Effects of traditional oriental medicines as anti-cytotoxic agents in radiotherapy
- PMID: 28599460
- PMCID: PMC5452946
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6042
Effects of traditional oriental medicines as anti-cytotoxic agents in radiotherapy
Abstract
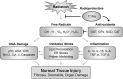
The primary goal of radiotherapy in oncology is to enhance the efficacy of tumor cell death while decreasing damage to surrounding normal cells. Positive therapeutic outcomes may be accomplished by improved targeting, precisely targeting tumor cells or protecting normal cells against radiation-induced damage. The potential for antioxidants to decrease normal tissue damage induced by radiation has been investigated in animal models for a number of decades. In attempts for radioprotection, certain synthetic chemicals are suggested as antioxidants and normal tissue protectors against radiation-induced damage, but they have exhibited limitations in pharmacological application due to undesirable effects and high toxicities at clinical doses. The present review focuses on the radioprotective efficacy of traditional oriental medicines with the advantage of low toxicity at pharmacological doses and how such treatments may influence various harmful effects induced by radiation in vitro and in vivo. In addition, medicinal plants and their active constituents with biological activities that may be associated with alleviation of radiation-induced damage through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, wound healing and immunostimulatory properties are discussed.
Keywords: antioxidant; cancer; natural product; radioprotector; radiotherapy; reactive oxygen species; traditional oriental medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protection against ionizing radiation by antioxidant nutrients and phytochemicals.Toxicology. 2003 Jul 15;189(1-2):1-20. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(03)00149-5. Toxicology. 2003. PMID: 12821279 Review.
-
Exploring Natural Products as Radioprotective Agents for Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 12;15(14):3585. doi: 10.3390/cancers15143585. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37509245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radioprotection by plant products: present status and future prospects.Phytother Res. 2005 Jan;19(1):1-22. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1605. Phytother Res. 2005. PMID: 15799007 Review.
-
A radiobiological review on melatonin: a novel radioprotector.J Radiat Res. 2007 Jul;48(4):263-72. doi: 10.1269/jrr.06070. J Radiat Res. 2007. PMID: 17641465 Review.
-
Radioprotective potential of ginseng.Mutagenesis. 2005 Jul;20(4):237-43. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gei041. Epub 2005 Jun 14. Mutagenesis. 2005. PMID: 15956041 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
