Effectiveness of the liver micronucleus assay using juvenile mice
- PMID: 28603212
- PMCID: PMC5559381
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.17-0116
Effectiveness of the liver micronucleus assay using juvenile mice
Abstract
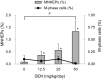
This study investigated the effectiveness of the liver micronucleus (MN) assay using juvenile mice. Therefore, we analyzed various hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP)- mediated activities of ethoxyresorufin O-deethylation, pentoxyresorufin O-dealkylation, tolbutamide hydroxylation, bufuralol 1'-hydroxylation, aniline hydroxylation and midazolam 4-hydroxylation by CYP1A, CYP2B, CYP2C, CYP2D, CYP2E and CYP3A, respectively, in non-treated male ICR mice aged between 3 and 8 weeks. The enzyme efficiency levels in 3- and 4-week-old mice were approximately similar to or higher than those in 8-week-old mice, except for CYP1A and CYP2E in 3- and 4-week-old mice, respectively. Since these results suggest that juvenile mice have sufficient activities for most CYP enzymes, we also conducted a liver MN assay using diethylnitrosamine (DEN), a rodent hepatocarcinogen, on male ICR mice aged between 3 and 6 weeks. A peripheral blood (PB) MN assay was performed simultaneously in 4-week-old mice. Assays incorporating DEN produced positive results in 3- and 4-week-old mice and showed a dose-dependent increase in the micronucleated hepatocyte frequencies at 4 weeks. Both the liver MN assay in 5- and 6-week-old mice and the PB MN assay had negative results when using DEN. These results suggest that 3- and 4-week-old mice have micronuclei-inducing potential in the liver to detect genotoxic compounds using the liver MN assay.
Keywords: CYP; genotoxicity assay; juvenile mouse; liver micronucleus assay.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Micronucleus induction in rat liver and bone marrow by acute vs. repeat doses of the genotoxic hepatocarcinogen monocrotaline.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Mar;780-781:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2014.12.008. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015. PMID: 25892625
-
Characterization of cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism in cats.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Oct;30(5):422-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2007.00902.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17803734
-
Assessment of genotoxicity induced by 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene or diethylnitrosamine in the Pig-a, micronucleus and Comet assays integrated into 28-day repeat dose studies.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2011 Dec;52(9):711-20. doi: 10.1002/em.20678. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2011. PMID: 21976072
-
Repeated dose liver micronucleus assay using adult mice with multiple genotoxicity assays concurrently performed as a combination test.J Toxicol Sci. 2014 Jun;39(3):437-45. doi: 10.2131/jts.39.437. J Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24849678
-
Cytochrome P450-mediated hepatic metabolism of new fluorescent substrates in cats and dogs.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Dec;33(6):519-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2010.01199.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 21062303 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic toxicity assessment using liver cell models: past, present, and future.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2020;23(1):27-50. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2019.1692744. Epub 2019 Nov 20. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2020. PMID: 31746269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hen's egg test for micronucleus induction (HET-MN): validation data set.Mutagenesis. 2022 May 4;37(2):61-75. doi: 10.1093/mutage/geab016. Mutagenesis. 2022. PMID: 34080017 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

