The energy landscape underpinning module dynamics in the human brain connectome
- PMID: 28602945
- PMCID: PMC5600845
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.05.067
The energy landscape underpinning module dynamics in the human brain connectome
Abstract
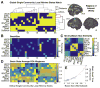
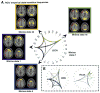
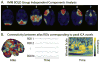
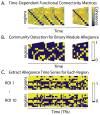
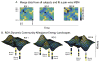
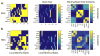
Human brain dynamics can be viewed through the lens of statistical mechanics, where neurophysiological activity evolves around and between local attractors representing mental states. Many physically-inspired models of these dynamics define brain states based on instantaneous measurements of regional activity. Yet, recent work in network neuroscience has provided evidence that the brain might also be well-characterized by time-varying states composed of locally coherent activity or functional modules. We study this network-based notion of brain state to understand how functional modules dynamically interact with one another to perform cognitive functions. We estimate the functional relationships between regions of interest (ROIs) by fitting a pair-wise maximum entropy model to each ROI's pattern of allegiance to functional modules. This process uses an information theoretic notion of energy (as opposed to a metabolic one) to produce an energy landscape in which local minima represent attractor states characterized by specific patterns of modular structure. The clustering of local minima highlights three classes of ROIs with similar patterns of allegiance to community states. Visual, attention, sensorimotor, and subcortical ROIs are well-characterized by a single functional community. The remaining ROIs affiliate with a putative executive control community or a putative default mode and salience community. We simulate the brain's dynamic transitions between these community states using a random walk process. We observe that simulated transition probabilities between basins are statistically consistent with empirically observed transitions in resting state fMRI data. These results offer a view of the brain as a dynamical system that transitions between basins of attraction characterized by coherent activity in groups of brain regions, and that the strength of these attractors depends on the ongoing cognitive computations.
Keywords: Community structure; Energy landscape; Functional brain network; Graph theory; Maximum entropy model; Modularity.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

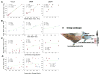
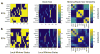
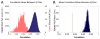
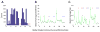
Similar articles
-
Bayesian estimation of maximum entropy model for individualized energy landscape analysis of brain state dynamics.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 Aug 1;42(11):3411-3428. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25442. Epub 2021 May 2. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 33934421 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory, somatomotor and internal mentation networks emerge dynamically in the resting brain with internal mentation predominating in older age.Neuroimage. 2021 Aug 15;237:118188. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118188. Epub 2021 May 18. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 34020018
-
Beyond modularity: Fine-scale mechanisms and rules for brain network reconfiguration.Neuroimage. 2018 Feb 1;166:385-399. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.11.015. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 29138087
-
Spatio-temporal modeling of connectome-scale brain network interactions via time-evolving graphs.Neuroimage. 2018 Oct 15;180(Pt B):350-369. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.10.067. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 29102809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bottom up modeling of the connectome: linking structure and function in the resting brain and their changes in aging.Neuroimage. 2013 Oct 15;80:318-29. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.055. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23629050 Review.
Cited by
-
Fractal basins as a mechanism for the nimble brain.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 27;13(1):20860. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45664-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38012212 Free PMC article.
-
Functional MRI Changes in Patients after Thyroidectomy under General Anesthesia.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jun 21;2022:1935125. doi: 10.1155/2022/1935125. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35774279 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Connectivity Biomarker Extraction for Schizophrenia Based on Energy Landscape Machine Learning Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 4;24(23):7742. doi: 10.3390/s24237742. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39686279 Free PMC article.
-
Energy landscape of resting magnetoencephalography reveals fronto-parietal network impairments in epilepsy.Netw Neurosci. 2020 Apr 1;4(2):374-396. doi: 10.1162/netn_a_00125. eCollection 2020. Netw Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32537532 Free PMC article.
-
The alterations of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on the energy landscape of resting-state networks differ across the human cortex.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Oct 15;45(15):e70029. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70029. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 39465912 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

