Interaction of Immunoglobulin with Cytomegalovirus-Infected Cells
- PMID: 28598267
- PMCID: PMC5610397
- DOI: 10.1089/vim.2016.0151
Interaction of Immunoglobulin with Cytomegalovirus-Infected Cells
Abstract
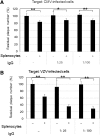
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is used to treat or prevent severe viral infection, especially cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections. IVIG was characterized to understand its interaction with CMV-infected cells. IVIG retarded CMV spread and reduced virus yields depending on the neutralizing (NT) antibody titer. Immediate early protein synthesis was reduced by IVIG in 3 to 15 h, and IVIG specifically reduced the ratio of 66/68k protein synthesis among immediate early proteins in an NT antibody-dependent manner between 4 and 8 h after infection, indicating that antigenic modulation of CMV-infected cells by IVIG reduced viral protein synthesis and virus production. The half-life of antibody bound to CMV-infected cells was 3.8 h. NT antibody titers to varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and CMV in IVIG were dose dependently absorbed by cells infected with VZV and CMV, respectively, but the antibody titers to CMV and VZV, respectively, were not affected. NT antibody in 0.3 mL of IVIG (15 mg) was specifically absorbed by 108 CMV-infected cells and 107 VZV-infected cells, suggesting that the NT antibody in IVIG might be inactivated by one-tenth of a similar volume of CMV-infected or VZV-infected cells. Various antiviral activities of IVIG may contribute to control and alleviation of CMV infection.
Keywords: ADCC; antigenic modulation; cytomegalovirus; intravenous immunoglobulin; varicella-zoster virus.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Beers SA, French RR, Chan HT, et al. . Antigenic modulation limits the efficacy of anti-CD20 antibodies: implications for antibody selection. Blood 2010;115:5191–5201 - PubMed
-
- Beum PV, Mack DA, Pawluczkowycz AW, Lindorfer MA, and Taylor RP. Binding of rituximab, trastuzumab, cetuximab, or mAb T101 to cancer cells promotes trogocytosis mediated by THP-1 cells and monocytes. J Immunol 2008;181:8120–8132 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

