Oxytocin and Serotonin Brain Mechanisms in the Nonhuman Primate
- PMID: 28607170
- PMCID: PMC6596550
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0659-17.2017
Oxytocin and Serotonin Brain Mechanisms in the Nonhuman Primate
Abstract
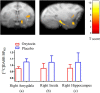
Oxytocin (OT) is increasingly studied for its therapeutic potential in psychiatric disorders, which are associated with the deregulation of several neurotransmission systems. Studies in rodents demonstrated that the interaction between OT and serotonin (5-HT) is critical for several aspects of social behavior. Using PET scan in humans, we have recently found that 5-HT 1A receptor (5-HT1AR) function is modified after intranasal oxytocin intake. However, the underlying mechanism between OT and 5-HT remains unclear. To understand this interaction, we tested 3 male macaque monkeys using both [11C]DASB and [18F]MPPF, two PET radiotracers, marking the serotonin transporter and the 5-HT1AR, respectively. Oxytocin (1 IU in 20 μl of ACSF) or placebo was injected into the brain lateral ventricle 45 min before scans. Additionally, we performed postmortem autoradiography. Compared with placebo, OT significantly reduced [11C]DASB binding potential in right amygdala, insula, and hippocampus, whereas [18F]MPPF binding potential increased in right amygdala and insula. Autoradiography revealed that [11C]DASB was sensitive to physiological levels of 5-HT modification, and that OT does not act directly on the 5-HT1AR. Our results show that oxytocin administration in nonhuman primates influences serotoninergic neurotransmission via at least two ways: (1) by provoking a release of serotonin in key limbic regions; and (2) by increasing the availability of 5-HT1AR receptors in the same limbic areas. Because these two molecules are important for social behavior, our study sheds light on the specific nature of their interaction, therefore helping to develop new mechanisms-based therapies for psychiatric disorders.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Social behavior is largely controlled by brain neuromodulators, such as oxytocin and serotonin. While these are currently targeted in the context of psychiatric disorders such as autism and schizophrenia, a new promising pharmaceutical strategy is to study the interaction between these systems. Here we depict the interplay between oxytocin and serotonin in the nonhuman primate brain. We found that oxytocin provokes the release of serotonin, which in turn impacts on the serotonin 1A receptor system, by modulating its availability. This happens in several key brain regions for social behavior, such as the amygdala and insula. This novel finding can open ways to advance treatments where drugs are combined to influence several neurotransmission networks.
Keywords: PET scan; nonhuman primate; oxytocin; serotonin.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/376741-10$15.00/0.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oxytocin Fails to Recruit Serotonergic Neurotransmission in the Autistic Brain.Cereb Cortex. 2018 Dec 1;28(12):4169-4178. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx272. Cereb Cortex. 2018. PMID: 29045584
-
Switching brain serotonin with oxytocin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 10;111(23):8637-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319810111. Epub 2014 May 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24912179 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oxytocin--a neuropeptide for affiliation: evidence from behavioral, receptor autoradiographic, and comparative studies.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1992;17(1):3-35. doi: 10.1016/0306-4530(92)90073-g. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1992. PMID: 1319071 Review.
-
Oxytocin modulates fMRI responses to facial expression in macaques.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jun 16;112(24):E3123-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508097112. Epub 2015 May 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26015576 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin and social cognition in rhesus macaques: implications for understanding and treating human psychopathology.Brain Res. 2014 Sep 11;1580:57-68. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24231551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxytocin promotes prosocial behavior and related neural responses in infant macaques at-risk for compromised social development.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2021 Apr;48:100950. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2021.100950. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33831822 Free PMC article.
-
Brain serotonin, oxytocin, and their interaction: Relevance for eating disorders.J Psychopharmacol. 2025 Mar;39(3):187-200. doi: 10.1177/02698811241309617. Epub 2025 Jan 2. J Psychopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39745000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Oxytocin in Abnormal Brain Development: Effect on Glial Cells and Neuroinflammation.Cells. 2022 Dec 2;11(23):3899. doi: 10.3390/cells11233899. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opportunities and challenges for intranasal oxytocin treatment studies in nonhuman primates.Am J Primatol. 2018 Oct;80(10):e22913. doi: 10.1002/ajp.22913. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Am J Primatol. 2018. PMID: 30281820 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of SERE training on selected neurotransmitter secretion in special forces soldiers.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21853. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06270-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amico JA, Levin SC, Cameron JL (1989) Circadian rhythm of oxytocin in the cerebrospinal fluid of rhesus and cynomolgus monkeys: effects of castration and adrenalectomy and presence of a caudal-rostral gradient. Neuroendocrinology 50:624–632. - PubMed
-
- Bandelow B, Zohar J, Hollander E, Kasper S, Möller HJ (2002) World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of anxiety, obsessive-compulsive and posttraumatic stress disorders. World J Biol Psychiatry 3:171–199. 10.3109/15622970209150621 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
