Role of the terminator hairpin in the biogenesis of functional Hfq-binding sRNAs
- PMID: 28606943
- PMCID: PMC5558911
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.060756.117
Role of the terminator hairpin in the biogenesis of functional Hfq-binding sRNAs
Abstract
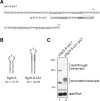
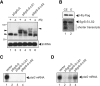
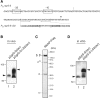
Rho-independent transcription terminators of the genes encoding bacterial Hfq-binding sRNAs possess a set of seven or more T residues at the 3' end, as noted in previous studies. Here, we have studied the role of the terminator hairpin in the biogenesis of sRNAs focusing on SgrS and RyhB in Escherichia coli. We constructed variant sRNA genes in which the GC-rich inverted repeat sequences are extended to stabilize the terminator hairpins. We demonstrate that the extension of the hairpin stem leads to generation of heterogeneous transcripts in which the poly(U) tail is shortened. The transcripts with shortened poly(U) tails no longer bind to Hfq and lose the ability to repress the target mRNAs. The shortened transcripts are generated in an in vitro transcription system with purified RNA polymerase, indicating that the generation of shortened transcripts is caused by premature transcription termination. We conclude that the terminator structure of sRNA genes is optimized to generate functional sRNAs. Thus, the Rho-independent terminators of sRNA genes possess two common features: a long T residue stretch that is a prerequisite for generation of functional sRNAs and a moderate strength of hairpin structure that ensures the termination at the seventh or longer position within the consecutive T stretch. The modulation of the termination position at the Rho-independent terminators is critical for biosynthesis of functional sRNAs.
Keywords: Hfq; RNA hairpin; Rho-independent terminator; bacterial sRNA; premature termination.
© 2017 Morita et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures




References
-
- Aiba H, Adhya S, de Crombrugghe B. 1981. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem 256: 11905–11910. - PubMed
-
- Argaman L, Hershberg R, Vogel J, Bejerano G, Wagner EG, Margalit H, Altuvia S. 2001. Novel small RNA-encoding genes in the intergenic regions of Escherichia coli. Curr Biol 11: 941–950. - PubMed
-
- Cheng SW, Lynch EC, Leason KR, Court DL, Shapiro BA, Friedman DI. 1991. Functional importance of sequence in the stem-loop of a transcription terminator. Science 254: 1205–1207. - PubMed
-
- d'Aubenton Carafa Y, Brody E, Thermes C. 1990. Prediction of rho-independent Escherichia coli transcription terminators. A statistical analysis of their RNA stem-loop structures. J Mol Biol 216: 835–858. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
