The Importance of Being Modified: The Role of RNA Modifications in Translational Fidelity
- PMID: 28601219
- PMCID: PMC8118379
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.enz.2017.03.005
The Importance of Being Modified: The Role of RNA Modifications in Translational Fidelity
Abstract
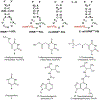
The posttranscriptional modifications of tRNA's anticodon stem and loop (ASL) domain represent a third level, a third code, to the accuracy and efficiency of translating mRNA codons into the correct amino acid sequence of proteins. Modifications of tRNA's ASL domain are enzymatically synthesized and site specifically located at the anticodon wobble position-34 and 3'-adjacent to the anticodon at position-37. Degeneracy of the 64 Universal Genetic Codes and the limitation in the number of tRNA species require some tRNAs to decode more than one codon. The specific modification chemistries and their impact on the tRNA's ASL structure and dynamics enable one tRNA to decode cognate and "wobble codons" or to expand recognition to synonymous codons, all the while maintaining the translational reading frame. Some modified nucleosides' chemistries prestructure tRNA to read the two codons of a specific amino acid that shares a twofold degenerate codon box, and other chemistries allow a different tRNA to respond to all four codons of a fourfold degenerate codon box. Thus, tRNA ASL modifications are critical and mutations in genes for the modification enzymes and tRNA, the consequences of which is a lack of modification, lead to mistranslation and human disease. By optimizing tRNA anticodon chemistries, structure, and dynamics in all organisms, modifications ensure translational fidelity of mRNA transcripts.
Keywords: Codon degeneracy and decoding; Human disease and tRNA modifications; Modification chemistry and structure; Modifications 3′-adjacent to the anticodon; Modifications prestructure tRNA; Wobble position tRNA modifications.
© 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
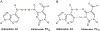
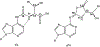
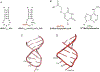

References
-
- Zimmerman E, Yonath A Biological implications of the ribosome's stunning stereochemistry. ChemBioChem. 2009;10(1):63–72. - PubMed
-
- Greber BJ, Ban N Structure and function of the mitochondrial ribosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2016;85:103–132. - PubMed
-
- Kurland C, Hughes D, Ehrenberg M Limitations of translational accuracy. In: Neidhardt FC, Curtis JL III Ingraham R, Lin ECC, Low JKB, Magasarák B, Reznikoff WS, Riley M, Schaachler M, Umbarger HE, eds. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 1996:979–1004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
