MicroRNA-1296 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SRPK1-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 28606154
- PMCID: PMC5469159
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0675-y
MicroRNA-1296 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SRPK1-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidences demonstrate that miRNAs contribute to development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Underexpression of miR-1296 is recently reported to promote growth and metastasis of human cancers. However, the expression and role of miR-1296 in HCC remain unknown.
Methods: The levels of miR-1296 in HCC tissues and cells were detected by qRT-PCR. Immunoblotting and immunofluorescence were used for detection of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) progression in HCC cells. Transwell assays were performed to determine migration and invasion of HCC cells. A lung metastasis mouse model was used to evaluated metastasis of HCC in vivo. The putative targets of miR-1296 were disclosed by public databases and a dual-luciferase reporter assay.
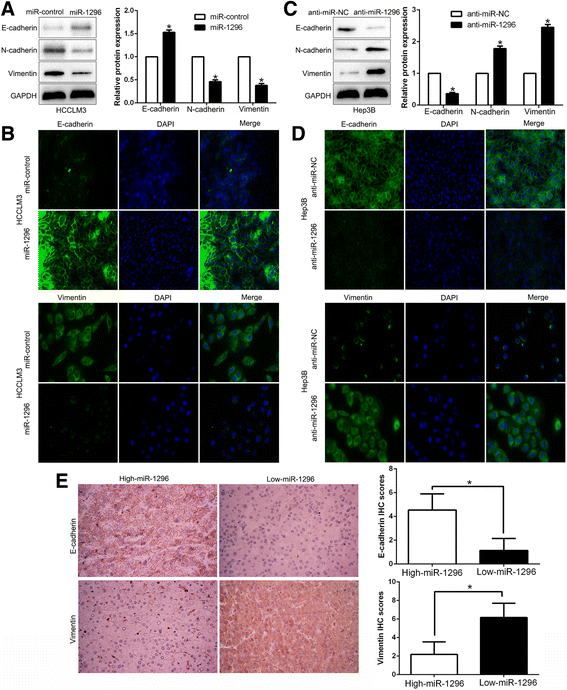
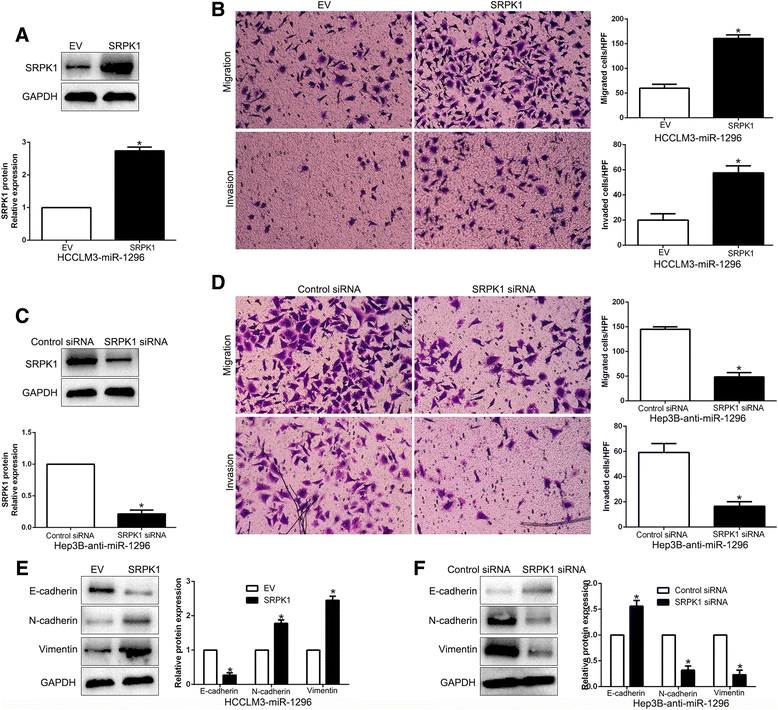
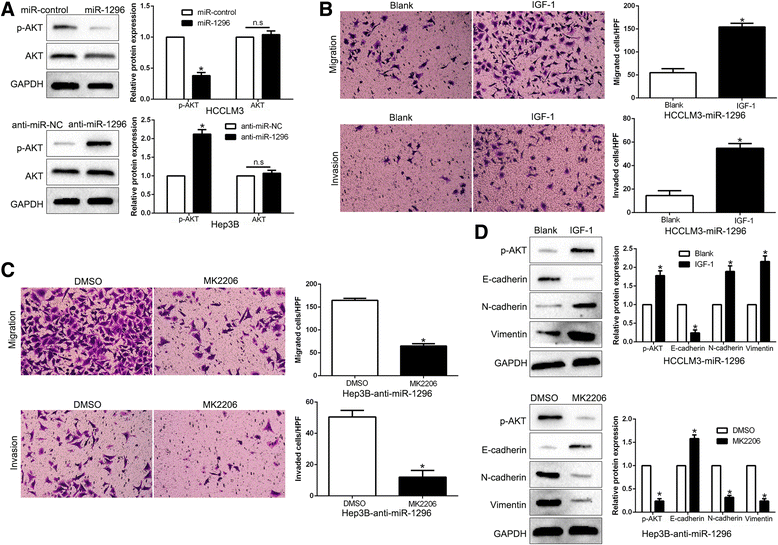
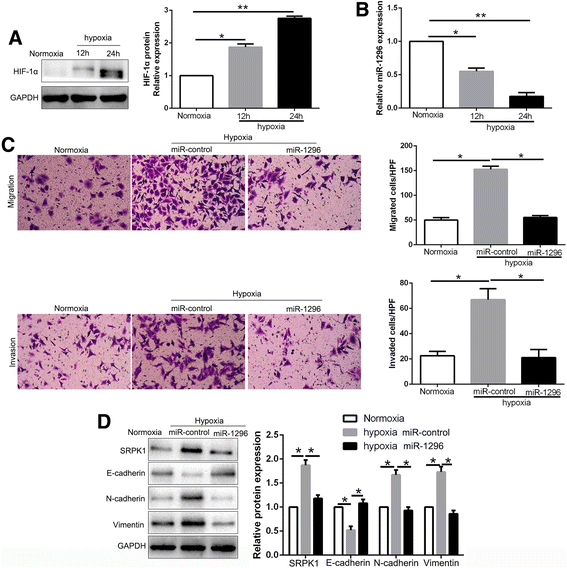
Results: We found that the expression of miR-1296 was reduced in HCC tissues and cell lines, and it was associated with metastasis and recurrence of HCC. Notably, miR-1296 overexpression inhibited migration, invasion and EMT progress of HCCLM3 cells, while miR-1296 loss facilitated these biological behaviors of Hep3B cells in vitro and in vivo. In addition, miR-1296 inversely regulated SRPK1 abundance by directly binding to its 3'-UTR, which subsequently resulted in suppression of p-AKT. Either SRPK1 re-expression or PI3K/AKT pathway activation, at least partially, abolished the effects of miR-1296 on migration, invasion and EMT progress of HCC cells. Furthermore, miR-1296 and SRPK1 expression were markedly correlated with adverse clinical features and poor prognosis of HCC patients. We showed that hypoxia was responsible for the underexpression of miR-1296 in HCC. And the promoting effects of hypoxia on metastasis and EMT of HCC cells were reversed by miR-1296.
Conclusions: Underexpression of miR-1296 potentially serves as a prognostic biomarker in HCC. Hypoxia-induced miR-1296 loss promotes metastasis and EMT of HCC cells probably by targeting SRPK1/AKT pathway.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Metastasis; MicroRNA-1296; PI3K/AKT pathway; SRPK1.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

