Amphiregulin contained in NSCLC-exosomes induces osteoclast differentiation through the activation of EGFR pathway
- PMID: 28600504
- PMCID: PMC5466625
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03460-y
Amphiregulin contained in NSCLC-exosomes induces osteoclast differentiation through the activation of EGFR pathway
Abstract
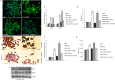
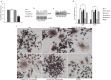
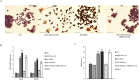
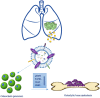
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The majority of patients are diagnosed in advanced disease stage. Bone metastasis is the most frequent complication in NSCLC resulting in osteolytic lesions. The perfect balance between bone-resorbing osteoclasts and bone-forming osteoblasts activity is lost in bone metastasis, inducing osteoclastogenesis. In NSCLC, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway is constitutively activated. EGFR binds Amphiregulin (AREG) that is overexpressed in several cancers such as colon, breast and lung. Its levels in plasma of NSCLC patients correlate with poor prognosis and AREG was recently found as a signaling molecule in exosomes derived from cancer cell lines. Exosomes have a key role in the cell-cell communication and they were recently indicated as important actors in metastatic niche preparation. In the present work, we hypothesize a role of AREG carried by exosomes derived from NSCLC in bone metastasis induction. We observed that NSCLC-exosomes, containing AREG, induce EGFR pathway activation in pre-osteoclasts that in turn causes an increased expression of RANKL. RANKL is able to induce the expression of proteolytic enzymes, well-known markers of osteoclastogenesis, triggering a vicious cycle in osteolytic bone metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
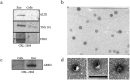
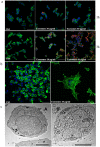
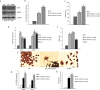
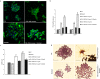

Similar articles
-
Multiple myeloma-derived exosomes are enriched of amphiregulin (AREG) and activate the epidermal growth factor pathway in the bone microenvironment leading to osteoclastogenesis.J Hematol Oncol. 2019 Jan 8;12(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0689-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30621731 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour-derived exosomal lncRNA-SOX2OT promotes bone metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the miRNA-194-5p/RAC1 signalling axis in osteoclasts.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 2;12(7):662. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03928-w. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34215717 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR4 Accelerates Osteoclastogenesis Induced by Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells Through Self-Potentiation and VCAM1 Secretion.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3):1084-1099. doi: 10.1159/000494533. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30355915
-
RANK pathway in giant cell tumor of bone: pathogenesis and therapeutic aspects.Tumour Biol. 2015 Feb;36(2):495-501. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3094-y. Epub 2015 Jan 25. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25618600 Review.
-
Amphiregulin.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Apr;28:31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.01.005. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24463227 Review.
Cited by
-
Restoring Tissue Homeostasis at Metastatic Sites: A Focus on Extracellular Vesicles in Bone Metastasis.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 22;11:644109. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.644109. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33869035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Connection: Extracellular Vesicles and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 9;19:8139-8157. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S477851. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39139506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impacts of exosomes on bone metastatic progression and their potential clinical utility.Bone Rep. 2022 Jul 21;17:101606. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2022.101606. eCollection 2022 Dec. Bone Rep. 2022. PMID: 35910404 Free PMC article.
-
Bone-organ axes: bidirectional crosstalk.Mil Med Res. 2024 Jun 12;11(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40779-024-00540-9. Mil Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38867330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Synovial Exosomes in Osteoclast Differentiation in Inflammatory Arthritis.Cells. 2021 Jan 10;10(1):120. doi: 10.3390/cells10010120. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33435236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riess JW, Wakelee HA. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer management: novel targets and recent clinical advances. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2012;10:226–234. - PubMed
-
- Perisano C, et al. Soft tissue metastases in lung cancer: a review of the literature. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012;16:1908–1914. - PubMed
-
- Roato, I. et al. Spontaneous osteoclastogenesis is a predictive factor for bone metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer61, doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.10.016 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

