Elotuzumab as a novel anti-myeloma immunotherapy
- PMID: 28604269
- PMCID: PMC5557243
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1327487
Elotuzumab as a novel anti-myeloma immunotherapy
Abstract
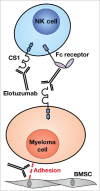
Treatment of multiple myeloma has undergone significant change in the last decade with the introduction of new immunomodulatory agents, proteasome inhibitors, and immunotherapeutic approaches. Elotuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting CS1, which is a member of the SLAM (Signaling Lymphocyte Activation Molecule) family of proteins, expressed on the surface of myeloma plasma cells. Here we review the preclinical investigations that led to the development of elotuzumab and the clinical studies that resulted in its approval for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Although preclinical data looked very promising, elotuzumab monotherapy did not result in objective clinical responses in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. However, combination treatment with immunomodulators and proteasome inhibitors resulted in substantial clinical activity in relapsed/refractory MM. Currently, there are several clinical trials ongoing investigating the role of elotuzumab in newly diagnosed myeloma patients and in patients receiving maintenance therapy.
Keywords: CS1; SLAM family of receptors; antibodies; elotuzumab; immunotherapy; monoclonal; multiple myeloma.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 2017; 67(1):7-30; https://doi.org/ 10.3322/caac.21387 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016; 66(1):7-30; https://doi.org/ 10.3322/caac.21332 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stefanova I, Horejsí V, Ansotegui IJ, Knapp W, Stockinger H. GPI-anchored cell-surface molecules complexed to protein tyrosine kinases. Science 1991; 254(5034):1016-9; https://doi.org/ 10.1126/science.1719635 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu N, Veillette A. SLAM family receptors in normal immunity and immune pathologies. Curr Opin Immunol 2016; 38:45-51; PMID:26682762; https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.coi.2015.11.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lonial S, Vij R, Harousseau JL, Facon T, Moreau P, Mazumder A, Kaufman JL, Leleu X, Tsao LC, Westland C, et al.. Elotuzumab in combination with lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30(16):1953-9; https://doi.org/ 10.1200/JCO.2011.37.2649 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
