Zinc-dependent regulation of zinc import and export genes by Zur
- PMID: 28598435
- PMCID: PMC5472717
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15812
Zinc-dependent regulation of zinc import and export genes by Zur
Abstract
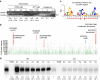
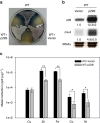
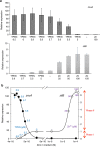
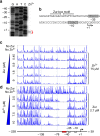
In most bacteria, zinc depletion is sensed by Zur, whereas the surplus is sensed by different regulators to achieve zinc homeostasis. Here we present evidence that zinc-bound Zur not only represses genes for zinc acquisition but also induces the zitB gene encoding a zinc exporter in Streptomyces coelicolor, a model actinobacteria. Zinc-dependent gene regulation by Zur occurs in two phases. At sub-femtomolar zinc concentrations (phase I), dimeric Zur binds to the Zur-box motif immediately upstream of the zitB promoter, resulting in low zitB expression. At the same time, Zur represses genes for zinc uptake. At micromolar zinc concentrations (phase II), oligomeric Zur binding with footprint expansion upward from the Zur box results in high zitB induction. Our findings reveal a mode of zinc-dependent gene activation that uses a single metalloregulator to control genes for both uptake and export over a wide range of zinc concentrations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Finney L. A. & O'Halloran T. V. Transition metal speciation in the cell: insights from the chemistry of metal ion receptors. Science 300, 931–936 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Waldron K. J., Rutherford J. C., Ford D. & Robinson N. J. Metalloproteins and metal sensing. Nature 460, 823–830 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Giedroc D. P. & Arunkumar A. I. Metal sensor proteins: nature's metalloregulated allosteric switches. Dalton Trans. 29, 3107–3120 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

