Exercise interventions for cerebral palsy
- PMID: 28602046
- PMCID: PMC6481791
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011660.pub2
Exercise interventions for cerebral palsy
Abstract
Background: Cerebral palsy (CP) is a neurodevelopmental disorder resulting from an injury to the developing brain. It is the most common form of childhood disability with prevalence rates of between 1.5 and 3.8 per 1000 births reported worldwide. The primary impairments associated with CP include reduced muscle strength and reduced cardiorespiratory fitness, resulting in difficulties performing activities such as dressing, walking and negotiating stairs.Exercise is defined as a planned, structured and repetitive activity that aims to improve fitness, and it is a commonly used intervention for people with CP. Aerobic and resistance training may improve activity (i.e. the ability to execute a task) and participation (i.e. involvement in a life situation) through their impact on the primary impairments of CP. However, to date, there has been no comprehensive review of exercise interventions for people with CP.
Objectives: To assess the effects of exercise interventions in people with CP, primarily in terms of activity, participation and quality of life. Secondary outcomes assessed body functions and body structures. Comparators of interest were no treatment, usual care or an alternative type of exercise intervention.
Search methods: In June 2016 we searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, nine other databases and four trials registers.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs of children, adolescents and adults with CP. We included studies of aerobic exercise, resistance training, and 'mixed training' (a combination of at least two of aerobic exercise, resistance training and anaerobic training).
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently screened titles, abstracts and potentially relevant full-text reports for eligibility; extracted all relevant data and conducted 'Risk of bias' and GRADE assessments.
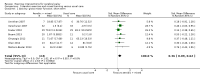
Main results: We included 29 trials (926 participants); 27 included children and adolescents up to the age of 19 years, three included adolescents and young adults (10 to 22 years), and one included adults over 20 years. Males constituted 53% of the sample. Five trials were conducted in the USA; four in Australia; two in Egypt, Korea, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan, the Netherlands, and the UK; three in Greece; and one apiece in India, Italy, Norway, and South Africa.Twenty-six trials included people with spastic CP only; three trials included children and adolescents with spastic and other types of CP. Twenty-one trials included people who were able to walk with or without assistive devices, four trials also included people who used wheeled mobility devices in most settings, and one trial included people who used wheeled mobility devices only. Three trials did not report the functional ability of participants. Only two trials reported participants' manual ability. Eight studies compared aerobic exercise to usual care, while 15 compared resistance training and 4 compared mixed training to usual care or no treatment. Two trials compared aerobic exercise to resistance training. We judged all trials to be at high risk of bias overall.We found low-quality evidence that aerobic exercise improves gross motor function in the short term (standardised mean difference (SMD) 0.53, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.02 to 1.04, N = 65, 3 studies) and intermediate term (mean difference (MD) 12.96%, 95% CI 0.52% to 25.40%, N = 12, 1 study). Aerobic exercise does not improve gait speed in the short term (MD 0.09 m/s, 95% CI -0.11 m/s to 0.28 m/s, N = 82, 4 studies, very low-quality evidence) or intermediate term (MD -0.17 m/s, 95% CI -0.59 m/s to 0.24 m/s, N = 12, 1 study, low-quality evidence). No trial assessed participation or quality of life following aerobic exercise.We found low-quality evidence that resistance training does not improve gross motor function (SMD 0.12, 95% CI -0.19 to 0.43, N = 164, 7 studies), gait speed (MD 0.03 m/s, 95% CI -0.02 m/s to 0.07 m/s, N = 185, 8 studies), participation (SMD 0.34, 95% CI -0.01 to 0.70, N = 127, 2 studies) or parent-reported quality of life (MD 12.70, 95% CI -5.63 to 31.03, n = 12, 1 study) in the short term. There is also low-quality evidence that resistance training does not improve gait speed (MD -0.03 m/s, 95% CI -0.17 m/s to 0.11 m/s, N = 84, 3 studies), gross motor function (SMD 0.13, 95% CI -0.30 to 0.55, N = 85, 3 studies) or participation (MD 0.37, 95% CI -6.61 to 7.35, N = 36, 1 study) in the intermediate term.We found low-quality evidence that mixed training does not improve gross motor function (SMD 0.02, 95% CI -0.29 to 0.33, N = 163, 4 studies) or gait speed (MD 0.10 m/s, -0.07 m/s to 0.27 m/s, N = 58, 1 study) but does improve participation (MD 0.40, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.67, N = 65, 1 study) in the short-term.There is no difference between resistance training and aerobic exercise in terms of the effect on gross motor function in the short term (SMD 0.02, 95% CI -0.50 to 0.55, N = 56, 2 studies, low-quality evidence).Thirteen trials did not report adverse events, seven reported no adverse events, and nine reported non-serious adverse events.
Authors' conclusions: The quality of evidence for all conclusions is low to very low. As included trials have small sample sizes, heterogeneity may be underestimated, resulting in considerable uncertainty relating to effect estimates. For children with CP, there is evidence that aerobic exercise may result in a small improvement in gross motor function, though it does not improve gait speed. There is evidence that resistance training does not improve gait speed, gross motor function, participation or quality of life among children with CP.Based on the evidence available, exercise appears to be safe for people with CP; only 55% of trials, however, reported adverse events or stated that they monitored adverse events. There is a need for large, high-quality, well-reported RCTs that assess the effectiveness of exercise in terms of activity and participation, before drawing any firm conclusions on the effectiveness of exercise for people with CP. Research is also required to determine if current exercise guidelines for the general population are effective and feasible for people with CP.
Conflict of interest statement
Jennifer M Ryan, Elizabeth E Cassidy, and Neil E O'Connell are chartered physiotherapists and lecturers in physiotherapy. As professionals who might be involved in the delivery of exercise interventions, it is plausible that they might be perceived as having a bias favouring the effectiveness of exercise.
Jennifer M Ryan is receiving funding from Action Medical Research and the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy Charitable Trust, to evaluate the feasibility, acceptability and efficacy of resistance training for adolescents with CP.
Elizabeth E Cassidy: none known.
Stephen G Noorduyn: Stephen was lead author on Noorduyn 2011, which was screened by JR and EC.
Neil E O'Connell: none known.
Figures
















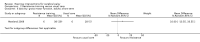




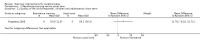




















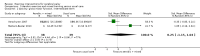



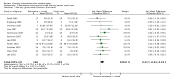



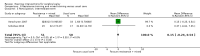


Comment in
-
Are exercise interventions effective in patients with cerebral palsy? A Cochrane Review summary with commentary.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2020 Jan;62(1):18-20. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.14400. Epub 2019 Nov 17. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31736047 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Bryant 2013 {published and unpublished data}
Chen 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chen CL, Hong WH, Cheng HY, Liaw MY, Chung CY, Chen CY. Muscle strength enhancements following home‐based virtual cycling training in ambulatory children with cerebral palsy. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2012;33(4):1087‐94. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ridd.2012.01.017; PUBMED: 22502833] - DOI - PubMed
Chrysagis 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chrysagis N, Douka A, Nikopoulos M, Apostolopoulou F, Koutsouki D. Effects of an aquatic program on gross motor function of children with spastic cerebral palsy. Biology of Exercise 2009;5(2):13‐25. [DOI: 10.4127/jbe.2009.0027] - DOI
Chrysagis 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chrysagis N, Skordilis EK, Stavrou N, Grammatopoulou E, Koutsouki D. The effect of treadmill training on gross motor function and walking speed in ambulatory adolescents with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2012;91(9):747‐60. [DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0b013e3182643eba; PUBMED: 22902937] - DOI - PubMed
Dodd 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dodd KJ, Taylor NF, Graham HK. A randomized clinical trial of strength training in young people with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2003;45(10):652‐7. [PUBMED: 14515935] - PubMed
Emara 2015 {published data only}
-
- Emara H. Effect of a new physical therapy concept on dynamic balance in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 2015;16(1):77‐83. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmhg.2014.09.001] - DOI
Engsberg 2006 {published and unpublished data}
Fowler 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- DeMuth SK, Knutson LM, Fowler EG. The PEDALS stationary cycling intervention and health‐related quality of life in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2012;54(7):654‐61. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04321.x; PUBMED: 22582760] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fowler EG, Knutson LM, DeMuth SK, Siebert KL, Simms VD, Sugi MH, et al. Pediatric endurance and limb strengthening (PEDALS) for children with cerebral palsy using stationary cycling: a randomized controlled trial. Physical Therapy 2010;90(3):367‐81. [DOI: 10.2522/ptj.20080364; PUBMED: 20093327] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fowler EG, Knutson LM, DeMuth SK, Sugi M, Siebert K, Simms V, et al. Pediatric endurance and limb strengthening for children with cerebral palsy (PEDALS) ‐ a randomized controlled trial protocol for a stationary cycling intervention. BMC Pediatrics 2007;7:14. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-7-14; PMC1838902; PUBMED: 17374171] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Gharib 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gharib NM, El‐Maksoud GM, Rezk‐Allah SS. Efficacy of gait trainer as an adjunct to traditional physical therapy on walking performance in hemiparetic cerebral palsied children: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2011;25(10):924‐34. [DOI: 10.1177/0269215511400768; PUBMED: 21427153] - DOI - PubMed
Johnston 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gates PE, Banks D, Johnston TE, Campbell SR, Gaughan JP, Ross SA, et al. Randomized controlled trial assessing participation and quality of life in a supported speed treadmill training exercise program vs. a strengthening program for children with cerebral palsy. Journal of Pediatric Rehabilitation Medicine 2012;5(2):75‐88. [DOI: 10.3233/PRM-2012-0199; PUBMED: 22699098] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Johnston TE, Watson KE, Ross SA, Gates PE, Gaughan JP, Lauer RT, et al. Effects of a supported speed treadmill training exercise program on impairment and function for children with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2011;53(8):742‐50. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.03990.x; PUBMED: 21679357] - DOI - PubMed
Lee 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lee JH, Sung IY, Yoo JY. Therapeutic effects of strengthening exercise on gait function of cerebral palsy. Disability and Rehabilitation 2008;30(19):1439‐44. [PUBMED: 19230216] - PubMed
Lee 2015 {published data only}
Liao 2007 {published and unpublished data}
Maeland 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Maeland S, Jahnsen R, Opheim A, Froslie KF, Moe‐Nilssen R, Stanghelle JK. No effect on gait function of progressive resistance exercise in adults with cerebral palsy ‐ a single‐blind randomized controlled trial. Advances in Physiotherapy 2009;11(4):227‐33. [DOI: 10.3109/14038190902912423] - DOI
Mattern‐Baxter 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mattern‐Baxter K, McNeil S, Mansoor JK. Effects of home‐based locomotor treadmill training on gross motor function in young children with cerebral palsy: a quasi‐randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2013;94(11):2061‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2013.05.012; PUBMED: 23747646] - DOI - PubMed
McCubbin 1985 {published data only}
-
- McCubbin JA, Shasby GB. Effects of isokinetic exercise on adolescents with cerebral palsy. Adapted Physical Activity Quarterly 1985;2(1):56‐64. [DOI: 10.1123/apaq.2.1.56] - DOI
Mitchell 2016 {published data only}
Olama 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Olama KA. Endurance exercises versus treadmill training in improving muscle strength and functional activities in hemiparetic cerebral palsy. The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 2011;12(2):193‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmhg.2011.07.002] - DOI
Pandey 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pandey DP, Tyagi V. Effect of functional strength training on functional motor performance in young children with cerebral palsy. Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy 2011;5(1):52‐5.
Reid 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Scholtes 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Scholtes VA, Becher JG, Comuth A, Dekkers H, Dijk L, Dallmeijer AJ. Effectiveness of functional progressive resistance exercise strength training on muscle strength and mobility in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2010;52(6):e107‐13. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03604.x; PUBMED: 20132136] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scholtes VA, Becher JG, Janssen‐Potten YJ, Dekkers H, Smallenbroek L, Dallmeijer AJ. Effectiveness of functional progressive resistance exercise training on walking ability in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2012;33(1):181‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ridd.2011.08.026; PUBMED: 22093663] - DOI - PubMed
Seniorou 2007 {published data only}
Smania 2011 {published and unpublished data}
Taylor 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bania TA, Dodd KJ, Baker RJ, Graham HK, Taylor NF. The effects of progressive resistance training on daily physical activity in young people with cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial. Disability and Rehabilitation 2016;38(7):620‐6. [DOI: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1055376; PUBMED: 26056856] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Taylor NF, Dodd KJ, Baker RJ, Willoughby K, Thomason P, Graham HK. Progressive resistance training and mobility‐related function in young people with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2013;55(9):806‐12. [DOI: 10.1111/dmcn.12190; PUBMED: 23789741] - DOI - PubMed
Tedla 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tedla JS. Strength training effects on balance in spastic diplegia subjects: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Pediatric Neurology 2014;12(1):15‐28. [DOI: 10.3233/JPN-140634] - DOI
Unger 2006 {published and unpublished data}
Unnithan 2007 {published and unpublished data}
Van den Berg‐Emons 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Berg‐Emons RJ, Baak MA, Speth L, Saris WH. Physical training of school children with spastic cerebral palsy: effects on daily activity, fat mass and fitness. International Journal of Rehabilitation 1998;21(2):179‐94. [PUBMED: 9924680] - PubMed
Verschuren 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Verschuren O, Ketelaar M, Gorter JW, Helders PJ, Uiterwaal CS, Takken T. Exercise training program in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 2007;161(11):1075‐81. [DOI: 10.1001/archpedi.161.11.1075; PUBMED: 17984410] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abd El‐Kafy 2014 {published data only}
Ahlborg 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ahlborg L, Andersson C, Julin P. Whole‐body vibration training compared with resistance training: effect on spasticity, muscle strength and motor performance in adults with cerebral palsy. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2006;38(5):302‐8. [DOI: 10.1080/16501970600680262; PUBMED: 16931460] - DOI - PubMed
AlSaif 2015 {published data only}
Angulo‐Barroso 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Angulo‐Barroso RM, Tiernan C, Chen LC, Valentin‐Gudiol M, Ulrich D. Treadmill training in moderate risk preterm infants promotes stepping quality ‐ results of a small randomised controlled trial. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2013;34(11):3629‐38. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ridd.2013.07.037; PUBMED: 24012586] - DOI - PubMed
Ayhan 2014 {published and unpublished data}
Bandholm 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bandholm T, Jensen BR, Nielsen LM, Rasmussen H, Bencke J, Curtis D, et al. Neurorehabilitation with versus without resistance training after botulinum toxin treatment in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized pilot study. NeuroRehabilitation 2012;30(4):277‐86. [DOI: 10.3233/NRE-2012-0756; PUBMED: 22672941] - DOI - PubMed
Bar‐Haim 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bar‐Haim S, Harries N, Belokopytov M, Lahat E, Kaplanski J. Random perturbation: a potential aid in treatment of children with cerebral palsy. Disability and Rehabilitation 2008;30(19):1420‐8. [PUBMED: 19230215] - PubMed
Bar‐or 1976 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bar‐or O, Inbar O, Spira R. Physiological effects of a sports rehabilitation program on cerebral palsied and post‐poliomyelitic adolescents. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 1976;8(3):157‐61. [PUBMED: 979561] - PubMed
Batista 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Batista KG, Lopes PO, Serradilha SM, Souza GAF, Bella GP, Souza RCT. Benefits of cardiorespiratory training in children or adolescents with cerebral palsy [Benefícios do condicionamento cardiorrespiratório em crianças ou adolescentes com paralisia cerebral]. Fisioterapia em Movimento 2010;23(2):201‐9. [DOI: 10.1590/S0103-51502010000200004] - DOI
Batra 2011 {published data only}
-
- Batra M, Sharma VP, Malik GK, Batra V, Agarwal GG. Intervention based on dynamics of postural control in children with cerebral palsy ‐‐ an integral approach. Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy 2011;5(3):68‐73.
Benda 2003 {published data only}
Blundell 2003 {published and unpublished data}
Bohm 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bohm H, Rammelmayr MK, Doderlein L. Effects of climbing therapy on gait function in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy ‐ a randomized, controlled crossover trial. European Journal of Physiotherapy 2015;17(1):1‐8. [DOI: 10.3109/21679169.2014.955525] - DOI
Boyd 2010 {published data only}
-
- Boyd R, Sakzewski L, Ziviani J, Abbott DF, Badawy R, Gilmore R, et al. INCITE: a randomised trial comparing constraint induced movement therapy and bimanual training in children with congenital hemiplegia. BMC Neurology 2010;10(4):15. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2377-10-4; PMC2832893; PUBMED: 20064275] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Brown 2010 {published data only}
Capio 2015 {published data only}
-
- Capio CM, Sit CH, Eguia KF, Abernethy B, Masters RS. Fundamental movement skills training to promote physical activity in children with and without disability: a pilot study. Journal of Sport and Health Science 2015;4(3):235‐43. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jshs.2014.08.001] - DOI
Chang 2013 {published and unpublished data}
Chen 2015 {published data only}
Cherng 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cherng R, Liao H, Leung HW, Hwang A. The effectiveness of therapeutic horseback riding in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Adapted Physical Activity Quarterly 2004;21(2):103‐21. [DOI: 10.1123/apaq.21.2.103] - DOI
Chiu 2014 {published and unpublished data}
Choi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Choi M, Lee D, Ro H. Effect of task‐oriented training and neurodevelopmental treatment on the sitting posture in children with cerebral palsy. Journal of Physical Therapy Science 2011;23(2):323‐5. [DOI: 10.1589/jpts.23.323] - DOI
Davis 2009 {published data only}
-
- Davis E, Davies B, Wolfe R, Raadsveld R, Heine B, Thomason P, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the impact of therapeutic horse riding on the quality of life, health, and function of children with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2009;51(2):111‐9. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03245.x; PUBMED: 19191844] - DOI - PubMed
Declerck 2016 {published data only}
Dimitrijević 2012 {published data only}
Dodd 2007 {published and unpublished data}
El‐Basatiny 2015 {published data only}
-
- El‐Basatiny HMY, Abdel‐Aziem AA. Effect of backward walking training on postural balance in children with hemiparetic cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled study [with consumer summary]. Clinical Rehabilitation 2015;29(5):457‐67. - PubMed
Fedrizzi 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fedrizzi E, Rosa‐Rizzotto M, Turconi AC, Pagliano E, Fazzi E, Pozza LV, et al. Unimanual and bimanual intensive training in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy and persistence in time of hand function improvement: 6‐month follow‐up results of a multisite clinical trial. Journal of Child Neurology 2013;28(2):161‐75. [DOI: 10.1177/0883073812443004; PUBMED: 22580904] - DOI - PubMed
Fernandes 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fernandes LC, Chitra J, Metgud D, Khatri SM. Effectiveness of artificial horse riding on postural control in spastic diplegics ‐ RCT. Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy 2008;2(4):36‐40.
Franki 2014 {published data only}
-
- Franki I, Broeck C, Cat J, Tijhuis W, Molenaers G, Vanderstraeten G, et al. A randomized, single‐blind cross‐over design evaluating the effectiveness of an individually defined, targeted physical therapy approach in treatment of children with cerebral palsy. Clinical Rehabilitation 2014;28(10):1039‐52. [DOI: 10.1177/0269215514544984; PUBMED: 25147350] - DOI - PubMed
Gillaux 2015 {published data only}
Gordon 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gordon AM, Schneider JA, Chinnan A, Charles JR. Efficacy of a hand‐arm bimanual intensive therapy (HABIT) in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy: a randomized control trial. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2007;49(11):830‐8. [10.1111/j.1469‐8749.2007.00830.x; PUBMED: 17979861] - PubMed
Grecco 2013a {published and unpublished data}
Grecco 2013b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Grecco LA, Tomita SM, Christovão TL, Pasini H, Sampaio LM, Oliveira CS. Effect of treadmill gait training on static and functional balance in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy/Revista Brasileira de Fisioterapia 2013;17(1):17‐23. [PUBMED: 23538455] - PubMed
Green 2013 {published data only}
-
- Green D, Schertz M, Gordon AM, Moore A, Schejter Margalit T, Farquharson Y, et al. A multi‐site study of functional outcomes following a themed approach to hand‐arm bimanual intensive therapy for children with hemiplegia. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2013;55(6):527‐33. [DOI: 10.1111/dmcn.12113; PUBMED: 23458353] - DOI - PubMed
Hamah 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hamah E. Effect of a new physical therapy concept on dynamic balance in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 2015;16(1):77‐83. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmhg.2014.09.001] - DOI
Hammond 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hammond J, Jones V, Hill EL, Green D, Male I. An investigation of the impact of regular use of the Wii Fit to improve motor and psychosocial outcomes in children with movement difficulties: a pilot study. Child Care Health and Development 2014;40(2):165‐75. [DOI: 10.1111/cch.12029; PUBMED: 23363371] - DOI - PubMed
Harbourne 2010 {published data only}
Herrero 2010 {published data only}
-
- Herrero P, Asensio Á, García E, Marco Á, Oliván B, Ibarz A, et al. Study of the therapeutic effects of an advanced hippotherapy simulator in children with cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2010;11:71. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-11-71; PMC2864204] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Herrero 2012 {published data only}
-
- Herrero P, Gómez‐Trullén EM, Asensio A, García E, Casas R, Monserrat E, et al. Study of the therapeutic effects of a hippotherapy simulator in children with cerebral palsy: a stratified single‐blind randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2012;26(12):1105‐13. [DOI: 10.1177/0269215512444633; PUBMED: 22610128] - DOI - PubMed
Hornyak 2008 {published data only}
Hsieh 2016 {published data only}
Hung 2011 {published data only}
Hussein 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hussein ZA, Abd‐Elwahab MS, El‐Shennawy SW. Effect of arm cycling on gait of children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 2014;15(3):273‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmhg.2014.02.008] - DOI
Hutzler 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hutzler Y, Chacham A, Bergman U, Szeinberg A. Effects of a movement and swimming program on vital capacity and water orientation skills of children with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 1998;40(3):176‐81. [PUBMED: 9566654] - PubMed
Hutzler 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hutzler Y, Lamela Rodríguez B, Mendoza LN, Díez I, Barak S. The effects of an exercise training program on hand and wrist strength, and function, and activities of daily living, in adults with severe cerebral palsy. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2013;34(12):4343‐54. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ridd.2013.09.015; PUBMED: 24145046] - DOI - PubMed
Jannink 2008 {published data only}
Jeng 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Jeng SC, Yeh KK, Liu WY, Huang WP, Chuang YF, Wong AM, et al. A physical fitness follow‐up in children with cerebral palsy receiving 12‐week individualized exercise training. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2013;34(11):4017‐24. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ridd.2013.08.032; PUBMED: 24036390] - DOI - PubMed
Jones 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jones JA, Heinemann AW. Exercise & recreation for individuals with a disability: assessment and intervention. tinyurl.com/kt7dhy8 (accessed 10 April 2017).
Kandrali 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kandrali I, Katsimanis G, Christoulas K, Evaggelinou C, Aggelopoulou N. The influence of an adapted exercise program on the development of the gross motor function and performance in adolescents with spastic hemiplegia. Inquiries in Sport & Physical Education 2006;4(1):45‐56.
Kang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kang H, Jung J, Yu J. Effects of hippotherapy on the sitting balance of children with cerebral palsy: a randomized control trial. Journal of Physical Therapy Science 2012;24(9):833‐6. [DOI: 10.1589/jpts.24.833] - DOI
Katz‐Leurer 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Katz‐Leurer M, Rotem H, Keren O, Meyer S. The effects of a 'home‐based' task‐oriented exercise programme on motor and balance performance in children with spastic cerebral palsy and severe traumatic brain injury. Clinical Rehabilitation 2009;23(8):714‐24. [DOI: 10.1177/0269215509335293; PUBMED: 19506005] - DOI - PubMed
Ketelaar 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ketelaar M, Vermeer A, Hart H, Petegem‐van Beek E, Helders PJM. Effects of a functional therapy program on motor abilities of children with cerebral palsy. Physical Therapy 2001;81:1534‐45. [PUBMED: 11688590] - PubMed
Kim 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kim D‐A, Lee J‐A, Hwang P‐W, Lee M‐J, Kim H‐K, Park J‐J, et al. The effect of comprehensive hand repetitive intensive strength training (CHRIST) using motion analysis in children with cerebral palsy. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine 2012;36(1):39‐46. [10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.39; PMC3309323] - PMC - PubMed
Kim 2015 {published data only}
Kumar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kumar A, Kabeer S, Aikat R, Juneja M. Effect of strength training of muscles of lower limb of young children with cerebral palsy on gross motor function. Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy 2010;4(1):4‐7.
Kumar 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kumar C, Kataria S. Effectiveness of task oriented circuit training on functional mobility and balance in cerebral palsy. Indian Journal of Physiotherapy or Occupational Therapy 2013;7(4):23‐28. [DOI: 10.5958/j.0973-5674.7.4.116] - DOI
Lai 2015 {published data only}
Lee 2014a {published data only}
Lee 2014b {published data only}
-
- Lee DR, Kim YH, Kim DA, Lee JA, Hwang PW, Lee MJ, et al. Innovative strength training‐induced neuroplasticity and increased muscle size and strength in children with spastic cerebral palsy: an experimenter‐blind case study‐‐three‐month follow‐up. NeuroRehabilitation 2014;35(1):131‐6. [DOI: 10.3233/NRE-131036; PUBMED: 24419014] - DOI - PubMed
Lowe 2015 {published data only}
Maher 2010 {published and unpublished data}
McGibbon 2009 {published data only}
-
- McGibbon NH, Benda W, Duncan BR, Silkwood‐Sherer D. Immediate and long‐term effects of hippotherapy on symmetry of adductor muscle activity and functional ability in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Archives Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009;90(6):966‐74. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2009.01.011; PUBMED: 19480872] - DOI - PubMed
Mehta 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mehta P, Singh J, Vij J. Efficacy of intensive neurodevelopment therapy versus conventional physiotherapy in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Indian Journal of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy 2010;4(4):96‐101.
Moreau 2013 {published data only}
Nsenga Leunkeu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Nsenga Leunkeu A, Shephard RJ, Ahmaidi S. Six‐minute walk test in children with cerebral palsy gross motor function classification system levels I and II: reproducibility, validity, and training effects. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2012;93(12):2333‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2012.06.005; PUBMED: 22721868] - DOI - PubMed
Nsenga Leunkeu 2013 {published data only}
Olama 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Olama KA, Hegazy FA, Thabt NS. Combined effects of myofeedback and isokinetic training on hand function in spastic hemiplegic children. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 2012;13(2):183‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmhg.2012.03.005] - DOI
Ozer 2007 {published and unpublished data}
Park 2014a {published data only}
Patikas 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Patikas D, Wolf SI, Armbrust P, Mund K, Schuster W, Dreher T, et al. Effects of a postoperative resistive exercise program on the knee extension and flexion torque in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized clinical trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2006;87(9):1161‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2006.05.014; PUBMED: 16935049] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patikas D, Wolf SI, Mund K, Armbrust P, Schuster W, Döderlein L. Effects of a postoperative strength‐training program on the walking ability of children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2006;87(5):619‐26. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2006.01.023; PUBMED: 16635623] - DOI - PubMed
Preston 2015 {published data only}
-
- Preston N, Weightman A, Gallagher J, Levesley M, Mon‐Williams M, Clarke M, et al. A pilot single‐blind multicentre randomized controlled trial to evaluate the potential benefits of computer‐assisted arm rehabilitation gaming technology on the arm function of children with spastic cerebral palsy. Clinical Rehabilitation 2015;30(10):1004‐15. [DOI: 10.1177/0269215515604699; PUBMED: 26370148] - DOI - PubMed
Reid 2006 {published data only}
-
- Reid D, Campbell K. The use of virtual reality with children with cerebral palsy: a pilot randomized trial. Therapeutic Recreation Journal 2006;40(4):255‐68.
Rimmer 2013 {published and unpublished data}
Roberti 2011 {published data only}
-
- Roberti L, Biagini E. Effectiveness of static weight‐bearing exercises in children with cerebral palsy [Efficacia degli esercizi di carico statico nei bambini affetti da paralisi cerebrale infantile]. Scienza Riabilitativa Associazione Italiana Fisioterapisti 2011; Vol. 13, issue 1:1‐14.
Sakzewski 2011a {published data only}
-
- Sakzewski L, Carlon S, Shields N, Ziviani J, Ware RS, Boyd RN. Impact of intensive upper limb rehabilitation on quality of life: a randomized trial in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2012;54(5):415‐23. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04272.x; PUBMED: 22429002] - DOI - PubMed
Sakzewski 2011b {published data only}
-
- Sakzewski L, Ziviani J, Abbott DF, Macdonell RA, Jackson GD, Boyd RN. Equivalent retention of gains at 1 year after training with constraint‐induced or bimanual therapy in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2011;25(7):664‐71. [DOI: 10.1177/1545968311400093; PUBMED: 21427273] - DOI - PubMed
Sakzewski 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sakzewski L, Ziviani J, Abbott DF, Macdonell RA, Jackson GD, Boyd RN. Participation outcomes in a randomized trial of 2 models of upper‐limb rehabilitation for children with congenital hemiplegia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2011;92(4):531‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2010.11.022; PUBMED: 21440700] - DOI - PubMed
Salem 2009 {published data only}
Salem 2012 {published data only}
Schroeder 2014 {published data only}
-
- Schroeder AS, Homburg M, Warken B, Auffermann H, Koerte I, Berweck S, et al. Prospective controlled cohort study to evaluate changes of function, activity and participation in patients with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy after Robot‐enhanced repetitive treadmill therapy. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology 2014;18(4):502‐10. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2014.04.012; PUBMED: 24821475] - DOI - PubMed
Sherief AEAA 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sherief AEAA, Abo Gazya AA, Abd el Gafaar MA. Integrated effect of treadmill training combined with dynamic ankle foot orthosis on balance in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics 2015;16(2):173‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmhg.2014.11.002] - DOI
Silva e Borges 2011 {published data only}
-
- Silva e Borges MB, Werneck MJ, Silva Mde L, Gandolfi L, Pratesi R. Therapeutic effects of a horse riding simulator in children with cerebral palsy [Efeitos terapêuticos de um simulador de equitação em crianças portadoras de paralisia cerebral]. Arquivos de Neuro‐Psiquiatria 2011;69(5):799‐804. [PUBMED: 22042184] - PubMed
Slaman 2014 {published data only}
-
- Slaman J, Roebroeck M, Dallmijer A, Twisk J, Stam H, Berg‐Emons R, Learn 2 Move Research Group. Can a lifestyle intervention programme improve physical behaviour among adolescents and young adults with spastic cerebral palsy? A randomized controlled trial. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2015;57(2):159‐66. [DOI: 10.1111/dmcn.12602; PUBMED: 25303096] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Slaman J, Roebroeck M, Slot W, Twisk J, Wensink A, Stam H, et al. Learn 2 Move Research Group. Can a lifestyle intervention improve physical fitness in adolescents and young adults with spastic cerebral palsy? A randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2014;95(9):1646‐55. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2014.05.011; PUBMED: 25067790] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Slaman J, Berg‐Emons HJ, Meeteren J, Twisk J, Markus F, Stam HJ, et al. A lifestyle intervention improves fatigue, mental health and social support among adolescents and young adults with cerebral palsy: focus on mediating effects. Clinical Rehabilitation 2015;29(7):717‐27. [DOI: 10.1177/0269215514555136; PUBMED: 25352613] - DOI - PubMed
Sorsdahl 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sorsdahl AB, Moe‐Nilssen R, Kaale HK, Rieber J, Strand LI. Change in basic motor abilities, quality of movement and everyday activities following intensive, goal‐directed, activity‐focused physiotherapy in a group setting for children with cerebral palsy. BMC Pediatrics 2010;10:26‐36. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-10-26; PMC2878295; PUBMED: 20423507] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Speyer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Speyer E, Vuillemin A, Herbinet A, Chastagner P, Briançon S. Effect of adapted physical activity on health‐related quality of life among hospitalized children and adolescents (the ACTIV'HOP randomized controlled trial): Design and methods. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2010;31(2):165‐71. [DOI: 10.1016/j.cct.2009.12.003; PUBMED: 20004740] - DOI - PubMed
Stackhouse 2007 {published data only}
-
- Stackhouse SK, Binder‐Macleod SA, Stackhouse CA, McCarthy JJ, Prosser LA, Lee SC. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation versus volitional isometric strength training in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy: a preliminary study. Neurorehabilitation & Neural Repair 2007;21(6):475‐85. [DOI: 10.1177/1545968306298932; PMC3069852] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Su 2013 {published data only}
-
- Su IY, Chung KK, Chow DH. Treadmill training with partial body weight support compared with conventional gait training for low‐functioning children and adolescents with nonspastic cerebral palsy: a two‐period crossover study. Prosthetics and Orthotics International 2013;37(6):445‐53. [DOI: 10.1177/0309364613476532; PUBMED: 23436693] - DOI - PubMed
Swe 2015 {published data only}
Taylor 2009 {published data only}
-
- Taylor NF. Is progressive resistance exercise ineffective in increasing muscle strength in young people with cerebral palsy?. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 2009;55(3):222. [PUBMED: 19681747] - PubMed
Temcharoensuk 2015 {published data only}
-
- Temcharoensuk P, Lekskulchai R, Akamanon C, Ritruechai P, Sutcharitpongsa S. Effect of horseback riding versus a dynamic and static horse riding simulator on sitting ability of children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Physical Therapy Science 2015;27(1):273‐7. [DOI: 10.1589/jpts.27.273; PMC4305581; PUBMED: 25642090] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Van Wely 2014 {published data only}
-
- Wely L, Balemans AC, Becher JG, Dallmeijer AJ. The effectiveness of a physical activity stimulation programme for children with cerebral palsy on social participation, self‐perception and quality of life: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2014;28(10):972‐82. [DOI: 10.1177/0269215513500971; PUBMED: 24047644] - DOI - PubMed
Verschuren 2014 {published data only}
Walsh 2014 {published data only}
Weindling 2007 {published data only}
-
- Weindling AM, Cunningham CC, Glenn SM, Edwards RT, Reeves DJ. Additional therapy for young children with spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial. Health Technology Assessment 2007;11(16):1‐71. [PUBMED: 17462166] - PubMed
Williams 2013 {published data only}
-
- Williams SA, Elliott C, Valentine J, Gubbay A, Shipman P, Reid S. Combining strength training and botulinum neurotoxin intervention in children with cerebral palsy: the impact on muscle morphology and strength. Disability and Rehabilitation 2013;35(7):596‐605. [DOI: 10.3109/09638288.2012.711898; PUBMED: 22928803] - DOI - PubMed
Williams 2014 {published data only}
Willoughby 2010 {published data only}
-
- Willoughby KL, Dodd KJ, Shields N, Foley S. Efficacy of partial body weight‐supported treadmill training compared with overground walking practice for children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2010;91(3):333‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2009.10.029; PUBMED: 20298820] - DOI - PubMed
Yabunaka 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yabunaka Y, Kondo I, Sonoda S, Saitoh E, Tsuruta Y, Konaka M, et al. Evaluating the effect of intensive intervention in children with cerebral palsy using a hypothetical matched control group. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2011;90(2):128‐36. [DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0b013e3181fc7ddf; PUBMED: 20975523] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Carlon 2014 {published data only}
-
- Carlon SL, Taylor NF, Shields N, Dodd KJ. Aerobic training for young people with cerebral palsy in specialist schools: a pilot randomised controlled trial. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2014;56(s2):12.
References to ongoing studies
Gillett 2015 {published data only}
-
- Gillett JG, Lichtwark GA, Boyd RN, Barber LA. FAST CP: protocol of a randomised controlled trial of the efficacy of a 12‐week combined Functional Anaerobic and Strength Training programme on muscle properties and mechanical gait deficiencies in adolescents and young adults with spastic‐type cerebral palsy. BMJ Open 2015;5(6):e008059. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008059; PMC4486965; PUBMED: 26116614] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
ISRCTN90378161 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN90378161. Feasibility and efficacy of resistance training in adolescents with cerebral palsy [An evaluation of the feasibility, acceptability and efficacy of resistance training in adolescents with cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial.]. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN90378161 (first received 26 August 2015). [DOI: 10.1186/ISRCTN90378161] - DOI
NCT02754128 {published data only}
-
- NCT02754128. BeFAST or BeSTRONG: brain change after fun athletic sports‐skill training or brain change after strength training focusing on gait [Linking neuroplasticity with the outcomes of walking‐based interventions: a feasibility trial comparing a motor learning versus a strength‐based program in children with cerebral palsy]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02754128 (first received 6 April 2016).
NCT02766491 {published data only}
-
- NCT02766491. Improving stretching interventions for children with cerebral palsy [Improving stretching interventions for children with cerebral palsy]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02766491 (first received 19 April 2016).
RBR‐5rh6cg {published data only}
-
- RBR‐5rh6cg. Benefits aquatic physical therapy in the trunk control in children with cerebral palsy [Aquatic physical therapy in the trunk control in children with cerebral palsy: randomized clinical trial]. www.ensaiosclinicos.gov.br/rg/RBR‐5rh6cg (first received 2 September 2015).
Additional references
Abraha 2015
American College of Sports Medicine 2009
-
- Kraemer WJ, Adams K, Cafarelli E, Dudley GA, Dooly C, Feigenbaum MS, et al. American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2009;41(3):687‐708. [PUBMED: 11828249]
Andersen 2011
-
- Andersen GL, Romundstad P, Cruz J, Himmelmann K, Sellier E, Cans C, et al. Cerebral palsy among children born moderately preterm or at moderately low birthweight between 1980 and 1998: a European register‐based study. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2011;53(10):913‐9. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.04079.x; PUBMED: 21838820] - DOI - PubMed
Anttila 2008
Armijo‐Olivo 2015
Armijo‐Olivo 2017
-
- Armijo‐Olivo S, Fuentes J, Costa BR, Saltaji H, Ha C, Cummings GG. Blinding in physical therapy trials and its association with treatment effects: a meta‐epidemiological study. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2017;96(1):34‐44. [DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000521; PUBMED: 27149591] - DOI - PubMed
Arnould 2004
-
- Arnould C, Penta M, Renders A, Thonnard JL. ABILHAND‐Kids: a measure of manual ability in children with cerebral palsy. Neurology 2004;63(6):1045‐52. [PUBMED: 15452296] - PubMed
Ashwal 2004
-
- Ashwal S, Russman BS, Blasco PA, Miller G, Sandler A, Shevell M, et al. Practice parameter: diagnostic assessment of the child with cerebral palsy: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2004;62(6):851‐63. [PUBMED: 15037681] - PubMed
Beckung 2008
Bjornson 2008
Bjornson 2014
-
- Bjornson KF, Zhou C, Stevenson RD, Christakis D. Relation of stride activity and participation in mobility‐based life habits among children with cerebral palsy. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2014;95(2):360‐8. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2013.10.022; PMC3946862; PUBMED: 24231402] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Blair 2001
Bottos 2001
Brooks 2014
-
- Brooks JC, Strauss DJ, Shavelle RM, Tran LM, Rosenbloom L, Wu YW. Recent trends in cerebral palsy survival. Part II: individual survival prognosis. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2014;56(11):1065‐71. [PUBMED: 25041081] - PubMed
Butler 2010
Button 2013
-
- Button KS, Ioannidis JP, Mokrysz C, Nosek BA, Flint J, Robinson ES, et al. Power failure: why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience 2013;14(5):365‐76. [PUBMED: 23571845] - PubMed
Caspersen 1985
Chan 2004
-
- Chan AW, Hrobjartsson A, Haahr MT, Gotzsche PC, Altman DG. Empirical evidence for selective reporting of outcomes in randomized trials: comparison of protocols to published articles. JAMA 2004;291(20):2457‐65. [PUBMED: 15161896] - PubMed
Chan 2005
-
- Chan KS, Mangione‐Smith R, Burwinkle TM, Rosen M, Varni JW. The PedsQL: reliability and validity of the short‐form generic core scales and Asthma Module. Medical Care 2005;43(3):256‐65. - PubMed
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis in the Behavioural Sciences. 2nd Edition. Hillsdale (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc, 1988.
Craig 2003
Daltroy 1998
-
- Daltroy LH, Liang MH, Fossel AH, Goldberg MJ. The PO‐SNA pediatric musculoskeletal functional questionnaire: report on reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change. Pediatric Outcomes Instrument Development Group. Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 1998;18:561‐71. - PubMed
Day 2007
Dechartres 2013
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Dodd 2002
-
- Dodd KJ, Taylor NF, Damiano DL. A systematic review of the effectiveness of strength‐training programs for people with cerebral palsy. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2002;83(8):1157‐64. [PUBMED: 12161840] - PubMed
Eek 2008
Egger 1997
Eliasson 2006
-
- Eliasson AC, Krumlinde‐Sundholm L, Rösblad B, Beckung E, Arner M, Ohrvall AM, et al. The Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) for children with cerebral palsy: scale development and evidence of validity and reliability. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2006;48(7):549‐54. [DOI: 10.1017/S0012162206001162; PUBMED: 16780622] - DOI - PubMed
Engel 2002
-
- Engel JM, Kartin D, Jensen MP. Pain treatment in persons with cerebral palsy: frequency and helpfulness. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2002;81(4):291‐6. [PUBMED: 11953547] - PubMed
Faigenbaum 2009
-
- Faigenbaum AD, Kraemer WJ, Blimkie CJ, Jeffreys I, Micheli LJ, Nitka M, et al. Youth resistance training: updated position statement paper from the national strength and conditioning association. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 2009;23(5 Suppl):S60‐79. [PUBMED: 19620931] - PubMed
Fougeyrollas 1998
-
- Fougeyrollas P, Noreau L, Bergeron H, Cloutier R, Dion SA, St‐Michel G. Social consequences of long term impairments and disabilities: a conceptual approach and assessment of handicap. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 1998;21(2):127‐41. [PUBMED: 9924676] - PubMed
Garber 2011
-
- Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, et al. American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2011;43(7):1334‐59. [DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318213fefb; PUBMED: 21694556] - DOI - PubMed
Giné‐Garriga 2014
-
- Giné‐Garriga M, Roqué‐Fíguls M, Coll‐Planas L, Sitjà‐Rabert M, Salvà A. Physical exercise interventions for improving performance‐based measures of physical function in community‐dwelling, frail older adults: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2014;95(4):753‐69.e3. [DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2013.11.007; PUBMED: 24291597] - DOI - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT 2014 [Computer program]
-
- GRADE Working Group, McMaster University. GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 10 April 2017. Hamilton (ON): GRADE Working Group, McMaster University, 2014.
Guyatt 2008
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck‐Ytter Y, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008;336(7650):924‐6. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD; PMC2335261] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Guyatt 2011
Haley 1992
-
- Haley SM, Coster WJ, Ludlow LH, Haltiwanger JT, Andrellos PJ. Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI). Development, Standardization and Administration Manual. Boston (MA): New England Medical Centre, 1992.
Hanna 2009
-
- Hanna SE, Rosenbaum PL, Bartlett DJ, Palisano RJ, Walter SD, Avery L, et al. Stability and decline in gross motor function among children and youth with cerebral palsy aged 2 to 21 years. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2009;51(4):295‐302. [PUBMED: 19391185] - PubMed
Hassani 2014
-
- Hassani S, Krzak JJ, Johnson B, Flanagan A, Gorton G 3rd, Bagley A, et al. One‐Minute Walk and modified Timed Up and Go tests in children with cerebral palsy: performance and minimum clinically important differences. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2014;56(5):482‐9. [PUBMED: 24843890] - PubMed
Herbison 2011
-
- Herbison P, Hay‐Smith J, Gillespie WJ. Different methods of allocation to groups in randomized trials are associated with different levels of bias. A meta‐epidemiological study. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(10):1070‐5. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.12.018; PUBMED: 21474279] - DOI - PubMed
Herskind 2015
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Chapter 4: Guide to the contents of a Cochrane protocol and review. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011c
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hirsh 2011
Hoffmann 2014
Holsbeeke 2009
Jahnsen 2004
Jeglinsky 2010
Kerr 2006
Kerr 2011
King 2004
-
- King G, Law M, King S, Hurley P, Hanna S, Kertoy M, et al. Children's Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment (CAPE) and Preferences for Activities of Children (PAC). San Antonio (TX): Harcourt Assessment Inc, 2004.
Kirby 2011
-
- Kirby RS, Wingate MS, Naarden Braun K, Doernberg NS, Arneson CL, Benedict RE, et al. Prevalence and functioning of children with cerebral palsy in four areas of the United States in 2006: a report from the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2011;32(2):462‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ridd.2010.12.042; PUBMED: 21273041] - DOI - PubMed
Klingels 2012
-
- Klingels K, Demeyere I, Jaspers E, Cock P, Molenaers G, Boyd R, et al. Upper limb impairments and their impact on activity measures in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology 2012;16(5):475‐84. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2011.12.008; PUBMED: 22244966] - DOI - PubMed
Krumlinde‐Sundholm 2003
-
- Krumlinde‐Sundholm L, Eliasson A. Development of the Assisting Hand Assessment: a Rasch‐built measure intended for children with unilateral upper limb impairments. Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy 2003;10(1):16‐26. [DOI: 10.1080/11038120310004529] - DOI
Krupp 1989
-
- Krupp LB, LaRocca NG, Muir‐Nash J, Steinberg AD. The fatigue severity scale. Application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Archives of Neurology 1989;46(10):1121‐3. [PUBMED: 2803071] - PubMed
Landgraf 1998
-
- Landgraf JM, Maunsell E, Speechley KN, Bullinger M, Campbell S, Abetz L, et al. Canadian‐French, German and UK versions of the Child Health Questionnaire: methodology and preliminary item scaling results. Quality of Life Research 1998;7(5):433‐45. [PUBMED: 9691723] - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Liu 2009
Maenner 2013
-
- Maenner MJ, Smith LE, Hong J, Makuch R, Greenberg JS, Mailick MR. Evaluation of an activities of daily living scale for adolescents and adults with developmental disabilities. Disability and Health Journal 2013;6(1):8‐17. [DOI: 10.1016/j.dhjo.2012.08.005; PMC3531884; PUBMED: 23260606] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Maher 2016
McCormack 1988
-
- McCormack HM, Horne DJ, Sheather S. Clinical applications of visual analogue scales: a critical review. Psychological Medicine 1988;18(4):1007‐19. [PUBMED: 3078045] - PubMed
Mockford 2008
-
- Mockford M, Caulton JM. Systematic review of progressive strength training in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy who are ambulatory. Pediatric Physical Therapy 2008;20(4):318‐33. [PUBMED: 19011522] - PubMed
Moher 2009
Nieuwenhuijsen 2011
-
- Nieuwenhuijsen C, Slot WM, Dallmeijer AJ, Janssens PJ, Stam HJ, Roebroeck ME, et al. Physical fitness, everyday physical activity, and fatigue in ambulatory adults with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports 2011;21(4):535‐42. [PUBMED: 20459469] - PubMed
Nooijen 2014
-
- Nooijen C, Slaman J, Slot W, Stam H, Roebroeck M, Berg‐Emons R. Health‐related physical fitness of ambulatory adolescents and young adults with spastic cerebral palsy. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2014;46(7):642‐7. [PUBMED: 24714702] - PubMed
Noorduyn 2011
-
- Noorduyn SG, Gorter JW, Verschuren O, Timmons BW. Exercise intervention programs for children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: a descriptive review of the current research. Critical Reviews on Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine 2011;23(1‐4):31‐47. [DOI: 10.1615/CritRevPhysRehabilMed.v23.i1-4.30] - DOI
Novak 2013
-
- Novak I, McIntyre S, Morgan C, Campbell L, Dark L, Morton N, et al. A systematic review of interventions for children with cerebral palsy: state of the evidence. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2013;55(10):885‐910. [PUBMED: 23962350] - PubMed
Nusselder 2005
-
- Nusselder WJ, Looman CW, Mackenbach JP. Nondisease factors affected trajectories of disability in a prospective study. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(5):484‐94. [PUBMED: 15845335] - PubMed
Nüesch 2009
O'Callaghan 2011
-
- O'Callaghan ME, MacLennan AH, Gibson CS, McMichael GL, Haan EA, Broadbent JL, et al. Australian Collaborative Cerebral Palsy Research Group. Epidemiologic associations with cerebral palsy. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2011;118(3):576‐82. [DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31822ad2dc; PUBMED: 21860286] - DOI - PubMed
Oeffinger 2008
-
- Oeffinger D, Bagley A, Rogers S, Gorton G, Kryscio R, Abel M, et al. Outcome tools used for ambulatory children with cerebral palsy: responsiveness and minimum clinically important differences. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2008;50(12):918‐25. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03150.x; PMC2990955; PUBMED: 19046185] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Opheim 2009
Palisano 1997
-
- Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Walter S, Russell D, Wood E, Galuppi B. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 1997;39(4):214‐23. [PUBMED: 9183258] - PubMed
Palisano 2008
Park 2013
Park 2014b
Pereira 2012
Peterson 2015
Platt 2007
-
- Platt MJ, Cans C, Johnson A, Surman G, Topp M, Torrioli MG, et al. Trends in cerebral palsy among infants of very low birthweight (<1500 g) or born prematurely (<32 weeks) in 16 European centres: a database study. Lancet 2007;369(9555):43‐50. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60030-0; PUBMED: 17208641] - DOI - PubMed
Radloff 1977
-
- Radloff L. The CES‐D scale: a new self‐report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement 1977;1:385‐401.
Rameckers 2014
Randall 1999
-
- Randall M, Johnson L, Reddihough D. The Melbourne Assessment of Unilateral Upper Limb Function Test Administration Manual. Melbourne: Royal Children's Hospital, 1999.
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Riad 2012
-
- Riad J, Modlesky CM, Gutierrez‐Farewik EM, Broström E. Are muscle volume differences related to concentric muscle work during walking in spastic hemiplegic cerebral palsy?. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 2012;470(5):1278‐85. [DOI: 10.1007/s11999-011-2093-6; PMC3314764; PUBMED: 21918799] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Rogers 2008
Rosenbaum 2007
Rosenbaum 2012
-
- Rosenbaum P, Gorter JW. The 'F‐words' in childhood disability: I swear this is how we should think!. Child: care, health and development 2012;38(4):457‐63. [PUBMED: 22040377] - PubMed
Ross 2007
-
- Ross SA, Engsberg JR. Relationships between spasticity, strength, gait, and the GMFM‐66 in persons with spastic diplegia cerebral palsy. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2007;88(9):1114‐20. [PUBMED: 17826455] - PubMed
Russell 1989
-
- Russell DJ, Rosenbaum PL, Cadman DT, Gowland C, Hardy S, Jarvis S. The gross motor function measure: a means to evaluate the effects of physical therapy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 1989;31(3):341‐52. [PUBMED: 2753238] - PubMed
Sandström 2004
Savović 2012
-
- Savović J, Jones H, Altman D, Harris R, Juni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomised controlled trials: combined analysis of meta‐epidemiological studies. Health Technology Assessment 2012;16(35):1‐82. [DOI: 10.3310/hta16350; PUBMED: 22989478] - DOI - PubMed
Schipper 1996
-
- Schipper H, Clinch JJ, Olweny CL. Quality of life studies: definitions and conceptual issues. In: Spilker B editor(s). Quality of Life and Pharmoeconomics in Clinical Trials. Vol. 2, Philadelphia: Lippincott‐Raven, 1996:11‐23.
Scianni 2009
-
- Scianni A, Butler JM, Ada L, Teixeira‐Salmela LF. Muscle strengthening is not effective in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 2009;55(2):81‐7. [PUBMED: 19463078] - PubMed
SCOPE 2002
-
- SCOPE. Prevalence and characteristics of children with cerebral palsy in Europe. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2002;44(9):633‐40. [PUBMED: 12227618] - PubMed
Sellier 2010
-
- Sellier E, Surman G, Himmelmann K, Andersen G, Colver A, Krageloh‐Mann I, et al. Trends in prevalence of cerebral palsy in children born with a birthweight of 2,500 g or over in Europe from 1980 to 1998. European Journal of Epidemiology 2010;25(9):635‐42. [DOI: 10.1007/s10654-010-9474-0; PUBMED: 20532622] - DOI - PubMed
Shortland 2009
Solans 2008
-
- Solans M, Pane S, Estrada MD, Serra‐Sutton V, Berra S, Herdman M, et al. Health‐related quality of life measurement in children and adolescents: a systematic review of generic and disease‐specific instruments. Value in Health 2008;11(4):742‐64. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00293.x; PUBMED: 18179668] - DOI - PubMed
Soyupek 2010
Strauss 1998a
-
- Strauss DJ, Shavelle RM, Anderson TW. Life expectancy of children with cerebral palsy. Pediatric Neurology 1998;18(2):143‐9. [PUBMED: 9535300] - PubMed
Strauss 1998b
Taylor 2005
-
- Taylor NF, Dodd KJ, Damiano DL. Progressive resistance exercise in physical therapy: a summary of systematic reviews. Physical Therapy 2005;85(11):1208‐23. [PUBMED: 16253049] - PubMed
Tollånes 2014
Trønnes 2014
USDHHS 2008
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Physical activity guidelines for Americans. www.health.gov/paguidelines (accessed 31 January 2014).
Van der Linden 2003
-
- Linden ML, Hazlewood ME, Aitchison AM, Hillman SJ, Robb JE. Electrical stimulation of gluteus maximus in children with cerebral palsy: effects on gait characteristics and muscle strength. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2003;45(6):385‐90. [PUBMED: 12785439] - PubMed
Van Der Slot 2012
-
- Slot WM, Nieuwenhuijsen C, Berg‐Emons RJ, Bergen MP, Hilberink SR, Stam HJ, et al. Chronic pain, fatigue, and depressive symptoms in adults with spastic bilateral cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2012;54(9):836‐42. [PUBMED: 22809436] - PubMed
Vargus‐Adams 2011
Verhoef 2014
-
- Verhoef JA, Bramsen I, Miedema HS, Stam HJ, Roebroeck ME. Development of work participation in young adults with cerebral palsy: a longitudinal study. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2014;46(7):648‐55. [PUBMED: 24858956] - PubMed
Verschuren 2006
-
- Verschuren O, Takken T, Ketelaar M, Gorter JW, Helders PJ. Reliability and validity of data for 2 newly developed shuttle run tests in children with cerebral palsy. Physical Therapy 2006;86(8):1107‐17. [PUBMED: 16879044] - PubMed
Verschuren 2008
-
- Verschuren O, Ketelaar M, Takken T, Helders PJ, Gorter JW. Exercise programs for children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review of the literature. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2008;87(5):404‐17. [PUBMED: 17993987] - PubMed
Verschuren 2009
Verschuren 2010
-
- Verschuren O, Takken T. Aerobic capacity in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2010;31(6):1352‐7. [PUBMED: 20674266] - PubMed
Verschuren 2012
Verschuren 2016
Vogels 2000
-
- Vogels T, Verrips GHW, Koopman HM, Theunissen NCM, Fekkes M, Kamphuis RP. TACQOL Manual. Parent Form and Child Form. Leiden: Leiden Center for Child Health and Pediatrics, 2000.
Voorman 2007
-
- Voorman JM, Dallmeijer AJ, Knol DL, Lankhorst GJ, Becher JG. Prospective longitudinal study of gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2007;88(7):871‐6. [PUBMED: 17601467] - PubMed
Ware 1993
-
- Ware JE, Snow KK, Kilinski M, Gandeck B. SF‐36 Health Survey Manual and Interpretation Guide. Boston (MA): The Health Institute, New England Medical Center, 1993.
WHO 2001
-
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2001.
WHO 2013
-
- WHO. Definition of key terms. www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/arv2013/intro/keyterms/en/ (accessed 30 May 2017). [http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/arv2013/intro/keyterms/en/]
Wood 2008
Wu 2004
-
- Wu YW, Day SM, Strauss DJ, Shavelle RM. Prognosis for ambulation in cerebral palsy: a population‐based study. Pediatrics 2004;114(5):1264‐71. [PUBMED: 15520106] - PubMed
Young 2000
-
- Young NL, Williams JI, Yoshida KK, Wright JG. Measurement properties of the activities scale for kids. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2000;53(2):125‐37. [PUBMED: 10729684] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

