The novel lipid mediator PD1n-3 DPA: An overview of the structural elucidation, synthesis, biosynthesis and bioactions
- PMID: 28602942
- PMCID: PMC5720935
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2017.06.003
The novel lipid mediator PD1n-3 DPA: An overview of the structural elucidation, synthesis, biosynthesis and bioactions
Abstract
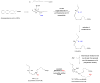
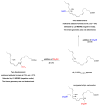
Resolvins, protectins and maresins are individual families of specialized pro-resolving mediators biosynthesized from the dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. These enzymatically oxygenated polyunsaturated lipid mediators were first elucidated during the resolution phase of acute inflammation in animal models of self-limited inflammation. Specialized pro-resolving mediators display potent bioactions when administrated in vivo. Biosynthetic pathway studies have revealed that individual lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenase-2 converts eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid into distinct families of the resolvins, protectins and maresins. Recently n-3 docosapentaenoic acid was found to be a substrate for the biosynthesis of several novel families of specialized pro-resolving mediators. One example is PD1n-3 DPA. During the 6th European Workshop on Lipid Mediators, Frankfurt, Germany, the structural elucidation, total organic synthesis, studies on the biosynthetic pathway, as well as the potent anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving properties of PD1n-3 DPA were presented. Herein, we provide an overview of these topics for the new member PD1n-3 DPA of the super-family of pro-resolving mediators.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Human leukocytes; Lipoxygenase; Pro-resolution; Protectin D1(n-3 DPA); Specialized pro-resolving mediators; n-3 Docosapentaenoic acid.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
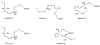

Similar articles
-
Synthesis, Structural Confirmation, and Biosynthesis of 22-OH-PD1n-3 DPA.Molecules. 2019 Sep 5;24(18):3228. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183228. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31491851 Free PMC article.
-
Protectins: Their biosynthesis, metabolism and structure-functions.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Dec;206:115330. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115330. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36341938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the chemistry and biology of anti-inflammatory and specialized pro-resolving mediators biosynthesized from n-3 docosapentaenoic acid.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Jun 1;27(11):2259-2266. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.03.079. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 28408222 Review.
-
A new synthetic protectin D1 analog 3-oxa-PD1n-3 DPA reduces neuropathic pain and chronic itch in mice.Org Biomol Chem. 2021 Mar 28;19(12):2744-2752. doi: 10.1039/d0ob02136a. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Org Biomol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33687402 Free PMC article.
-
Protectins and maresins: New pro-resolving families of mediators in acute inflammation and resolution bioactive metabolome.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1851(4):397-413. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25139562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids as a Nutritional Support of the Reproductive and Immune System of Cattle-A Review.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 20;13(22):3589. doi: 10.3390/ani13223589. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possibility of averting cytokine storm in SARS-COV 2 patients using specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;209:115437. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115437. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36731803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Angiogenesis via Resolution of Inflammation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2023 Mar 1;13(3):a041172. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041172. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2023. PMID: 35817542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Protectin Family of Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators: Potent Immunoresolvents Enabling Innovative Approaches to Target Obesity and Diabetes.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 17;9:1582. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01582. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30705632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First total syntheses of the pro-resolving lipid mediators 7(S),13(R),20(S)-Resolvin T1 and 7(S),13(R)-Resolvin T4.Tetrahedron Lett. 2020 Feb 6;61(6):151473. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.151473. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020. PMID: 32313313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calder PC, Willemsen LEM. Immunopharmacology of fatty acids. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;785:1. - PubMed
-
- Fetterman JW, Jr, Zdanowicz MM. Therapeutic potential of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in disease. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2009;66:1169–1179. - PubMed
-
- Simopoulos AP. Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases. J Am Coll Nutr. 2002;21:495–505. - PubMed
-
- Calder PC. Immunomodulation by omega-3 fatty acids. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes Essent Fatty Acids. 2007;77:327–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

