Impact of nutrition on social decision making
- PMID: 28607064
- PMCID: PMC5488927
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1620245114
Impact of nutrition on social decision making
Abstract
Food intake is essential for maintaining homeostasis, which is necessary for survival in all species. However, food intake also impacts multiple biochemical processes that influence our behavior. Here, we investigate the causal relationship between macronutrient composition, its bodily biochemical impact, and a modulation of human social decision making. Across two studies, we show that breakfasts with different macronutrient compositions modulated human social behavior. Breakfasts with a high-carbohydrate/protein ratio increased social punishment behavior in response to norm violations compared with that in response to a low carbohydrate/protein meal. We show that these macronutrient-induced behavioral changes in social decision making are causally related to a lowering of plasma tyrosine levels. The findings indicate that, in a limited sense, "we are what we eat" and provide a perspective on a nutrition-driven modulation of cognition. The findings have implications for education, economics, and public policy, and emphasize that the importance of a balanced diet may extend beyond the mere physical benefits of adequate nutrition.
Keywords: decision making; nutrition; social decision; tyrosine; ultimatum game.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

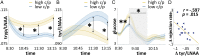



Comment in
-
Reply to Raison and Raichlen: Why does nutrition impact social decision making?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 13;115(7):E1332-E1333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1722569115. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29367418 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An evolutionary perspective on nutrition and social decision making.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 13;115(7):E1331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721889115. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29367419 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolever TM, Jenkins DJ. The use of the glycemic index in predicting the blood glucose response to mixed meals. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986;43:167–172. - PubMed
-
- Wurtman RJ, et al. Effects of normal meals rich in carbohydrates or proteins on plasma tryptophan and tyrosine ratios. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;77:128–132. - PubMed
-
- Gailliot MT, et al. Self-control relies on glucose as a limited energy source: Willpower is more than a metaphor. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2007;92:325–336. - PubMed
-
- Colzato LS, et al. Tryptophan promotes interpersonal trust. Psychol Sci. 2013;24:2575–2577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

