Revisiting radial forearm free flap for successful venous drainage
- PMID: 28603708
- PMCID: PMC5443734
- DOI: 10.1186/s40902-017-0110-8
Revisiting radial forearm free flap for successful venous drainage
Abstract
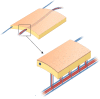
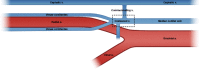
Tissue defect reconstruction using radial forearm free flap (RFFF) is a common surgical technique whose success or failure is mainly dependent on venous drainage. RFFF has two major venous outflow systems, superficial and deep vein. Drainage methods include combining both systems or using one alone. This review aims to recapitulate the vascular anatomy and network of RFFF as well as shed light on deep vein as a reliable venous drainage system. We also discuss basic evidence for and advantages of single microanastomosis with coalesced vein to overcome technical difficulties associated with the deep vein system.
Keywords: Coalesced vein; Radial forearm free flap; Venae comitantes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
"DO ONE, GET TWO": dual venous drainage of the radial forearm free flap by a single venous anastomosis.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023 Jun;27(2):283-288. doi: 10.1007/s10006-022-01060-3. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023. PMID: 35459977 Review.
-
Improved venous drainage of the radial artery forearm free flap: use of the profundus cubitalis vein.J Reconstr Microsurg. 1993 Jul;9(4):281-4; discussion 284-5. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1006668. J Reconstr Microsurg. 1993. PMID: 8410787
-
Venous drainage of the radial forearm flap: comparison of the deep and superficial systems.Ann Plast Surg. 2011 Apr;66(4):347-50. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181f46631. Ann Plast Surg. 2011. PMID: 21346537
-
The venae comitantes clipping test for the evaluation of the venous drainage of the radial forearm free flap.Microsurgery. 2016 Nov;36(8):647-650. doi: 10.1002/micr.22514. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Microsurgery. 2016. PMID: 26503001
-
Reliability of venous couplers for microanastomosis of the venae comitantes in free radial forearm flaps for head and neck reconstruction.J Reconstr Microsurg. 2013 Sep;29(7):433-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1343835. Epub 2013 Apr 15. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2013. PMID: 23588548 Review.
Cited by
-
The supraclavicular artery island flap: a salvage option for head and neck reconstruction.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018 Oct 4;40(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40902-018-0165-1. eCollection 2018 Dec. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018. PMID: 30363382 Free PMC article.
-
An important superficial vein of the radial aspect of the forearm: An anatomical study.Indian J Plast Surg. 2018 May-Aug;51(2):231-234. doi: 10.4103/ijps.IJPS_19_18. Indian J Plast Surg. 2018. PMID: 30505096 Free PMC article.
-
Revascularized Fibula Free Flap Reconstruction and Curvilinear Transport Distraction Osteogenesis in Closure of Large Postmaxillectomy Defects: A New Gold Standard?Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2020 Jul-Dec;10(2):304-311. doi: 10.4103/ams.ams_267_19. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2020. PMID: 33708572 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Single Anastomoses for Superficial and Deep-System Venous Drainage of Radial Forearm Free Flaps.OTO Open. 2021 Apr 26;5(2):2473974X211006927. doi: 10.1177/2473974X211006927. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. OTO Open. 2021. PMID: 33997587 Free PMC article.
-
Changes on noncontrast magnetic resonance imaging following lymphatic surgery for upper extremity secondary lymphedema.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2025 Jan;13(1):101962. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2024.101962. Epub 2024 Aug 6. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2025. PMID: 39117036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang G, Chen B, Gao Y. Forearm free skin flap transplantation. Natl Med J China. 1981;61:139–141.
-
- Song R, Gao Y, Song Y, Yu Y, Song Y. The forearm flap. Clin Plast Surg. 1982;9:21–26. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
