Anti-TNF-α effects on anemia in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 28604144
- PMCID: PMC5815256
- DOI: 10.1177/0394632017714695
Anti-TNF-α effects on anemia in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
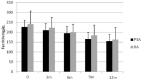
A key role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is played by inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), which are also involved in inducing inflammatory anemia. We have followed 67 RA patients and 64 PsA patients for 1 year to evaluate the effects of TNF-α inhibitors on disease activity and on inflammatory anemia. Patients were divided into three different treatment groups, according to a randomized assignment to receive therapy with etanercept, adalimumab, or infliximab. Treatment with anti-TNF-α resulted in a significant reduction in disease activity score-28 (DAS28) values both in RA and PsA patients, already from the third month of treatment ( P = 0.01). In both populations, there was an increase in hemoglobin (HB) levels already after 3 months of treatment ( P = 0.001), and HB levels were inversely proportional to the disease activity, regardless of the type of medication used. The increased HB values and the reduction of DAS28 values during the observation period suggest the existence of a negative correlation between them both in RA and PsA, regardless of the type of anti-TNF-α used. Our data suggest a pleiotropic action of anti-TNF-α, such as the well-known action on the activity of the disease, and the improvement in inflammatory anemia.
Keywords: anemia; anti-TNF-α; arthritis; hemoglobin; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Raj DSC. (2009) Role of interleukin-6 in the anemia of chronic disease. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 38: 382–388. - PubMed
-
- Papadaki HA, Kritikos HD, Valatas V, et al. (2002) Anemia of chronic disease in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with increased apoptosis of bone marrow erythroid cells: Improvement following anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody therapy. Blood 100: 474–482. - PubMed
-
- Weiss G, Goodnough LT. (2005) Anemia of chronic disease. New England Journal of Medicine 352: 1011–1023. - PubMed
-
- Han C, Rahman MU, Doyle MK, et al. (2007) Association of anemia and physical disability among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of rheumatology 34: 2177–2182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

