Alterations of anti-inflammatory lipids in plasma from women with chronic widespread pain - a case control study
- PMID: 28606089
- PMCID: PMC5469054
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0505-7
Alterations of anti-inflammatory lipids in plasma from women with chronic widespread pain - a case control study
Abstract
Background: Chronic widespread pain conditions (CWP) such as the pain associated with fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) are significant health problems with unclear aetiology. Although CWP and FMS can alter both central and peripheral pain mechanisms, there are no validated markers for such alterations. Pro- and anti-inflammatory components of the immune system such as cytokines and endogenous lipid mediators could serve as systemic markers of alterations in chronic pain. Lipid mediators associated with anti-inflammatory qualities - e.g., oleoylethanolamide (OEA), palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), and stearoylethanolamide (SEA) - belong to N-acylethanolamines (NAEs). Previous studies have concluded that these lipid mediators may modulate pain and inflammation via the activation of peroxisome proliferator activating receptors (PPARs) and the activation of PPARs may regulate gene transcriptional factors that control the expression of distinct cytokines.
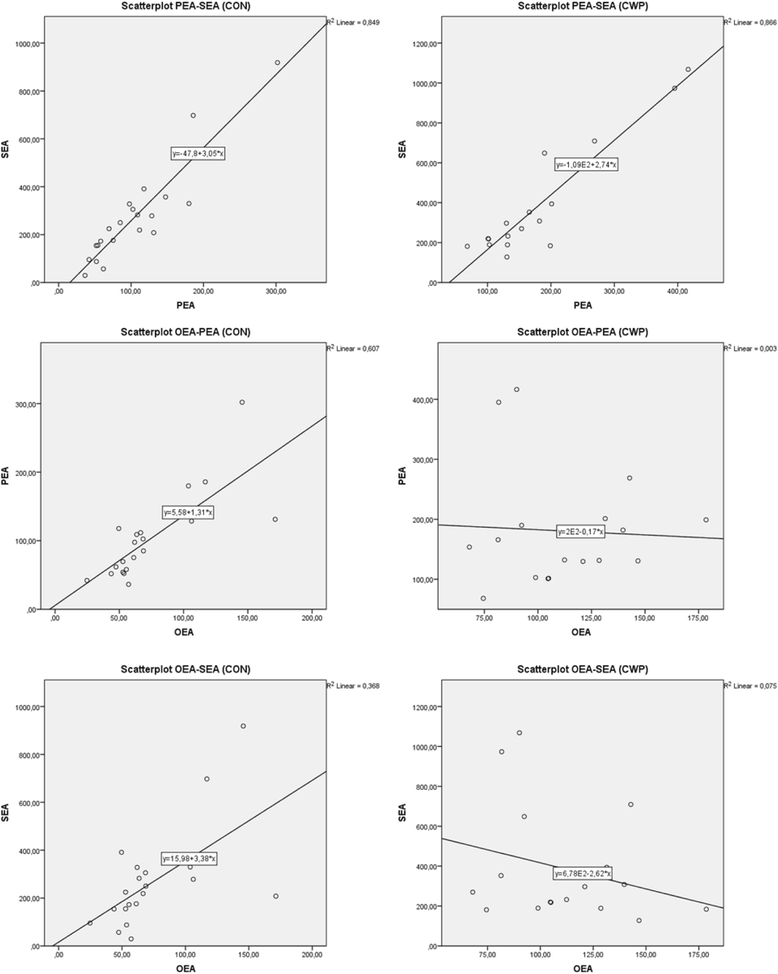
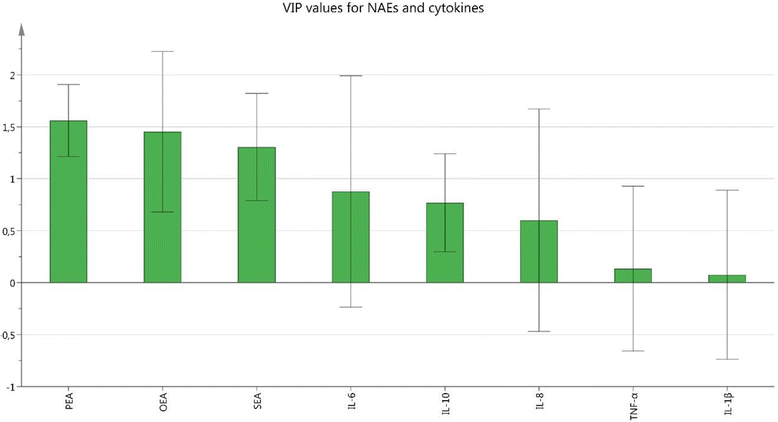
Methods: This study investigates NAEs and cytokines in 17 women with CWP and 21 healthy controls. Plasma levels of the anti-inflammatory lipids OEA, PEA, and SEA, the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8, and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 were investigated. T-test of independent samples was used for group comparisons. Bivariate correlation analyses, and multivariate regression analysis were performed between lipids, cytokines, and pain intensity of the participants.
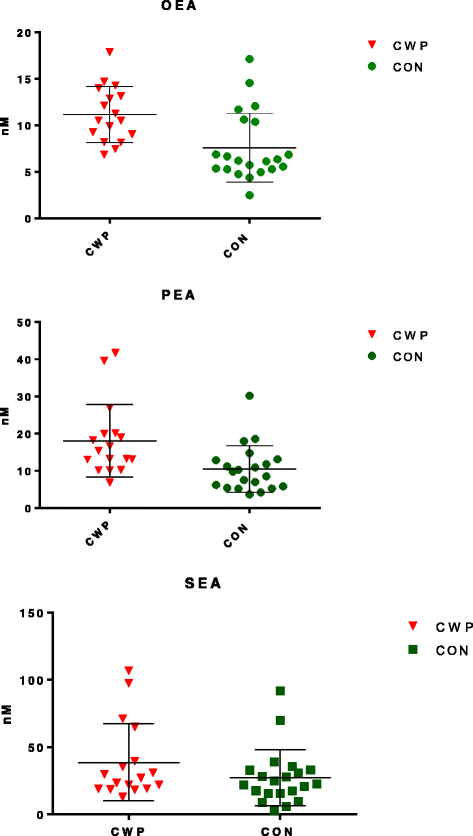
Results: Significantly higher levels of OEA and PEA in plasma were found in CWP. No alterations in the levels of cytokines existed and no correlations between levels of lipids and cytokines were found.
Conclusions: We conclude that altered levels of OEA and PEA might indicate the presence of systemic inflammation in CWP. In addition, we believe our findings contribute to the understanding of the biochemical mechanisms involved in chronic musculoskeletal pain.
Keywords: Chronic widespread pain; Cytokines; Inflammation; N-acylethanolamines; Oleoylethanolamide; Palmitoylethanolamide.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

