Sweet sorghum as biofuel feedstock: recent advances and available resources
- PMID: 28603553
- PMCID: PMC5465577
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-017-0834-9
Sweet sorghum as biofuel feedstock: recent advances and available resources
Abstract
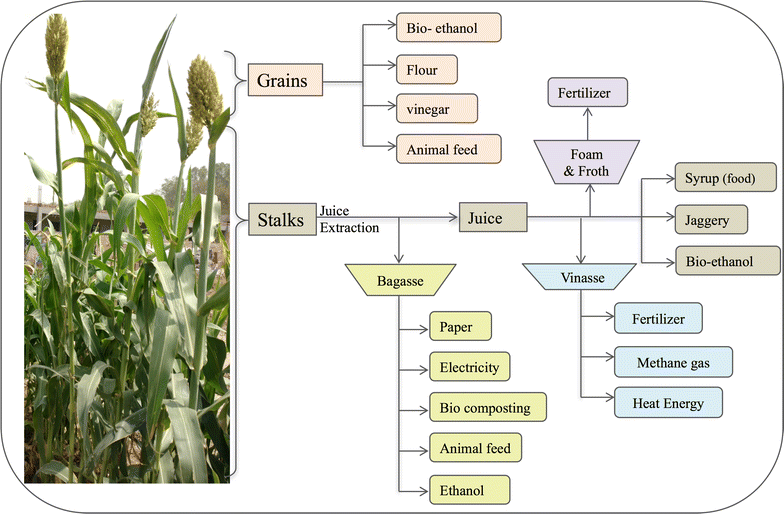
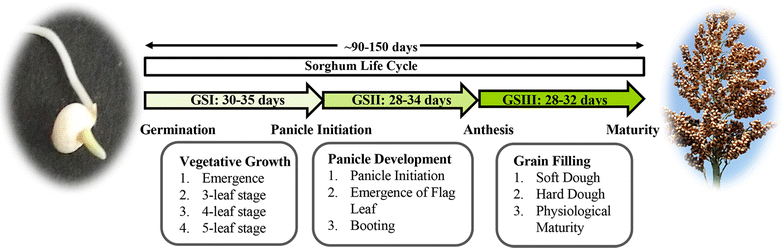
Sweet sorghum is a promising target for biofuel production. It is a C4 crop with low input requirements and accumulates high levels of sugars in its stalks. However, large-scale planting on marginal lands would require improved varieties with optimized biofuel-related traits and tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Considering this, many studies have been carried out to generate genetic and genomic resources for sweet sorghum. In this review, we discuss various attributes of sweet sorghum that make it an ideal candidate for biofuel feedstock, and provide an overview of genetic diversity, tools, and resources available for engineering and/or marker-assisting breeding of sweet sorghum. Finally, the progress made so far, in identification of genes/quantitative trait loci (QTLs) important for agronomic traits and ongoing molecular breeding efforts to generate improved varieties, has been discussed.
Keywords: Biofuel; Feedstock; Genomics; Grass genetics; Sorghum; Sorghum breeding.
Figures
References
-
- Melillo JM, Richmond T, Yohe GW, editors. Climate change impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment. US Global Research Program; 2014.
-
- British Petroleum. BP statistical review of world energy 2016. In: Statistical review of world energy, vol. 2016. 65 ed. London: BP P.L.C.; 2016.
-
- Shafiee S, Topal E. When will fossil fuel reserves be diminished? Energy Policy. 2009;37(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2008.08.016. - DOI
-
- Hubbert MK. Nuclear energy and fossil fuels. In: Presented before the spring meeting of the Southern District: March 7–9; American Petroleum Institute, Plaza Hotel, San Antonio, Texas, March 7–9; 1956.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous