Cell lineage of timed cohorts of Tbx6-expressing cells in wild-type and Tbx6 mutant embryos
- PMID: 28606934
- PMCID: PMC5550921
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.026203
Cell lineage of timed cohorts of Tbx6-expressing cells in wild-type and Tbx6 mutant embryos
Abstract
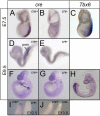
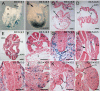
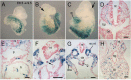
Tbx6 is a T-box transcription factor with multiple roles in embryonic development as evidenced by dramatic effects on mesoderm cell fate determination, left/right axis determination, and somite segmentation in mutant mice. The expression of Tbx6 is restricted to the primitive streak and presomitic mesoderm, but some of the phenotypic features of mutants are not easily explained by this expression pattern. We have used genetically-inducible fate mapping to trace the fate of Tbx6-expressing cells in wild-type and mutant embryos to explain some of the puzzling features of the mutant phenotype. We created an inducible Tbx6-creERT2 transgenic mouse in which cre expression closely recapitulates endogenous Tbx6 expression both temporally and spatially. Using a lacZ-based Cre reporter and timed tamoxifen injections, we followed temporally overlapping cohorts of cells that had expressed Tbx6 and found contributions to virtually all mesodermally-derived embryonic structures as well as the extraembryonic allantois. Contribution to the endothelium of major blood vessels may account for the embryonic death of homozygous mutant embryos. In mutant embryos, Tbx6-creERT2-traced cells contributed to the abnormally segmented anterior somites and formed the characteristic ectopic neural tubes. Retention of cells in the mutant tail bud indicates a deficiency in migratory behavior of the mutant cells and the presence of Tbx6-creERT2-traced cells in the notochord, a node derivative provides a possible explanation for the heterotaxia seen in mutant embryos.
Keywords: Cell fate; Lineage; Mouse; Mutant phenotype; T-box; Tbx6.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Beddington R. S. P. (1994). Induction of a second neural axis by the mouse node. Development 120, 613-620. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

