Dynamic subunit turnover in ESCRT-III assemblies is regulated by Vps4 to mediate membrane remodelling during cytokinesis
- PMID: 28604678
- PMCID: PMC5493987
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3559
Dynamic subunit turnover in ESCRT-III assemblies is regulated by Vps4 to mediate membrane remodelling during cytokinesis
Abstract
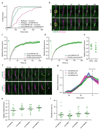
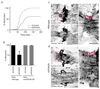
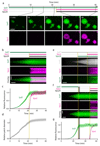
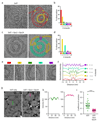
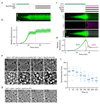
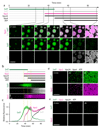
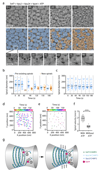
The endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT)-III mediates membrane fission in fundamental cellular processes, including cytokinesis. ESCRT-III is thought to form persistent filaments that over time increase their curvature to constrict membranes. Unexpectedly, we found that ESCRT-III at the midbody of human cells rapidly turns over subunits with cytoplasmic pools while gradually forming larger assemblies. ESCRT-III turnover depended on the ATPase VPS4, which accumulated at the midbody simultaneously with ESCRT-III subunits, and was required for assembly of functional ESCRT-III structures. In vitro, the Vps2/Vps24 subunits of ESCRT-III formed side-by-side filaments with Snf7 and inhibited further polymerization, but the growth inhibition was alleviated by the addition of Vps4 and ATP. High-speed atomic force microscopy further revealed highly dynamic arrays of growing and shrinking ESCRT-III spirals in the presence of Vps4. Continuous ESCRT-III remodelling by subunit turnover might facilitate shape adaptions to variable membrane geometries, with broad implications for diverse cellular processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hanson PI, Cashikar A. Multivesicular body morphogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2012;28:337–362. - PubMed
-
- Carlton JG, Martin-Serrano J. Parallels between cytokinesis and retroviral budding: a role for the ESCRT machinery. Science. 2007;316:1908–1912. - PubMed
-
- Guizetti J, et al. Cortical constriction during abscission involves helices of ESCRT-III-dependent filaments. Science. 2011;331:1616–1620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

