Targeting Oxygen-Sensing Prolyl Hydroxylase for Metformin-Associated Lactic Acidosis Treatment
- PMID: 28606929
- PMCID: PMC5533879
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00248-17
Targeting Oxygen-Sensing Prolyl Hydroxylase for Metformin-Associated Lactic Acidosis Treatment
Abstract
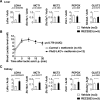
Metformin is one of the most widely used therapeutics for type 2 diabetes mellitus and also has anticancer and antiaging properties. However, it is known to induce metformin-associated lactic acidosis (MALA), a severe medical condition with poor prognosis, especially in individuals with renal dysfunction. Inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) is known to activate the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) that increases lactate efflux as a result of enhanced glycolysis, but it also enhances gluconeogenesis from lactate in the liver that contributes to reducing circulating lactate levels. Here, we investigated the outcome of pharmaceutical inhibition of PHD in mice with MALA induced through the administration of metformin per os and an intraperitoneal injection of lactic acid. We found that the PHD inhibitors significantly increased the expression levels of genes involved in gluconeogenesis in the liver and the kidney and significantly improved the survival of mice with MALA. Furthermore, the PHD inhibitor also improved the rate of survival of MALA induced in mice with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Thus, PHD represents a new therapeutic target for MALA, which is a critical complication of metformin therapy.
Keywords: CKD; Cori cycle; HIF; MALA; PHD; gluconeogenesis; hypoxia; lactic acidosis; metformin; prolyl hydroxylase.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures





References
-
- Suhara T, Hishiki T, Kasahara M, Hayakawa N, Oyaizu T, Nakanishi T, Kubo A, Morisaki H, Kaelin WG Jr, Suematsu M, Minamishima YA. 2015. Inhibition of the oxygen sensor PHD2 in the liver improves survival in lactic acidosis by activating the Cori cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:11642–11647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515872112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
