Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 and Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Expression in Osteoblasts
- PMID: 28600546
- PMCID: PMC5466660
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03310-x
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 and Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Expression in Osteoblasts
Abstract
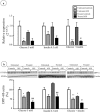
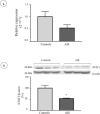
It has been proposed that girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) tend to have a taller stature and a lower body mass index. Energy homeostasis, that is known to affect bone growth, could contribute to these characteristics. In circulation, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inactivates glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), an incretin that promotes insulin secretion and sensitivity. Our objectives were to investigate DPP-4 status in plasma and in osteoblasts of AIS subjects and controls and to evaluate the regulatory role of metabolic effectors on DPP-4 expression. DPP-4 activity was assessed in plasma of 113 girls and 62 age-matched controls. Osteoblasts were isolated from bone specimens of AIS patients and controls. Human cells were incubated with glucose, insulin, GLP-1 and butyrate. Gene and protein expressions were evaluated by RT-qPCR and Western blot. Our results showed 14% inferior plasma DPP-4 activity in AIS patients when compared to healthy controls (P = 0.0357). Similarly, osteoblasts derived from AIS subjects had lower DPP-4 gene and protein expression than controls by 90.5% and 57.1% respectively (P < 0.009). DPP-4 expression was regulated in a different manner in osteoblasts isolated from AIS participants compared to controls. Our results suggest a role for incretins in AIS development and severity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 is associated with myogenesis in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis possibly via mediation of insulin sensitivity.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Feb 9;17(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-02978-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35139864 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of long-term dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibition on body composition and glucose tolerance in high fat diet-fed mice.Life Sci. 2009 Jun 19;84(25-26):876-81. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2009.03.022. Epub 2009 Apr 7. Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19358859
-
Plasma Incretin Levels and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Activity in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016 Aug;13(8):1378-87. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201510-697OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016. PMID: 27104640
-
Incretins: their physiology and application in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014 Jul;30(5):354-71. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2501. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014. PMID: 24989141 Review.
-
Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells.Metabolism. 2014 Jan;63(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140094 Review.
Cited by
-
Bufalin attenuates cancer-induced pain and bone destruction in a model of bone cancer.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;390(12):1211-1219. doi: 10.1007/s00210-017-1419-7. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28840279
-
A Differential Hypofunctionality of Gαi Proteins Occurs in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Correlates with the Risk of Disease Progression.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 11;9(1):10074. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46325-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31296888 Free PMC article.
-
Etiology of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Literature Review.Asian Spine J. 2019 Jun;13(3):519-526. doi: 10.31616/asj.2018.0096. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Asian Spine J. 2019. PMID: 30744305 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 is associated with myogenesis in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis possibly via mediation of insulin sensitivity.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Feb 9;17(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-02978-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35139864 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric expression of GPR126 in the convex/concave side of the spine is associated with spinal skeletal malformation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis population.Eur Spine J. 2019 Sep;28(9):1977-1986. doi: 10.1007/s00586-019-06001-5. Epub 2019 May 11. Eur Spine J. 2019. PMID: 31079250
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

