mTORC1 and mTORC2 as regulators of cell metabolism in immunity
- PMID: 28600802
- PMCID: PMC6322652
- DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.12711
mTORC1 and mTORC2 as regulators of cell metabolism in immunity
Abstract
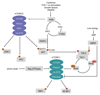
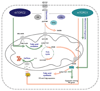
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway is an evolutionarily conserved signaling pathway that senses intra- and extracellular nutrients, growth factors, and pathogen-associated molecular patterns to regulate the function of innate and adaptive immune cell populations. In this review, we focus on the role of the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2 in the regulation of the cellular energy metabolism of these immune cells to regulate and support immune responses. In this regard, mTORC1 and mTORC2 generally promote an anabolic response by stimulating protein synthesis, glycolysis, mitochondrial functions, and lipid synthesis to influence proliferation and survival, effector and memory responses, innate training and tolerance as well as hematopoietic stem cell maintenance and differentiation. Deactivation of mTOR restores cell homeostasis after immune activation and optimizes antigen presentation and memory T-cell generation. These findings show that the mTOR pathway integrates spatiotemporal information of the environmental and cellular energy status by regulating cellular metabolic responses to guide immune cell activation. Elucidation of the metabolic control mechanisms of immune responses will help to generate a systemic understanding of the immune system.
Keywords: T-cell; dendritic cell; glycolysis; immune cell metabolism; lipid metabolism; mTORC1; mTORC2; macrophage; mitochondria.
© 2017 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures
References
-
- Haidinger M, Poglitsch M, Geyeregger R, Kasturi S, Zeyda M, Zlabinger GJ, Pulendran B, Horl WH, Saemann MD, Weichhart T. A versatile role of mammalian target of rapamycin in human dendritic cell function and differentiation. J Immunol. 2010;185:3919–31. - PubMed
-
- Lehman JA, Calvo V, Gomez-Cambronero J. Mechanism of ribosomal p70S6 kinase activation by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in neutrophils: cooperation of a MEK-related, THR421/SER424 kinase and a rapamycin-sensitive, m-TOR-related THR389 kinase. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:28130–8. - PubMed
-
- Fukao T, Tanabe M, Terauchi Y, Ota T, Matsuda S, Asano T, Kadowaki T, Takeuchi T, Koyasu S. PI3K-mediated negative feedback regulation of IL-12 production in DCs. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:875–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

