Identification of drought stress related proteins from 1Sl(1B) chromosome substitution line of wheat variety Chinese Spring
- PMID: 28597430
- PMCID: PMC5430570
- DOI: 10.1186/s40529-016-0134-x
Identification of drought stress related proteins from 1Sl(1B) chromosome substitution line of wheat variety Chinese Spring
Abstract
Background: Wheat, one of the most important crops, has a detrimental effect on both yield and quality under drought stress. As our preliminary experiment showed that the Chinese Spring wheat-Aegilops longissima chromosome substitution line CS-1Sl (1B) had a better drought tolerance than CS, the substitution line CS-1Sl(1B) was used to identify drought stress related proteins by means of a comparative proteome approach in this work. Our present study aimed to explore the gene resources for drought resistance in 1Sl genome.
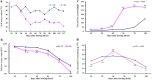
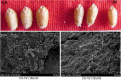
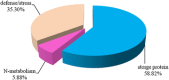
Result: Our results showed that drought stress induced downregulation of relative water and chlorophyll contents and the upregulation of proline content, and further influencing grain filling shortening and significant decrease of plant height, B-type starch granule numbers, grain number and weight. In total, 25 grain albumin and globulin protein spots were found to be specifically encoded by the 1Sl chromosome. In addition, 17 protein spots respected 13 unique proteins were identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF MS, which were mainly involved in adverse defense and gluten quality. Among them, ascorbate peroxidase, serpin-Z2B and alpha-amylase/trypsin inhibitor were upregulated under drought stress. These proteins play important roles in plant drought defenses through various metabolic pathways.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that the 1Sl chromosome of Aegilops longissima has potential gene resources that could be useful for improving wheat drought resistance.
Keywords: 2-DE; Aegilops longissima 1Sl chromosome; Drought tolerance; Proteome; Wheat.
Figures
References
-
- Altenbach SB, Tanaka CK, Hurkman WJ, Vensel WH. Expression of globulin-2, a member of the cupin superfamily of proteins with similarity to known food allergens, is increased under high temperature regimens during wheat grain development. J Cereal Sci. 2009;49:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2008.07.005. - DOI
-
- Bazargani MM, Sarhadi E, Bushehri AAS, Matros A, Mock HP, Naghavi MR, Hajihoseini V, Mardi M, Hajirezaei MR, Moradi F, Ehdaie B, Salekdeh GH. A proteomics view on the role of drought-induced senescence and oxidative stress defense in enhanced stem reserves remobilization in wheat. J Proteomics. 2011;74:1959–1973. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.05.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharjee L, Singh PK, Singh S, Nandi AK. Down-regulation of rice serpin gene ossrp-lrs exaggerates stress-induced cell death. J Plant Biol. 2015;58:327–332. doi: 10.1007/s12374-015-0283-6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

