima K, Yamashina S, Yamada T, Momose M, Kasama S, et al. A pooled analysis of multicenter cohort studies of 123I-mIBG imaging of sympathetic innervation for assessment of long-term prognosis in heart failure. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6:772–784. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.02.007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
