Analysis using size exclusion chromatography of poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) using methanol as an eluent
- PMID: 28602503
- PMCID: PMC5486375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2017.05.050
Analysis using size exclusion chromatography of poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) using methanol as an eluent
Abstract
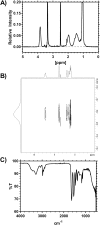
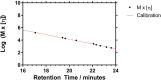
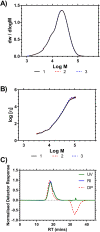
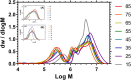
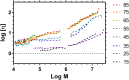
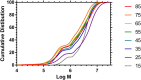
Size Exclusion Chromatography is traditionally carried out in either aqueous or non-polar solvents. A system to present molar mass distributions of polymers using methanol as a mobile phase is presented. This is shown to be a suitable system for determining the molar mass distributions poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)s (PNIPAM); a polymer class that is often difficult to analyze by size exclusion chromatography. DOSY NMR was used to provide intrinsic viscosity data that was used in conjunction with a viscometric detector to provide absolute calibration. Then the utility of the system was shown by providing the absolute molar mass distributions of dispersed highly branched PNIPAM with biologically functional end groups.
Keywords: DOSY NMR; Intrinsic viscosity; Methanol; PNIPAM; SEC; Size exclusion chromatography.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Vancoillie G., Vergaelen M., Hoogenboom R. Ultra-high performance size-exclusion chromatography in polar solvents. J. Chromatogr. A. 2016;1478:43–49. - PubMed
-
- Yohannes G., Shan J., Jussila M., Nuopponen M., Tenhu H., Riekkola M.-L. Characterisation of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation, dynamic light scattering, and size exclusion chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2005;28(5):435–442. - PubMed
-
- Ganachaud F., Monteiro M.J., Gilbert R.G., Dourges M.-A., Thang S.H., Rizzardo E. Molecular weight characterization of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) prepared by living free-radical polymerization. Macromolecules. 2000;33(18):6738–6745.
-
- Schulze M., Kilbinger A.F.M. Toward large tubular helices based on the polymerization of tri(benzamide)s. J. Polym. Sci. A: Polym. Chem. 2016;54(12):1731–1741.
-
- Masci G., Giacomelli L., Crescenzi V. Atom transfer radical polymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004;25(4):559–564.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

