Co-agonists differentially tune GluN2B-NMDA receptor trafficking at hippocampal synapses
- PMID: 28598327
- PMCID: PMC5466419
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.25492
Co-agonists differentially tune GluN2B-NMDA receptor trafficking at hippocampal synapses
Abstract
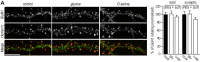
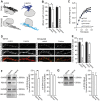
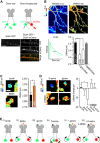
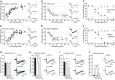
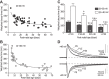
The subunit composition of synaptic NMDA receptors (NMDAR), such as the relative content of GluN2A- and GluN2B-containing receptors, greatly influences the glutamate synaptic transmission. Receptor co-agonists, glycine and D-serine, have intriguingly emerged as potential regulators of the receptor trafficking in addition to their requirement for its activation. Using a combination of single-molecule imaging, biochemistry and electrophysiology, we show that glycine and D-serine relative availability at rat hippocampal glutamatergic synapses regulate the trafficking and synaptic content of NMDAR subtypes. Acute manipulations of co-agonist levels, both ex vivo and in vitro, unveil that D-serine alter the membrane dynamics and content of GluN2B-NMDAR, but not GluN2A-NMDAR, at synapses through a process requiring PDZ binding scaffold partners. In addition, using FRET-based FLIM approach, we demonstrate that D-serine rapidly induces a conformational change of the GluN1 subunit intracellular C-terminus domain. Together our data fuels the view that the extracellular microenvironment regulates synaptic NMDAR signaling.
Keywords: NMDA; neuroscience; none; subunit trafficking; synapse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures



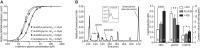

Similar articles
-
Identity of the NMDA receptor coagonist is synapse specific and developmentally regulated in the hippocampus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 13;112(2):E204-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1416668112. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25550512 Free PMC article.
-
ANKS1B Gene Product AIDA-1 Controls Hippocampal Synaptic Transmission by Regulating GluN2B Subunit Localization.J Neurosci. 2015 Jun 17;35(24):8986-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4029-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26085624 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Nanoscale Topography and Functional Role of GluN2-NMDA Receptor Subtypes at Glutamatergic Synapses.Neuron. 2018 Oct 10;100(1):106-119.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 30269991
-
Role of nonsynaptic GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in excitotoxicity: evidence that fluoxetine selectively inhibits these receptors and may have neuroprotective effects.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Apr;93:32-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.10.005. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23089362 Review.
-
NMDA receptor activation: two targets for two co-agonists.Neurochem Res. 2013 Jun;38(6):1156-62. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-0987-2. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23389661 Review.
Cited by
-
NMDARs in Alzheimer's Disease: Between Synaptic and Extrasynaptic Membranes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;25(18):10220. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810220. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotection of retinal ganglion cells by the sigma-1 receptor agonist pridopidine in models of experimental glaucoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 9;11(1):21975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01077-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34753986 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Non-ionotropic NMDA Receptor Signaling in Dendritic Spine Shrinkage.J Neurosci. 2020 May 6;40(19):3741-3750. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0046-20.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 22. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32321746 Free PMC article.
-
Kainate Receptor Activation Shapes Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity by Controlling Receptor Lateral Mobility at Glutamatergic Synapses.Cell Rep. 2020 Jun 9;31(10):107735. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107735. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32521260 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of NMDA receptors and other ion channel types by membrane-associated drugs.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1561956. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1561956. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40371334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

