Prognostic Value of Serial N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Testing in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 28599802
- PMCID: PMC5821435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.04.004
Prognostic Value of Serial N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Testing in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
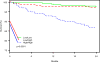
Natriuretic peptides (NPs) are important predictors of outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) but can change over time. The association of patterns of NP changes after AMI on outcomes is less clear. We measured N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) during the AMI admission and at 1 month in a prospective AMI registry. Outcomes included 1-year readmission and 2-year mortality. An elevated NT-proBNP was defined using age-specific criteria. Patients were classified into 3 groups (low/low [referent group], high/low, high/high) based on NT-proBNP value at enrollment and 1 month. The incremental predictive value of NT-proBNP was determined after adjusting for 6-month GRACE risk score, diabetes, and ejection fraction <40%. Among 773 patients, 303 (38%) were low/low, 240 (30%), and were high/high, 230 (29%) were high/low. Two-year mortality was highest in high/high patients but similar in the high/low and low/low patients (13.1% vs 2.7% and 2.3%, respectively). Similarly, readmission was significantly more likely in the high/high versus the high/low and low/low groups. After adjustment, mortality was significantly higher in the high/high group (hazard ratio 4.02, 95% CI 1.67 to 9.66) compared with the low/low group, although readmission was no longer statistically different (hazard ratio 1.37, 95% CI 0.93 to 2.03). In conclusion, a persistently elevated NT-proBNP assessed 1 month after discharge was associated with a higher risk of mortality in patient with AMI. Postdischarge risk stratification using NT-proBNP has the potential to identify higher risk patients after AMI.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Myocardial Infarction and N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide.Am J Cardiol. 2017 Nov 1;120(9):1697. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.07.073. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Am J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28844516 No abstract available.
References
-
- O’Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE, Jr, Chung MK, de Lemos JA, Ettinger SM, Fang JC, Fesmire FM, Franklin BA, Granger CB, Krumholz HM, Linderbaum JA, Morrow DA, Newby LK, Ornato JP, Ou N, Radford MJ, Tamis-Holland JE, Tommaso CL, Tracy CM, Woo YJ, Zhao DX, Anderson JL, Jacobs AK, Halperin JL, Albert NM, Brindis RG, Creager MA, DeMets D, Guyton RA, Hochman JS, Kovacs RJ, Kushner FG, Ohman EM, Stevenson WG, Yancy CW, American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013;127:e362–e425. - PubMed
-
- Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, Casey DE, Jr, Ganiats TG, Holmes DR, Jr, Jaffe AS, Jneid H, Kelly RF, Kontos MC, Levine GN, Liebson PR, Mukherjee D, Peterson ED, Sabatine MS, Smalling RW, Zieman SJ, American College of Cardiology.; American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines.; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions.; Society of Thoracic Surgeons.; American Association for Clinical Chemistry 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients with Non-ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:e139–e228. - PubMed
-
- Mair J, Hammerer-Lercher A, Puschendorf B. The impact of cardiac natriuretic peptide determination on the diagnosis and management of heart failure. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2001;39:571–588. - PubMed
-
- Morrow DA, de Lemos JA, Blazing MA, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Jarolim P, White HD, Fox KA, Califf RM, Braunwald E, Investigators Prognostic value of serial B-type natriuretic peptide testing during follow-up of patients with unstable coronary artery disease. JAMA. 2005;294:2866–2871. - PubMed
-
- Lindahl B, Lindbäck J, Jernberg T, Johnston N, Stridsberg M, Venge P, Wallentin L. Serial analyses of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: a Fragmin and fast Revascularisation during In Stability in Coronary artery disease (FRISC)-II substudy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:533–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous