Association Between Indulgent Descriptions and Vegetable Consumption: Twisted Carrots and Dynamite Beets
- PMID: 28604924
- PMCID: PMC5818791
- DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.1637
Association Between Indulgent Descriptions and Vegetable Consumption: Twisted Carrots and Dynamite Beets
Erratum in
-
Incorrect P Values in Results Section.JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Aug 1;177(8):1228. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.3703. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28738124 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
This observational study examines the association of labeling vegetables with indulgent descriptions and overall vegetable consumption compared with labeling vegetables with basic or health-focused labels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
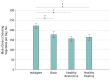
Comment in
-
Selection Does Not Equate Consumption.JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Dec 1;177(12):1875. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.6725. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 29204635 No abstract available.
-
Selection Does Not Equate Consumption-Reply.JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Dec 1;177(12):1875-1876. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.6728. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 29204642 No abstract available.
References
-
- Turnwald BP, Jurafsky D, Conner A, Crum AJ. Reading between the menu lines: are restaurants’ descriptions of “healthy” foods unappealing? Health Psychol. 2017. In press. - PubMed
-
- Raghunathan R, Naylor RW, Hoyer WD. The unhealthy=tasty intuition and its effects on taste inferences, enjoyment, and choice of food products. J Mark. 2006;70(4):170-184.
-
- Crum AJ, Corbin WR, Brownell KD, Salovey P. Mind over milkshakes: mindsets, not just nutrients, determine ghrelin response. Health Psychol. 2011;30(4):424-429. - PubMed
-
- Hanks AS, Just DR, Brumberg A. Marketing vegetables in elementary school cafeterias to increase uptake. Pediatrics. 2016;138(2):e20151720. - PubMed
-
- Wansink B, Just DR, Payne CR, Klinger MZ. Attractive names sustain increased vegetable intake in schools. Prev Med. 2012;55(4):330-332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

