The dynamic role of autophagy and MAPK signaling in determining cell fate under cisplatin stress in osteosarcoma cells
- PMID: 28598976
- PMCID: PMC5466322
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179203
The dynamic role of autophagy and MAPK signaling in determining cell fate under cisplatin stress in osteosarcoma cells
Abstract
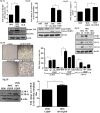
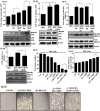
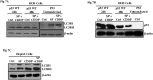
Osteosarcoma (OS) is an aggressive bone malignancy commonly observed in children and adolescents. Sub-optimal therapy for years has irretrievably compromised the chances of OS patient survival; also, lack of extensive research on this rare disease has hindered therapeutic development. Cisplatin, a common anti-tumor drug, is currently an integral part of treatment regime for OS along with methotrexate and doxorubicin. However, toxicity issues associated with combination module impede OS therapy. Also, despite the proven benefits of cisplatin, acquisition of resistance remains a concern with cisplatin-based therapy. This prompted us to investigate the molecular effects of cisplatin exposure and changes associated with acquired resistance in OS cells. Cisplatin shock was found to activate MAPK signaling and autophagy in OS cells. An activation of JNK and autophagy acted as pro-survival strategy, while ERK1/2 triggered apoptotic signals upon cisplatin stress. A crosstalk between JNK and autophagy was observed. Maximal sensitivity to cisplatin was obtained with simultaneous inhibition of both autophagy and JNK pathway. Cisplatin resistant cells were further developed by repetitive drug exposure followed by clonal selection. The resistant cells showed an altered signaling circuitry upon cisplatin exposure. Our results provide valuable cues to possible molecular alterations that can be considered for development of improved therapeutic strategy against osteosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting autophagy is a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome chemoresistance and reduce metastasis in osteosarcoma.Int J Oncol. 2019 Dec;55(6):1213-1222. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4902. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31638211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-apoptotic and pro-autophagic effects of the Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) on human osteosarcoma U-2 OS and MG-63 cells through the activation of mitochondria-mediated pathway and inhibition of p38 MAPK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Mar 12;9:1555-84. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S74197. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25792811 Free PMC article.
-
miR-223/Hsp70/JNK/JUN/miR-223 feedback loop modulates the chemoresistance of osteosarcoma to cisplatin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Mar 11;497(3):827-834. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.091. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29432736
-
Inhibition of beclin1 affects the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of osteosarcoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Sep 15;7(10):7114-22. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25400807 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR: An attractive therapeutic target for osteosarcoma?Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):50805-50813. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9305. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27177330 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting autophagy is a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome chemoresistance and reduce metastasis in osteosarcoma.Int J Oncol. 2019 Dec;55(6):1213-1222. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4902. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31638211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy and its role in osteosarcoma.Cancer Med. 2023 Mar;12(5):5676-5687. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5407. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36789748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome-wide expression profile of noncoding RNAs in human osteosarcoma cells as they acquire resistance to cisplatin.Discov Oncol. 2021 Oct 20;12(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s12672-021-00441-6. Discov Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35201486 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the interplay between mitochondria-regulated cell death and energetic metabolism in osteosarcoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 22;10:948097. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.948097. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36072341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Diet Restriction but Not Alternate Day Fasting Prevents Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Mice.Biomedicines. 2020 Feb 3;8(2):23. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8020023. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32028692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bielack SS, Carrle D, Hardes J, Schuck A, Paulussen M. Bone tumors in adolescents and young adults. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2008. February;9(1):67–80. doi: 10.1007/s11864-008-0057-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bacci G, Ferrari S, Bertoni F, Picci P, Bacchini P, Longhi A, et al. Histologic response of high-grade nonmetastatic osteosarcoma of the extremity to chemotherapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. May(386):186–96. - PubMed
-
- Bacci G, Rocca M, Salone M, Balladelli A, Ferrari S, Palmerini E, et al. High grade osteosarcoma of the extremities with lung metastases at presentation: treatment with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and simultaneous resection of primary and metastatic lesions. J Surg Oncol. 2008. November 1;98(6):415–20. doi: 10.1002/jso.21140 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blay JY. Chemotherapy for osteosarcoma without high-dose methotrexate: another piece in the puzzle. Onkologie. 2007. May;30(5):226–7. - PubMed
-
- Chou AJ, Geller DS, Gorlick R. Therapy for osteosarcoma: where do we go from here? Paediatr Drugs. 2008;10(5):315–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

