Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults
- PMID: 28597471
- PMCID: PMC6452908
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub4
Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults
Abstract
Background: Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000.
Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain in adults.
Search methods: For this update we searched CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and Embase for randomised controlled trials from January 2014 to January 2017. We also searched the reference lists of retrieved studies and reviews, and online clinical trials registries.
Selection criteria: We included randomised, double-blind trials of two weeks' duration or longer, comparing gabapentin (any route of administration) with placebo or another active treatment for neuropathic pain, with participant-reported pain assessment.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data and assessed trial quality and potential bias. Primary outcomes were participants with substantial pain relief (at least 50% pain relief over baseline or very much improved on Patient Global Impression of Change scale (PGIC)), or moderate pain relief (at least 30% pain relief over baseline or much or very much improved on PGIC). We performed a pooled analysis for any substantial or moderate benefit. Where pooled analysis was possible, we used dichotomous data to calculate risk ratio (RR) and number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNT) or harmful outcome (NNH). We assessed the quality of the evidence using GRADE and created 'Summary of findings' tables.
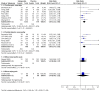
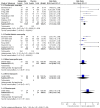
Main results: We included four new studies (530 participants), and excluded three previously included studies (126 participants). In all, 37 studies provided information on 5914 participants. Most studies used oral gabapentin or gabapentin encarbil at doses of 1200 mg or more daily in different neuropathic pain conditions, predominantly postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. Study duration was typically four to 12 weeks. Not all studies reported important outcomes of interest. High risk of bias occurred mainly due to small size (especially in cross-over studies), and handling of data after study withdrawal.In postherpetic neuralgia, more participants (32%) had substantial benefit (at least 50% pain relief or PGIC very much improved) with gabapentin at 1200 mg daily or greater than with placebo (17%) (RR 1.8 (95% CI 1.5 to 2.1); NNT 6.7 (5.4 to 8.7); 8 studies, 2260 participants, moderate-quality evidence). More participants (46%) had moderate benefit (at least 30% pain relief or PGIC much or very much improved) with gabapentin at 1200 mg daily or greater than with placebo (25%) (RR 1.8 (95% CI 1.6 to 2.0); NNT 4.8 (4.1 to 6.0); 8 studies, 2260 participants, moderate-quality evidence).In painful diabetic neuropathy, more participants (38%) had substantial benefit (at least 50% pain relief or PGIC very much improved) with gabapentin at 1200 mg daily or greater than with placebo (21%) (RR 1.9 (95% CI 1.5 to 2.3); NNT 5.9 (4.6 to 8.3); 6 studies, 1277 participants, moderate-quality evidence). More participants (52%) had moderate benefit (at least 30% pain relief or PGIC much or very much improved) with gabapentin at 1200 mg daily or greater than with placebo (37%) (RR 1.4 (95% CI 1.3 to 1.6); NNT 6.6 (4.9 to 9.9); 7 studies, 1439 participants, moderate-quality evidence).For all conditions combined, adverse event withdrawals were more common with gabapentin (11%) than with placebo (8.2%) (RR 1.4 (95% CI 1.1 to 1.7); NNH 30 (20 to 65); 22 studies, 4346 participants, high-quality evidence). Serious adverse events were no more common with gabapentin (3.2%) than with placebo (2.8%) (RR 1.2 (95% CI 0.8 to 1.7); 19 studies, 3948 participants, moderate-quality evidence); there were eight deaths (very low-quality evidence). Participants experiencing at least one adverse event were more common with gabapentin (63%) than with placebo (49%) (RR 1.3 (95% CI 1.2 to 1.4); NNH 7.5 (6.1 to 9.6); 18 studies, 4279 participants, moderate-quality evidence). Individual adverse events occurred significantly more often with gabapentin. Participants taking gabapentin experienced dizziness (19%), somnolence (14%), peripheral oedema (7%), and gait disturbance (14%).
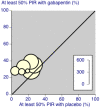
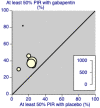
Authors' conclusions: Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain is very limited. The outcome of at least 50% pain intensity reduction is regarded as a useful outcome of treatment by patients, and the achievement of this degree of pain relief is associated with important beneficial effects on sleep interference, fatigue, and depression, as well as quality of life, function, and work. Around 3 or 4 out of 10 participants achieved this degree of pain relief with gabapentin, compared with 1 or 2 out of 10 for placebo. Over half of those treated with gabapentin will not have worthwhile pain relief but may experience adverse events. Conclusions have not changed since the previous update of this review.
Conflict of interest statement
PW: none known
SD: none known
RFB: none known. RFB is a retired specialist pain physician who has managed patients with neuropathic pain.
ASCR: undertakes consultancy and advisory board work for Imperial College Consultants ‐ since June 2013 this has included remunerated work for: Spinifex, Abide, Astellas, Neusentis, Merck, Medivir, Mitsubishi, Aquilas, Asahi Kasei, Relmada, Novartis, and Orion. All consultancy activity relates to consultancy advice on the preclinical/clinical development of drugs for neuropathic pain. Neusentis was a subsidiary of Pfizer. He owned share options in Spinifex Pharmaceuticals which was acquired by Novartis in July 2015. ASCR was a Principal Investigator in the EuroPain consortium. EuroPain has received support from the Innovative Medicines Initiative Joint Undertaking under grant agreement number 115007, resources for which are composed of financial contribution from the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/20072013) and European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) companies (
TRT is a site investigator for the Neuropain project, funded by Pfizer. Since 2014 TRT has consulted with or received lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies related to chronic pain and analgesics: Astellas, Eli Lilly, Grünenthal, Pfizer, and Mundipharma.
TP: none known. TP is a specialist pain physician who has managed patients with neuropathic pain.
RAM has received grant support from Grünenthal relating to individual participant‐level analyses of trial data regarding tapentadol in osteoarthritis and back pain (2015) and from Novartis for network meta‐analyses in acute pain. He has received honoraria for attending boards with Menarini concerning methods of analgesic trial design (2014), with Novartis (2014) about the design of network meta‐analyses, and RB on understanding pharmacokinetics of drug uptake (2015). He has received honoraria from Omega Pharma (2016) and Futura Pharma (2016) for providing advice on trial and data analysis methods.
This review was identified in a 2019 audit as not meeting the current definition of the Cochrane Commercial Sponsorship policy. At the time of its publication it was compliant with the interpretation of the existing policy. As with all reviews, new and updated, at update this review will be revised according to 2020 policy update.
Figures






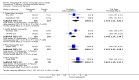


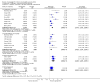









Update of
-
Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 27;2014(4):CD007938. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 09;6:CD007938. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub4. PMID: 24771480 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Atkinson 2016 {published data only}
Backonja 1998 {published data only}
-
- Trial summary ‐ Parke Davis/Pfizer 945‐210. Unpublished report.
Backonja 2011 {published data only}
Bone 2002 {published data only}
Caraceni 2004 {published data only}
Chandra 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chandra K, Shafiq N, Pandhi P, Gupta S, Malhotra S. Gabapentin versus nortriptyline in post‐herpetic neuralgia patients: a randomized, double‐blind clinical trial ‐ the GONIP Trial. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2006;44(8):358‐63. [PUBMED: 16961166] - PubMed
Cohen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cohen SP, Hanling S, Bicket MC, White RL, Veizi E, Kurihara C, et al. Epidural steroid injections compared with gabapentin for lumbosacral radicular pain: multicenter randomized double blind comparative efficacy study. BMJ 2015;350:h1748. [CTG: NCT01495923; DOI: 10.1136/bmj.h1748] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
CTR 945‐1008 {unpublished data only}
-
- Protocol A9451008. A 15 week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group, multi‐center study of Neurontin (gabapentin) for efficacy and quality of life in patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. PhrmaWebSynopsis ‐ Final 2 June 2005.
CTR 945‐224 {unpublished data only}
-
- Protocol 945‐224. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial with 3 doses of gabapentin for treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. May 29, 1998 through September 7, 1999. Unpublished.
Gilron 2005 {published data only}
Gilron 2009 {published data only}
Gong 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gong Z‐Y, Ye T‐H, Hao R‐R, Shi Y‐X, Xiong L‐Z, Wang Q‐S, et al. The efficacy and safety of gabapentin in postherpetic neuralgia. Chinese Journal of Pain Medicine 2008;2.
Gordh 2008 {published data only}
Gorson 1999 {published data only}
Hahn 2004 {published data only}
Harden 2013 {published data only}
Irving 2009 {published data only}
-
- Irving G, Jensen M, Cramer M, Wu J, Chiang YK, Tark M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of gastric‐retentive gabapentin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: results of a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2009;25(3):185‐92. [DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181934276] - DOI - PubMed
Levendoglu 2004 {published data only}
Mishra 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mishra S, Bhatnagar S, Goyal GN, Rana SP, Upadhya SP. A comparative efficacy of amitriptyline, gabapentin, and pregabalin in neuropathic cancer pain: a prospective randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. American Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care 2012;29(3):177‐82. [DOI: 10.1177/1049909111412539] - DOI - PubMed
Morello 1999 {published data only}
-
- Morello CM, Leckband SG, Stoner CP, Moorhouse DF, Sahagian GA. Randomized double‐blind study comparing the efficacy of gabapentin with amitriptyline on diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain. Archives of Internal Medicine 1999;159(16):1931‐7. [PUBMED: 10493324] - PubMed
NCT00475904 {published data only}
-
- A Phase II, double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled non‐inferiority trial of EpiCept™ NP‐1 topical cream (2% ketamine/4% amitriptyline) vs. oral gabapentin in postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00475904 (accessed 13 February 2017). [CTG: NCT00475904]
NCT00904202 {published data only}
-
- A study of lidocaine patch 5% alone, gabapentin alone, and lidocaine patch 5% and gabapentin in combination for the relief of pain in patients with diverse peripheral neuropathic pain conditions. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00904202 (accessed 13 February 2017). [CTG: NCT00904202]
-
- Clinical trial results summary: a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group study of lidocaine patch 5% alone, gabapentin alone, and lidocaine patch 5% and gabapentin in combination for the relief of pain in patients with diverse peripheral neuropathic pain conditions. endo.com/home/search?k=EN3220‐009 (accessed 13 February 2017).
Perez 2000 {published data only}
Rao 2007 {published data only}
-
- Rao RD, Michalak JC, Sloan JA, Loprinzi CL, Soori GS, Nikcevich DA, et al. North Central Cancer Treatment Group. Efficacy of gabapentin in the management of chemotherapy‐induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase 3 randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, crossover trial (N00C3). Cancer 2007;110(9):2110‐8. [CTG: NCT00027963; DOI: 10.1002/cncr.23008] - DOI - PubMed
Rauck 2013a {published data only}
-
- Rauck R, Makumi CW, Schwartz S, Graff O, Meno‐Tetang G, Bell CF, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pain Practice 2013;13(6):485‐96. [CTG: NCT02074267; DOI: 10.1111/papr.12014] - DOI - PubMed
Rauck 2013b {published data only}
Rice 2001 {published data only}
-
- Study detail and analysis, Parke‐Davis 945‐295. Unpublished Report No. RR‐430‐00124 2000.
Rintala 2007 {published data only}
-
- Rintala DH, Holmes SA, Courtade D, Fiess RN, Tastard LV, Loubser PG. Comparison of the effectiveness of amitriptyline and gabapentin on chronic neuropathic pain in persons with spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2007;88(12):1547‐60. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.038] - DOI - PubMed
Rowbotham 1998 {published data only}
-
- Detailed summary, study No.4, Parke‐Davis 945‐211. Unpublished Report No. RR‐995‐00070 1998.
Sandercock 2012 {published data only}
-
- Sandercock D, Cramer M, Biton V, Cowles VE. A gastroretentive gabapentin formulation for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: efficacy and tolerability in a double‐blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2012;97(3):438‐45. [DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2012.03.010] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sandercock D, Cramer M, Wu J, Chiang YK, Biton V, Heritier M. Gabapentin extended release for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: efficacy and tolerability in a double‐blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2009;32(2):e20. [CTG: NCT00712439; DOI: 10.2337/dc08-1450] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Sang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mehta N, Bucior I, Bujanover S, Shah R, Gulati A. Relationship between pain relief, reduction in pain‐associated sleep interference, and overall impression of improvement in patients with postherpetic neuralgia treated with extended‐release gabapentin. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2016;14:54. [DOI: 10.1186/s12955-016-0456-0] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Serpell 2002 {published data only}
Simpson 2001 {published data only}
-
- Simpson DA. Gabapentin and venlafaxine for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease 2001;3(2):53‐62. [PUBMED: 19078655] - PubMed
Smith 2005 {published data only}
Tai 2002 {published data only}
-
- Tai Q, Kirshblum S, Chen B, Millis S, Johnston M, DeLisa JA. Gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury: a prospective, randomized, double‐blind, crossover trial. Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine 2002;25(2):100‐5. [PUBMED: 12137213] - PubMed
Wallace 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mehta N, Bucior I, Bujanover S, Shah R, Gulati A. Relationship between pain relief, reduction in pain‐associated sleep interference, and overall impression of improvement in patients with postherpetic neuralgia treated with extended‐release gabapentin. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2016;14:54. [DOI: 10.1186/s12955-016-0456-0] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Zhang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Calkins AM, Gudin J, Gidal B, Jaros MJ, Kim R, Shang G. Impact of data imputation methodology on pain assessment over 24 hours in a randomized, placebo‐controlled study of gabapentin enacarbil in patients with neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia. Pain Medicine 2016;17(4):728‐36. [DOI: 10.1093/pm/pnv072] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Rainka M, Freeman R, Harden RN, Bell CF, Chen C, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial to assess the efficacy and safety of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with neuropathic pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia (PXN110748). Journal of Pain 2013;14(6):590‐603. [CTG: NCT00619476; DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2013.01.768] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Arai 2010 {published data only}
Berry 2005 {published data only}
Dallocchio 2000 {published data only}
Ding 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ding Y, Yao P, Lan P, Ma J, Wang Z, Hong T, et al. Assessment of transdermal fentanyl combined with gabapentin for malignant neuropathic pain treatment. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014;41(20):1307‐11. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.20141212] - DOI
Dworkin 2009 {published data only}
Ho 2009 {published data only}
Jean 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jean WH, Wu CC, Mok MS, Sun WZ. Starting dose of gabapentin for patients with post‐herpetic neuralgia‐‐a dose‐response study. Acta Anaesthesiologica Taiwan 2005;43(2):73‐7. [PUBMED: 16060401] - PubMed
Kasimcan 2010 {published data only}
Keskinbora 2007 {published data only}
-
- Keskinbora K, Pekel AF, Aydinli I. Gabapentin and an opioid combination versus opioid alone for the management of neuropathic cancer pain: a randomized open trial. Journal of Pain Symptom Management 2007;34(2):183‐9. [10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.11.013] - PubMed
Kimos 2007 {published data only}
Ko 2010 {published data only}
McCleane 2001 {published data only}
-
- McCleane GJ. Does gabapentin have an analgesic effect on background, movement and referred pain? A randomised, double‐blind, placebo controlled study. The Pain Clinic 2001;13:103.
NCT00634543 {published data only}
-
- A study to compare safety and efficacy of tramadol hydrochloride/acetaminophen with gabapentin in participants with diabetic neuropathy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00634543 (accessed 13 February 2017). [CTG: NCT00634543]
NCT01263132 {published data only}
-
- Neuropathic pain treatment using F0434 vs. gabapentin in patients with chronic distal diabetic polyneuropathy: a randomized, controlled, double‐blind study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01263132 (accessed 13 February 2017). [CTG: NCT01263132]
NCT01623271 {published data only}
-
- Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome with once daily gastric‐retentive gabapentin (Gralise). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01623271 (accessed 13 February 2017). [CTG: NCT01623271]
Nikolajsen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nikolajsen L, Finnerup NB, Kramp S, Vimtrup AS, Keller J, Jensen TS. A randomized study of the effects of gabapentin on postamputation pain. Anesthesiology 2006;105(5):1008‐15. [PUBMED: 17065896] - PubMed
Pandey 2002 {published data only}
Pandey 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pandey CK, Raza M, Tripathi M, Navkar DV, Kumar A, Singh UK. The comparative evaluation of gabapentin and carbamazepine for pain management in Guillain‐Barre syndrome patients in the intensive care unit. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2005;101(1):220‐5. [DOI: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000152186.89020.36] - DOI - PubMed
Salvaggio 2008 {published data only}
Sator‐Katzenschlager 2005 {published data only}
Tanenberg 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tanenberg RJ, Irving GA, Risser RC, Ahl J, Robinson MJ, Skljarevski V, et al. Duloxetine, pregabalin, and duloxetine plus gabapentin for diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain management in patients with inadequate pain response to gabapentin: an open‐label, randomized, noninferiority comparison. Mayo Clinic proceedings 2011;86(7):615‐26. [CTG: NCT00385671; DOI: 10.4065/mcp.2010.0681] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Van de Vusse 2004 {published data only}
Yaksi 2007 {published data only}
Yelland 2009 {published data only}
Yildrim 2003 {published data only}
-
- Yildirim K, Siseciolglu M, Karatay S, Erdal A, Levent A, Ugur M. The effectiveness of gabapentin in patients with chronic radiculopathy. The Pain Clinic 2003;15(3):213‐8.
References to ongoing studies
Fleckstein 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fleckenstein J, Kramer S, Hoffrogge P, Thoma S, Lang PM, Lehmeyer L, et al. Acupuncture in acute herpes zoster pain therapy (ACUZoster) ‐ design and protocol of a randomised controlled trial. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2009;9:31. [CTG: NCT00885586; DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-9-31] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
IRCT201212019014N14 {published data only}
-
- Vasheghani M (contact person). Effect of gabapentin on heart rate variability in diabetic painful peripheral neuropathy: a double blinded randomized clinical trial. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=IRCT201212019014N14 (accessed 13 February 2017).
NCT00674687 {published data only}
-
- A study of the efficacy of gabapentin in neuropathic pain patients as measured by quantitative sensory testing. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00674687 (accessed 13 February 2017). [NCT: NCT00674687]
Additional references
AlBalawi 2013
Baron 2012
Baron 2017
Berger 2004
Berger 2009
Berger 2012
Bouhassira 2008
-
- Bouhassira D, Lantéri‐Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 2008;136(3):380‐7. - PubMed
Boyle 2014
Brok 2009
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta‐analyses may be inconclusive‐‐Trial sequential analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data in apparently conclusive neonatal meta‐analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):287‐98. [DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyn188] - DOI - PubMed
Calvo 2012
Chang 2014
Chaparro 2012
Chou 2009
-
- Chou R, Carson S, Chan BK. Gabapentin versus tricyclic antidepressants for diabetic neuropathy and post‐herpetic neuralgia: discrepancies between direct and indirect meta‐analyses of randomized controlled trials. Journal of General Internal Medicine 2009;24(2):178‐88. [DOI: 10.1007/s11606-008-0877-5] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Colloca 2017
Cooper 2017
Dechartres 2013
Dechartres 2014
Demant 2014
-
- Demant DT, Lund K, Vollert J, Maier C, Segerdahl M, Finnerup NB, et al. The effect of oxcarbazepine in peripheral neuropathic pain depends on pain phenotype: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phenotype‐stratified study. Pain 2014;155(11):2263‐73. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.08.014] - DOI - PubMed
Derry 2012
Derry 2014
Derry 2016
Derry 2017
Dworkin 2008
Dworkin 2013
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JP, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
EMC 2017
-
- Electronic Medicines Compendium. emc.medicines.org.uk/ (accessed 13 February 2017).
EPOC 2015
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). 23. Worksheets for preparing a Summary of Findings using GRADE. Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services. Available at: epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors (accessed 13 February 2017).
Eroglu 2009
Evoy 2017
Fanelli 2017
Finnerup 2005
Finnerup 2013
Finnerup 2015
Gaskell 2016
Gustorff 2008
Guyatt 2011
Guyatt 2013a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 11. Making an overall rating of confidence in effect estimates for a single outcome and for all outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66:151‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.006] - DOI - PubMed
Guyatt 2013b
Hall 2008
Hall 2013
Hauser 2009
Helfert 2015
Hempenstall 2005
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Hoffman 2010
Jadad 1996
Jensen 2011
Jensen 2012
-
- Jensen MP, Hsu PH, Vanhove GF. Early pain reduction can predict treatment response: results of integrated efficacy analyses of a once‐daily gastroretentive formulation of gabapentin in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Pain Medicine 2012;13(8):1059‐66. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2012.01427.x.] - DOI - PubMed
Kalso 2013
Katusic 1991
-
- Katusic S, Williams DB, Beard CM, Bergstralh EJ, Kurland LT. Epidemiology and clinical features of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: similarities and differences, Rochester, Minnesota, 1945‐1984. Neuroepidemiology 1991;10(5‐6):276‐81. [DOI: 10.1159/000110284] - DOI - PubMed
Khan 1996
Koopman 2009
L'Abbé 1987
Landefeld 2009
Lunn 2009
Lunn 2014
McQuay 1995
McQuay 1996
-
- McQuay H, Carroll D, Moore A. Variation in the placebo effect in randomised controlled trials of analgesics: all is as blind as it seems. Pain 1996;64(2):331‐5. - PubMed
McQuay 1998
-
- McQuay H, Moore R. An evidence‐based resource for pain relief. An evidence‐based resource for pain relief. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998. [ISBN: 0‐19‐263048‐2]
McQuay 2007
-
- McQuay HJ, Smith LA, Moore RA. Chronic Pain. In: Stevens A, Raftery J, Mant J, Simpson S editor(s). Health Care Needs Assessment: The Epidemiologically Based Needs Assessment Reviews: Third Series. Oxford: Radcliffe Publishing, 2007. [ISBN: 978‐1‐84619‐063‐6]
McQuay 2008
Moore 1998
Moore 2008
-
- Moore RA, Barden J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Managing potential publication bias. In: McQuay HJ, Kalso E, Moore RA editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Pain Research: Methodology Refined. Seattle: IASP Press, 2008:15‐24. [ISBN: 978‐0‐931092‐69‐5]
Moore 2009
Moore 2010a
-
- Moore RA, Eccleston C, Derry S, Wiffen P, Bell RF, Straube S, McQuay H, ACTINPAIN Writing Group of the IASP Special Interest Group on Systematic Reviews in Pain Relief, Cochrane Pain, Palliative and Supportive Care Systematic Review Group Editors. "Evidence" in chronic pain‐‐establishing best practice in the reporting of systematic reviews. Pain 2010;150(3):386‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.05.011] - DOI - PubMed
Moore 2010b
Moore 2010c
Moore 2010d
Moore 2010e
-
- Moore RA, Moore OA, Derry S, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni AR, Wang H. Responder analysis for pain relief and numbers needed to treat in a meta‐analysis of etoricoxib osteoarthritis trials: bridging a gap between clinical trials and clinical practice. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(2):374‐9. [DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.107805] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Moore 2010f
-
- Moore RA, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Straube S, Aldington D, Wiffen P, et al. for the ACTINPAIN writing group of the IASP Special Interest Group (SIG) on Systematic Reviews in Pain Relief. Clinical effectiveness: an approach to clinical trial design more relevant to clinical practice, acknowledging the importance of individual differences. Pain 2010;149(2):173‐6. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.08.007] - DOI - PubMed
Moore 2011b
-
- Moore RA, Straube S, Paine J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Minimum efficacy criteria for comparisons between treatments using individual patient meta‐analysis of acute pain trials: examples of etoricoxib, paracetamol, ibuprofen, and ibuprofen/paracetamol combinations after third molar extraction. Pain 2011;152(5):982‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.11.030] - DOI - PubMed
Moore 2012a
Moore 2012b
Moore 2013a
Moore 2013b
Moore 2013c
Moore 2014b
Moore 2014c
Moore 2015a
Moore 2015b
Moore 2015c
Moulin 2014
Nguyen 2017
NICE 2013
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Neuropathic pain ‐ pharmacological management: the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain in adults in non‐specialist settings, 2013. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg173 (accessed 13 February 2017). - PubMed
Nüesch 2010
O'Brien 2010
PaPaS 2012
-
- Cochrane Pain, Palliative and Supportive Care Group. PaPaS Author and Referee Guidance. papas.cochrane.org/papas‐documents (accessed 7 February 2017).
Perloff 2011
Perry 2008
-
- Perry T. Neurontin ‐ expert opinion on efficacy and effectiveness for pain. industrydocumentslibrary.ucsf.edu/drug/docs/#id=fhhw0217 (accessed 13 February 2017).
Phillips 2010
Quilici 2009
Quintero 2017
Rappaport 1994
Rauck 2013c
-
- Rauck RL, Irving GA, Wallace MS, Vanhove GF, Sweeney M. Once‐daily gastroretentive gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia: integrated efficacy, time to onset of pain relief and safety analyses of data from two phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled studies. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2013;46(2):219‐28. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2012.07.011] - DOI - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roberts 2015
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Scott 2006
SIGN 2013
-
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. SIGN Guideline 136: Management of Chronic Pain. sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/136/contents.html 2013; Vol. (accessed 1 March 2017).
Smalldone 2004
Soni 2013
Stannard 2016
Straube 2008
-
- Straube S, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Enriched enrollment: definition and effects of enrichment and dose in trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in neuropathic pain. A systematic review. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2008;66(2):266‐75. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03200.x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Straube 2010
Sultan 2008
Thorlund 2011
Torrance 2006
-
- Torrance N, Smith BH, Bennett MI, Lee AJ. The epidemiology of chronic pain of predominantly neuropathic origin. Results from a general population survey. Journal of Pain 2006;7(4):281‐9. - PubMed
Treede 2008
Turner 2013
Tzellos 2008
Tzellos 2010
-
- Tzellos TG, Toulis KA, Goulis DG, Papazisis G, Zampeli VA, Vakfari A, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a systematic review and a meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2010;35(6):369‐56. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01144.x] - DOI - PubMed
Tölle 2013
-
- Tölle TR, Backonja M. Pharmacological Therapy for Neuropathic Pain. In: McMahon SB, Koltenburg M, Tracey I, Turk DC editor(s). Wall and Melzack's Textbook of Pain. 5. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2013:1003‐1011. [ISBN 978‐0‐7020‐4059‐7]
Van Hecke 2014
Van Hoek 2009
Vedula 2009
von Hehn 2012
Vos 2012
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2163‐96. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Wang 2017
Wiffen 2010
Wiffen 2013
Wiffen 2015
References to other published versions of this review
Moore 2011a
Moore 2014a
Wiffen 2000
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

