Serum fibrinogen and cardiovascular events in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes and stable coronary artery disease: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 28601829
- PMCID: PMC5734258
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015041
Serum fibrinogen and cardiovascular events in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes and stable coronary artery disease: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate the association of serum fibrinogen with cardiovascular events (CVE) in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and stable coronary artery disease (CAD).
Design: An observational study.
Setting: FuWai Hospital in Beijing, China.
Participants: A cohort of 1466 patients with T2DM and angiographic-proven stable CAD was evaluated.
Outcome measures: Baseline serum fibrinogen levels were measured and trisected into 'low', 'middle' and 'high'. Their association with CVE was explored using Cox proportional hazard models.
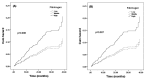
Results: With 20.2 months (average) follow-up, 44 (3%) were lost to follow-up and 96 patients developed CVE. Compared with the patients without CVE, the ones who developed CVE had higher levels of fibrinogen. Univariable regression revealed a significant relation of fibrinogen to CVE (HR (HR) 1.25, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.47, p=0.010) per SD increase of fibrinogen at baseline. After adjusting for multiple established cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, the association persisted (HR 1.30, 95% CI 1.02 to 1.66, p=0.037). Moreover, after adjusting for CVD risk factors, the HRs for middle-serum and high-serum fibrinogen concentration, using 'low' group as reference, were 1.23 (95% CI 0.69 to 2.20) and 2.20 (95% CI 1.11 to 3.36, p=0.049).
Conclusions: We first indicated that elevated fibrinogen level was independently associated with increased CVE in Chinese patients with T2DMand stable CAD.
Keywords: Fibrinogen; coronary artery disease; outcome; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibrinogen is associated with glucose metabolism and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Mar 19;19(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01012-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32192491 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of cardiovascular events and vascular interventions in patients with type 2 diabetes.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Dec 1;248:301-307. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.07.081. Epub 2017 Jul 23. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28802735
-
Long-term prognostic utility of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) triglyceride in real-world patients with coronary artery disease and diabetes or prediabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Sep 27;19(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01125-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32981521 Free PMC article.
-
Role of relationship between HbA1c, fibrinogen and HDL-cholesterol on cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Atherosclerosis. 2013 May;228(1):247-8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.02.010. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Atherosclerosis. 2013. PMID: 23466074
-
Blood fibrinogen level as a biomarker of adverse outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Aug 19;101(33):e30117. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030117. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35984145 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential of Raman spectroscopy for the analysis of plasma/serum in the liquid state: recent advances.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020 Apr;412(9):1993-2007. doi: 10.1007/s00216-019-02349-1. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020. PMID: 31900532 Review.
-
Fibrinogen is associated with glucose metabolism and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Mar 19;19(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01012-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32192491 Free PMC article.
-
The association between fibrinogen levels and severity of coronary artery disease and long-term prognosis following percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 29;14:1287855. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1287855. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38093962 Free PMC article.
-
Precision prognostics for cardiovascular disease in Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Commun Med (Lond). 2024 Jan 22;4(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00429-z. Commun Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38253823 Free PMC article.
-
D-Dimer to Fibrinogen Ratio as a Novel Prognostic Marker in Patients After Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020 Jan-Dec;26:1076029620948586. doi: 10.1177/1076029620948586. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 32842770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Willeit P, Thompson SG, Agewall S, et al. . Inflammatory markers and extent and progression of early atherosclerosis: meta-analysis of individual-participant-data from 20 prospective studies of the PROG-IMT collaboration. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2016;23:194–205. 10.1177/2047487314560664 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous